Bromine is a chemical element; it has symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured vapour. Its properties are intermediate between those of chlorine and iodine. Isolated independently by two chemists, Carl Jacob Löwig and Antoine Jérôme Balard, its name was derived from the Ancient Greek βρῶμος (bromos) meaning "stench", referring to its sharp and pungent smell.

The halogens are a group in the periodic table consisting of six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and the radioactive elements astatine (At) and tennessine (Ts), though some authors would exclude tennessine as its chemistry is unknown and is theoretically expected to be more like that of gallium. In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is known as group 17.
The haloalkanes are alkanes containing one or more halogen substituents. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes that contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compound a non-ozone layer depleter. For more information, see Halomethane. Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula "RX" where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen.
Bromomethane, commonly known as methyl bromide, is an organobromine compound with formula CH3Br. This colorless, odorless, nonflammable gas is produced both industrially and biologically. It is a recognized ozone-depleting chemical. It was used extensively as a pesticide until being phased out by most countries in the early 2000s. From the chemistry perspective, it is one of the halomethanes.
Chloromethane, also called methyl chloride, Refrigerant-40, R-40 or HCC 40, is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3Cl. One of the haloalkanes, it is a colorless, sweet-smelling, flammable gas. Methyl chloride is a crucial reagent in industrial chemistry, although it is rarely present in consumer products, and was formerly utilized as a refrigerant. Most chloromethane is biogenic.

Iodoform is the organoiodine compound with the chemical formula CHI3. It is a pale yellow, crystalline, volatile substance, with a penetrating and distinctive odor and, analogous to chloroform, sweetish taste. It is occasionally used as a disinfectant.
In chemistry, halogenation is a chemical reaction which introduces of one or more halogens into a chemical compound. Halide-containing compounds are pervasive, making this type of transformation important, e.g. in the production of polymers, drugs. This kind of conversion is in fact so common that a comprehensive overview is challenging. This article mainly deals with halogenation using elemental halogens. Halides are also commonly introduced using salts of the halides and halogen acids. Many specialized reagents exist for and introducing halogens into diverse substrates, e.g. thionyl chloride.
Methyl ethyl ketone peroxide (MEKP) is an organic peroxide with the formula [(CH3)(C2H5)C(O2H)]2O2. MEKP is a colorless oily liquid. It is widely used in vulcanization (crosslinking) of polymers.

Halomethane compounds are derivatives of methane with one or more of the hydrogen atoms replaced with halogen atoms. Halomethanes are both naturally occurring, especially in marine environments, and human-made, most notably as refrigerants, solvents, propellants, and fumigants. Many, including the chlorofluorocarbons, have attracted wide attention because they become active when exposed to ultraviolet light found at high altitudes and destroy the Earth's protective ozone layer.
Halocarbon compounds are chemical compounds in which one or more carbon atoms are linked by covalent bonds with one or more halogen atoms resulting in the formation of organofluorine compounds, organochlorine compounds, organobromine compounds, and organoiodine compounds. Chlorine halocarbons are the most common and are called organochlorides.
In organic chemistry, a substituent is one or a group of atoms that replaces atoms, thereby becoming a moiety in the resultant (new) molecule.
In organic chemistry, free-radical halogenation is a type of halogenation. This chemical reaction is typical of alkanes and alkyl-substituted aromatics under application of UV light. The reaction is used for the industrial synthesis of chloroform (CHCl3), dichloromethane (CH2Cl2), and hexachlorobutadiene. It proceeds by a free-radical chain mechanism.

Fluoromethane, also known as methyl fluoride, Freon 41, Halocarbon-41 and HFC-41, is a non-toxic, liquefiable, and flammable gas at standard temperature and pressure. It is made of carbon, hydrogen, and fluorine. The name stems from the fact that it is methane (CH4) with a fluorine atom substituted for one of the hydrogen atoms. It is used in semiconductor manufacturing processes as an etching gas in plasma etch reactors.
Cyclopentane (also called C pentane) is a highly flammable alicyclic hydrocarbon with chemical formula C5H10 and CAS number 287-92-3, consisting of a ring of five carbon atoms each bonded with two hydrogen atoms above and below the plane. It occurs as a colorless liquid with a petrol-like odor. Its freezing point is −94 °C and its boiling point is 49 °C. Cyclopentane is in the class of cycloalkanes, being alkanes that have one or more carbon rings. It is formed by cracking cyclohexane in the presence of alumina at a high temperature and pressure.
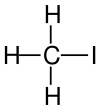
Iodomethane, also called methyl iodide, and commonly abbreviated "MeI", is the chemical compound with the formula CH3I. It is a dense, colorless, volatile liquid. In terms of chemical structure, it is related to methane by replacement of one hydrogen atom by an atom of iodine. It is naturally emitted by rice plantations in small amounts. It is also produced in vast quantities estimated to be greater than 214,000 tons annually by algae and kelp in the world's temperate oceans, and in lesser amounts on land by terrestrial fungi and bacteria. It is used in organic synthesis as a source of methyl groups.
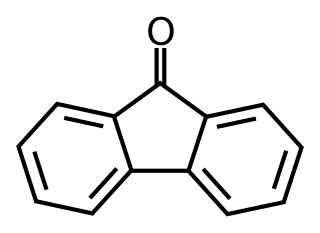
Fluorenone is an organic compound with the chemical formula (C6H4)2CO. It is bright fluorescent yellow solid.
Methylcyclohexane (cyclohexylmethane) is an organic compound with the molecular formula is CH3C6H11. Classified as saturated hydrocarbon, it is a colourless liquid with a faint odor. Methylcyclohexane is used as a solvent. It is mainly converted in naphtha reformers to toluene. Methylcyclohexane is also used in some correction fluids (such as White-Out) as a solvent.
The monochlorophenols are chemical compounds consisting of phenol substituted with a chlorine atom. There are three isomers, 2-chlorophenol, 3-chlorophenol, and 4-chlorophenol.
Arsenic pentafluoride is a chemical compound of arsenic and fluorine. It is a toxic, colorless gas. The oxidation state of arsenic is +5.
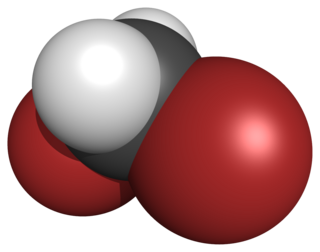
The dihalomethanes are organic compounds in which two hydrogen atoms in methane are replaced by halogen atoms. They belong to the haloalkanes, specifically the subgroup of halomethanes, and contains ten members.