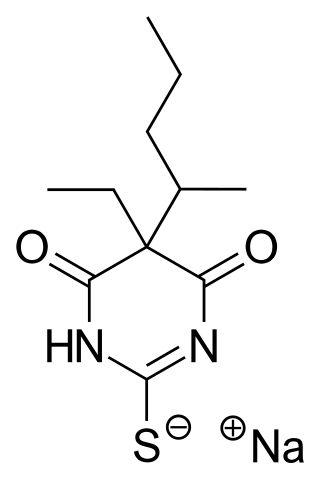
Sodium thiopental, also known as Sodium Pentothal, thiopental, thiopentone, or Trapanal, is a rapid-onset short-acting barbiturate general anesthetic. It is the thiobarbiturate analog of pentobarbital, and an analog of thiobarbital. Sodium thiopental was a core medicine in the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, but was supplanted by propofol. Despite this, thiopental is listed as an acceptable alternative to propofol, depending on local availability and cost of these agents. It was previously the first of three drugs administered during most lethal injections in the United States, but the US manufacturer Hospira stopped manufacturing the drug in 2011 and the European Union banned the export of the drug for this purpose. Although thiopental abuse carries a dependency risk, its recreational use is rare.
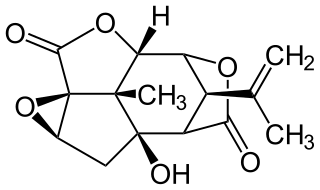
Picrotoxin, also known as cocculin, is a poisonous crystalline plant compound. It was first isolated by the French pharmacist and chemist Pierre François Guillaume Boullay (1777–1869) in 1812. The name "picrotoxin" is a combination of the Greek words "picros" (bitter) and "toxicon" (poison). A mixture of two different compounds, picrotoxin occurs naturally in the fruit of the Anamirta cocculus plant, although it can also be synthesized chemically.

Flurazepam is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, hypnotic, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. It produces a metabolite with a long half-life, which may stay in the bloodstream for days. Flurazepam was patented in 1968 and came into medical use the same year. Flurazepam, developed by Roche Pharmaceuticals, was one of the first benzodiazepine hypnotic medications to be marketed.
An induced coma – also known as a medically induced coma (MIC), barbiturate-induced coma, or drug-induced coma – is a temporary coma brought on by a controlled dose of an anesthetic drug, often a barbiturate such as pentobarbital or thiopental. Other intravenous anesthetic drugs such as midazolam or propofol may be used.

The GABAA receptor (GABAAR) is an ionotropic receptor and ligand-gated ion channel. Its endogenous ligand is γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Accurate regulation of GABAergic transmission through appropriate developmental processes, specificity to neural cell types, and responsiveness to activity is crucial for the proper functioning of nearly all aspects of the central nervous system (CNS). Upon opening, the GABAA receptor on the postsynaptic cell is selectively permeable to chloride ions (Cl−) and, to a lesser extent, bicarbonate ions (HCO3−).
Pentobarbital (US) or pentobarbitone is a short-acting barbiturate typically used as a sedative, a preanesthetic, and to control convulsions in emergencies. It can also be used for short-term treatment of insomnia but has been largely replaced by the benzodiazepine family of drugs.

Butalbital is a barbiturate with an intermediate duration of action. Butalbital is often combined with other medications, such as paracetamol (acetaminophen) or aspirin, for the treatment of pain and headache. The various formulations combined with codeine are FDA-approved for the treatment of tension headaches. Butalbital has the same chemical formula as talbutal but a different structure—one that presents as 5-allyl-5-isobutylbarbituric acid.
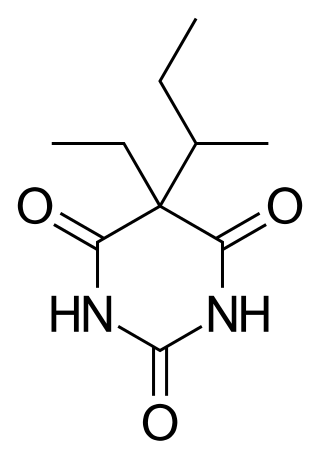
Butabarbital is a prescription barbiturate sleep aid and anxiety medication. Butabarbital has a particularly fast onset of effects and short duration of action compared to other barbiturates, which makes it useful for certain applications such as treating severe insomnia, relieving general anxiety and relieving anxiety before surgical procedures; however it is also relatively dangerous particularly when combined with alcohol, and so is now rarely used, although it is still prescribed in some Eastern European and South American countries. Its intermediate duration of action gives butabarbital an abuse potential slightly lower than secobarbital. Butabarbital can be hydrolyzed to valnoctamide.
Central nervous system (CNS) depression is a physiological state that can result in a decreased rate of breathing, decreased heart rate, and loss of consciousness, possibly leading to coma or death.

