The haloalkanes are alkanes containing one or more halogen substituents. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes that contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compound a non-ozone layer depleter. For more information, see Halomethane. Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula "RX" where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen.

Diborane(6), commonly known as diborane, is the chemical compound with the formula B2H6. It is a toxic, colorless, and pyrophoric gas with a repulsively sweet odor. Given its simple formula, borane is a fundamental boron compound. It has attracted wide attention for its electronic structure. Several of its derivatives are useful reagents.

Lithium aluminium hydride, commonly abbreviated to LAH, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Li[AlH4] or LiAlH4. It is a white solid, discovered by Finholt, Bond and Schlesinger in 1947. This compound is used as a reducing agent in organic synthesis, especially for the reduction of esters, carboxylic acids, and amides. The solid is dangerously reactive toward water, releasing gaseous hydrogen (H2). Some related derivatives have been discussed for hydrogen storage.

Sodium borohydride, also known as sodium tetrahydridoborate and sodium tetrahydroborate, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaBH4. It is a white crystalline solid, usually encountered as an aqueous basic solution. Sodium borohydride is a reducing agent that finds application in papermaking and dye industries. It is also used as a reagent in organic synthesis.

Lithium hydride is an inorganic compound with the formula LiH. This alkali metal hydride is a colorless solid, although commercial samples are grey. Characteristic of a salt-like (ionic) hydride, it has a high melting point, and it is not soluble but reactive with all protic organic solvents. It is soluble and nonreactive with certain molten salts such as lithium fluoride, lithium borohydride, and sodium hydride. With a molar mass of 7.95 g/mol, it is the lightest ionic compound.
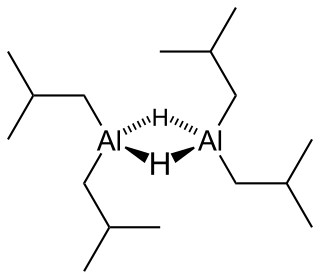
Diisobutylaluminium hydride (DIBALH, DIBAL, DIBAL-H or DIBAH) is a reducing agent with the formula (i-Bu2AlH)2, where i-Bu represents isobutyl (-CH2CH(CH3)2). This organoaluminium compound is a reagent in organic synthesis.

The Corey–Itsuno reduction, also known as the Corey–Bakshi–Shibata (CBS) reduction, is a chemical reaction in which a prochiral ketone is enantioselectively reduced to produce the corresponding chiral, non-racemic alcohol. The oxazaborolidine reagent which mediates the enantioselective reduction of ketones was previously developed by the laboratory of Itsuno and thus this transformation may more properly be called the Itsuno-Corey oxazaborolidine reduction.

Sodium bis(2-methoxyethoxy)aluminium hydride (SMEAH; trade names Red-Al, Synhydrid, Vitride) is a complex hydride reductant with the formula NaAlH2(OCH2CH2OCH3)2. The trade name Red-Al refers to its being a reducing aluminium compound. It is used predominantly as a reducing agent in organic synthesis. The compound features a tetrahedral aluminium center attached to two hydride and two alkoxide groups, the latter derived from 2-methoxyethanol. Commercial solutions are colorless/pale yellow and viscous. At low temperatures (below -60 °C), the solution solidifies to a glassy pulverizable substance with no sharp melting point.

Xenon difluoride is a powerful fluorinating agent with the chemical formula XeF
2, and one of the most stable xenon compounds. Like most covalent inorganic fluorides it is moisture-sensitive. It decomposes on contact with water vapor, but is otherwise stable in storage. Xenon difluoride is a dense, colourless crystalline solid.
The Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley (MPV) reduction in organic chemistry is the reduction of ketones and aldehydes to their corresponding alcohols utilizing aluminium alkoxide catalysis in the presence of a sacrificial alcohol. The advantages of the MPV reduction lie in its high chemoselectivity, and its use of a cheap environmentally friendly metal catalyst.
Organofluorine chemistry describes the chemistry of organofluorine compounds, organic compounds that contain a carbon–fluorine bond. Organofluorine compounds find diverse applications ranging from oil and water repellents to pharmaceuticals, refrigerants, and reagents in catalysis. In addition to these applications, some organofluorine compounds are pollutants because of their contributions to ozone depletion, global warming, bioaccumulation, and toxicity. The area of organofluorine chemistry often requires special techniques associated with the handling of fluorinating agents.

