
An antacid is a substance which neutralizes stomach acidity and is used to relieve heartburn, indigestion or an upset stomach. Some antacids have been used in the treatment of constipation and diarrhea. Marketed antacids contain salts of aluminium, calcium, magnesium, or sodium. Some preparations contain a combination of two salts, such as magnesium carbonate and aluminium hydroxide.
Benzocaine, sold under the brand name Orajel amongst others, is a local anesthetic, belonging to the amino ester drug class, commonly used as a topical painkiller or in cough drops. It is the active ingredient in many over-the-counter anesthetic ointments such as products for oral ulcers. It is combined with antipyrine to form A/B ear drops. In the US, products containing benzocaine for oral application are contraindicated in children younger than two years old. In the European Union, the contraindication applies to children under 12 years of age.
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes including creams, foams, gels, lotions, and ointments. Many topical medications are epicutaneous, meaning that they are applied directly to the skin. Topical medications may also be inhalational, such as asthma medications, or applied to the surface of tissues other than the skin, such as eye drops applied to the conjunctiva, or ear drops placed in the ear, or medications applied to the surface of a tooth. The word topical derives from Greek τοπικόςtopikos, "of a place".

Potassium alum, potash alum, or potassium aluminium sulfate is a chemical compound: the double sulfate of potassium and aluminium, with chemical formula KAl(SO4)2. It is commonly encountered as the dodecahydrate, KAl(SO4)2·12H2O. It crystallizes in an octahedral structure in neutral solution and cubic structure in an alkali solution with space group P a −3 and lattice parameter of 12.18 Å. The compound is the most important member of the generic class of compounds called alums, and is often called simply alum.

Sodium acetate, CH3COONa, also abbreviated NaOAc, is the sodium salt of acetic acid. This colorless deliquescent salt has a wide range of uses.

Betamethasone is a steroid medication. It is used for a number of diseases including rheumatic disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, skin diseases such as dermatitis and psoriasis, allergic conditions such as asthma and angioedema, preterm labor to speed the development of the baby's lungs, Crohn's disease, cancers such as leukemia, and along with fludrocortisone for adrenocortical insufficiency, among others. It can be taken by mouth, injected into a muscle, or applied to the skin, typically in cream, lotion, or liquid forms.

Lead(II) acetate (also known as lead acetate, lead diacetate, plumbous acetate, sugar of lead, lead sugar, salt of Saturn, or Goulard's powder), is a white crystalline chemical compound with a slightly sweet taste. Its chemical formula is usually expressed as Pb(CH3COO)2 or Pb(OAc)2, where Ac represents the acetyl group. Like many other lead compounds, it is toxic. Lead acetate is soluble in water and glycerin. With water it forms the trihydrate, Pb(OAc)2·3H2O, a colourless or white efflorescent monoclinic crystalline substance.

Fluticasone propionate, sold under the brand names Flovent and Flonase among others, is a steroid medication. When inhaled it is used for the long term management of asthma and COPD. In the nose it is used for hay fever and nasal polyps. It can also be used for mouth ulcers. It works by decreasing inflammation.
Burow's solution is an aqueous solution of aluminium triacetate. It is available in the U.S. as an over-the-counter drug for topical administration, with brand names including Domeboro, Domeboro Otic, Star-Otic, and Borofair. The preparation has astringent and antibacterial properties and may be used to treat a number of skin conditions, including insect bites and stings, rashes caused by poison ivy and poison sumac, swelling, allergies, and bruises. However, its main use is for treatment of otitis, including otomycosis.

Iron(II) acetate is a coordination complex with formula Fe(CH3COO)2. It is a white solid, although impure samples can be slightly colored. A light green tetrahydrate is also known, which is highly soluble in water.
Aluminium acetate or aluminium ethanoate (also "aluminum ~"), sometimes abbreviated AlAc in geochemistry, can refer to a number of different salts of aluminium with acetic acid. In the solid state, three salts exist under this name: basic aluminium monoacetate, (HO)2AlCH3CO2, basic aluminium diacetate, HOAl(CH3CO2)2, and neutral aluminium triacetate, Al(CH3CO2)3. In aqueous solution, aluminium triacetate hydrolyses to form a mixture of the other two, and all solutions of all three can be referred to as "aluminium acetate" as the species formed co-exist and inter-convert in chemical equilibrium.

Ear drops are a form of topical medication for the ears used to treat infection, inflammation, impacted ear wax and local anesthesia. They are commonly used for short-term treatment and can be purchased with or without a prescription. Before using ear drops, refer to the package insert or consult a health professional for the amount of drops to use and the duration of treatment.

Potassium acetate (also called potassium ethanoate), (CH3COOK) is the potassium salt of acetic acid. It is a hygroscopic solid at room temperature.

Apple cider vinegar, or cider vinegar, is a vinegar made from fermented apple juice, and used in salad dressings, marinades, vinaigrettes, food preservatives, and chutneys. It is made by crushing apples, then squeezing out the juice. Bacteria and yeast are added to the liquid to start the alcoholic fermentation process, which converts the sugars to alcohol. In a second fermentation step, the alcohol is converted into vinegar by acetic acid-forming bacteria. Acetic acid and malic acid combine to give vinegar its sour taste.
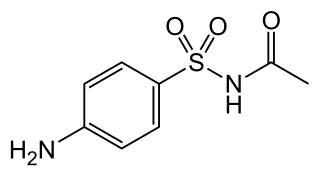
Sulfacetamide is a sulfonamide antibiotic.

Acetic acid, systematically named ethanoic acid, is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COOH. Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water and other trace elements.
Aluminium triacetate, formally named aluminium acetate, is a chemical compound with composition Al(CH
3CO
2)
3. Under standard conditions it appears as a white, water-soluble solid that decomposes on heating at around 200 °C. The triacetate hydrolyses to a mixture of basic hydroxide / acetate salts, and multiple species co-exist in chemical equilibrium, particularly in aqueous solutions of the acetate ion; the name aluminium acetate is commonly used for this mixed system.
Aluminium sulfacetate is a mixture of aluminium salts dissolved in water with formula Al
2SO
4(CH
3CO
2)
4.

Aluminium monoacetate, also known as dibasic aluminium acetate, and formally named dihydroxy aluminium acetate, is a salt of aluminium with acetic acid. It has the formula Al(OH)2(CH3COO), with aluminium in an oxidation state of +3, and appears under standard conditions as a white solid powder.
Topical antifungaldrugs are used to treat fungal infections on the skin, scalp, nails, vagina or inside the mouth. These medications come as creams, gels, lotions, ointments, powders, shampoos, tinctures and sprays. Most antifungal drugs induce fungal cell death by destroying the cell wall of the fungus. These drugs inhibit the production of ergosterol, which is a fundamental component of the fungal cell membrane and wall.















