Related Research Articles

C-C motif chemokine 22 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCL22 gene.

CD49d is an integrin alpha subunit. It makes up half of the α4β1 lymphocyte homing receptor.

CD5 is a cluster of differentiation expressed on the surface of T cells and in a subset of murine B cells known as B-1a. The expression of this receptor in human B cells has been a controversial topic and to date there is no consensus regarding the role of this receptor as a marker of human B cells. B-1 cells have limited diversity of their B-cell receptor due to their lack of the enzyme terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) and are potentially self-reactive. CD5 serves to mitigate activating signals from the BCR so that the B-1 cells can only be activated by very strong stimuli and not by normal tissue proteins. CD5 was used as a T-cell marker until monoclonal antibodies against CD3 were developed.

Leukocyte surface antigen CD53 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD53 gene.

T-cell surface glycoprotein CD3 gamma chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD3G gene.

TYRO protein tyrosine kinase-binding protein is an adapter protein that in humans is encoded by the TYROBP gene.

Chemokine receptor 8, also known as CCR8, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CCR8 gene. CCR8 has also recently been designated CDw198.

C-C chemokine receptor type 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCR9 gene.

C-C chemokine receptor type 11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCRL1 gene.

CD244 is a human protein encoded by the CD244 gene. It is also known as Natural Killer Cell Receptor 2B4

Interleukin-12 receptor, beta 1, or IL-12Rβ1 in short, is a subunit of the interleukin 12 receptor. IL12RB1, is the name of its human gene. IL-12Rβ1 is also known as CD212.

C-C motif chemokine 4-like is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCL4L1 gene.

HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DO beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DOB gene.
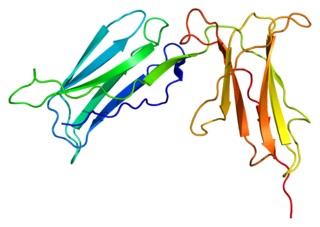
Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 2DS4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIR2DS4 gene.

Signal-regulatory protein beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SIRPB1 gene. SIRPB1 has also recently been designated CD172B.

TCR gamma alternate reading frame protein, also known as TARP, is a human gene.

CD79b molecule, immunoglobulin-associated beta, also known as CD79B, is a human gene.

CD8a, is a human gene.

T-cell surface glycoprotein CD3 delta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD3D gene.

CD300A is a human gene.
References
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Erikson J, Williams DL, Finan J, Nowell PC, Croce CM (Sep 1985). "Locus of the alpha-chain of the T-cell receptor is split by chromosome translocation in T-cell leukemias". Science. 229 (4715): 784–6. Bibcode:1985Sci...229..784E. doi:10.1126/science.3875152. PMID 3875152.
- ↑ Rabbitts TH, Lefranc MP, Stinson MA, Sims JE, Schroder J, Steinmetz M, Spurr NL, Solomon E, Goodfellow PN (Oct 1985). "The chromosomal location of T-cell receptor genes and a T cell rearranging gene: possible correlation with specific translocations in human T cell leukaemia". EMBO J. 4 (6): 1461–5. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03803.x. PMC 554368 . PMID 3875483.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: TRA@ T cell receptor alpha locus".