Aluminium hydride (also known as alane and alumane) is an inorganic compound with the formula AlH3. Alane and its derivatives are common reducing (hydride addition) reagents in organic synthesis that are used in solution at both laboratory and industrial scales. In solution—typically in etherial solvents such tetrahydrofuran or diethyl ether—aluminium hydride forms complexes with Lewis bases, and reacts selectively with particular organic functional groups (e.g., with carboxylic acids and esters over organic halides and nitro groups), and although it is not a reagent of choice, it can react with carbon-carbon multiple bonds (i.e., through hydroalumination). Given its density, and with hydrogen content on the order of 10% by weight, some forms of alane are, as of 2016, active candidates for storing hydrogen and so for power generation in fuel cell applications, including electric vehicles. As of 2006 it was noted that further research was required to identify an efficient, economical way to reverse the process, regenerating alane from spent aluminium product.
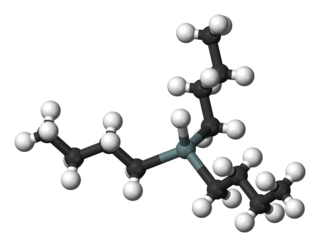
Tributyltin hydride is an organotin compound with the formula (C4H9)3SnH. It is a colorless liquid that is soluble in organic solvents. The compound is used as a source of hydrogen atoms in organic synthesis.

Dibromofluoromethane is a mixed halomethane. It is soluble in alcohol, acetone, benzene and chloroform.
Transition metal hydrides are chemical compounds containing a transition metal bonded to hydrogen. Most transition metals form hydride complexes and some are significant in various catalytic and synthetic reactions. The term "hydride" is used loosely: some of them are acidic (e.g., H2Fe(CO)4), whereas some others are hydridic, having H−-like character (e.g., ZnH2).
Zinc hydride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula ZnH2. It is a white, odourless solid which slowly decomposes into its elements at room temperature; despite this it is the most stable of the binary first row transition metal hydrides. A variety of coordination compounds containing Zn–H bonds are used as reducing agents, however ZnH2 itself has no common applications.
In organic chemistry, dehalogenation is a set of chemical reactions that involve the cleavage of carbon-halogen bonds; as such, it is the inverse reaction of halogenation. Dehalogenations come in many varieties, including defluorination, dechlorination, debromination, and deiodination. Incentives to investigate dehalogenations include both constructive and destructive goals. Complicated organic compounds such as pharmaceutical drugs are occasionally generated by dehalogenation. Many organohalides are hazardous, so their dehalogenation is one route for their detoxification.
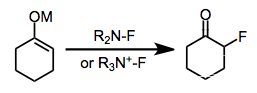
Electrophilic fluorination is the combination of a carbon-centered nucleophile with an electrophilic source of fluorine to afford organofluorine compounds. Although elemental fluorine and reagents incorporating an oxygen-fluorine bond can be used for this purpose, they have largely been replaced by reagents containing a nitrogen-fluorine bond.

Mercury(II) hydride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula HgH
2. It is both thermodynamically and kinetically unstable at ambient temperature, and as such, little is known about its bulk properties. However, it known as a white, crystalline solid, which is kinetically stable at temperatures below −125 °C (−193 °F), which was synthesised for the first time in 1951.

Copper hydride is inorganic compound with the chemical formula CuHn where n ~ 0.95. It is a red solid, rarely isolated as a pure composition, that decomposes to the elements. Copper hydride is mainly produced as a reducing agent in organic synthesis and as a precursor to various catalysts.
