Methohexital or methohexitone is a drug which is a barbiturate derivative. It is classified as short-acting, and has a rapid onset of action. It is similar in its effects to sodium thiopental, a drug with which it competed in the market for anesthetics.
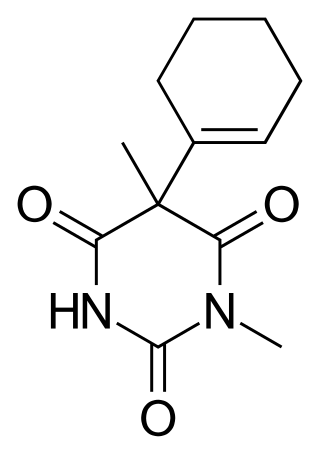
Hexobarbital or hexobarbitone, sold both in acid and sodium salt forms as Citopan, Evipan, and Tobinal, is a barbiturate derivative having hypnotic and sedative effects. It was used in the 1940s and 1950s as an agent for inducing anesthesia for surgery, as well as a rapid-acting, short-lasting hypnotic for general use, and has a relatively fast onset of effects and short duration of action. Modern barbiturates have largely supplanted the use of hexobarbital as an anesthetic, as they allow for better control of the depth of anesthesia. Hexobarbital is still used in some scientific research.

Butallylonal is a barbiturate derivative invented in the 1920s. It has sedative properties, and was used primarily as an anaesthetic in veterinary medicine. Butallylonal is considered similar in effects to pentobarbital but is longer in action, being considered an intermediate-acting barbiturate rather than short-acting.

Hexethal (Ortal) is a barbiturate derivative invented in the 1940s. It has sedative, anxiolytic, muscle relaxant, and anticonvulsant properties, and was used primarily as an anaesthetic in veterinary medicine.

A GABA receptor agonist is a drug that is an agonist for one or more of the GABA receptors, producing typically sedative effects, and may also cause other effects such as anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, and muscle relaxant effects. There are three receptors of the gamma-aminobutyric acid. The two receptors GABA-α and GABA-ρ are ion channels that are permeable to chloride ions which reduces neuronal excitability. The GABA-β receptor belongs to the class of G-Protein coupled receptors that inhibit adenylyl cyclase, therefore leading to decreased cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). GABA-α and GABA-ρ receptors produce sedative and hypnotic effects and have anti-convulsion properties. GABA-β receptors also produce sedative effects. Furthermore, they lead to changes in gene transcription.

Benzodiazepine overdose describes the ingestion of one of the drugs in the benzodiazepine class in quantities greater than are recommended or generally practiced. The most common symptoms of overdose include central nervous system (CNS) depression, impaired balance, ataxia, and slurred speech. Severe symptoms include coma and respiratory depression. Supportive care is the mainstay of treatment of benzodiazepine overdose. There is an antidote, flumazenil, but its use is controversial.

Barbiturates are a class of depressant drugs that are chemically derived from barbituric acid. They are effective when used medically as anxiolytics, hypnotics, and anticonvulsants, but have physical and psychological addiction potential as well as overdose potential among other possible adverse effects. They have been used recreationally for their anti-anxiety and sedative effects, and are thus controlled in most countries due to the risks associated with such use.
A coma blister, or coma bullae, is a skin lesion or blister that typically arises due to pressure in an individual with impaired consciousness. They vary in size, ranging from 4 to 5 centimeters in diameter, and may appear hemorrhagic or blood filled. Coma blisters are usually found in the extremities and trunk. These types of blisters have been associated with the overdose of central nervous system (CNS) depressants especially barbiturates, but also tricyclic antidepressants, hypnotics, benzodiazepines, opiates, antipsychotics, and alcohol. However, studies have found that coma blisters are not caused by the toxicity of these drugs, but due to hypoxia and external pressure on the comatose individual's skin from being immobilized. Coma blisters have been frequently found on individuals who have overdosed on drugs, but have also been found on individuals with chronic kidney failure, hypercalcemia, diabetic ketoacidosis, and a variety of neurologic conditions. Coma blisters are more frequent in adults and less common among children as demonstrated by the few cases published in literature.
Barbiturate dependence develops with regular use of barbiturates. This in turn may lead to a need for increasing doses of the drug to get the original desired pharmacological or therapeutic effect. Barbiturate use can lead to both addiction and physical dependence, and as such they have a high potential for excess or non-medical use, however, it does not affect all users. Management of barbiturate dependence involves considering the affected person's age, comorbidity and the pharmacological pathways of barbiturates.
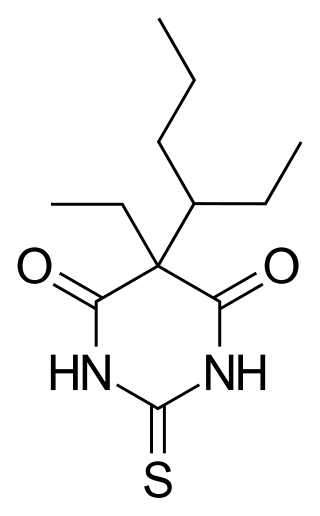
Thiotetrabarbital is a drug which is a short-acting barbiturate derivative that is used as an anesthetic. It has been used in veterinary medicine.

In pharmacology, GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators, also known as GABAkines or GABAA receptor potentiators, are positive allosteric modulator (PAM) molecules that increase the activity of the GABAA receptor protein in the vertebrate central nervous system.















