
Fluorometholone acetate, also known as oxylone acetate and sold under the brand names Flarex, Florate, and Omnitrol, is a synthetic glucocorticoid corticosteroid and a corticosteroid ester, as well as a progestogen and progestogen ester. It is the C17α acetate ester of fluorometholone.

Cyclofenil, sold under the brand name Sexovid among others, is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) medication which is used as a gonadotropin stimulant or ovulation inducer and in menopausal hormone therapy in women. It is mostly no longer available. The medication is taken by mouth.

Chlorproethazine, sold under the brand name Neuriplege, is a drug of the phenothiazine group described as a muscle relaxant or tranquilizer which is or has been marketed in Europe as a topical cream for the treatment of muscle pain. It has been associated with photoallergic contact dermatitis.

Prothipendyl, also known as azaphenothiazine or phrenotropin, is an anxiolytic, antiemetic, and antihistamine of the azaphenothiazine group which is marketed in Europe and is used to treat anxiety and agitation in psychotic syndromes. It differs from promazine only by the replacement of one carbon atom with a nitrogen atom in the tricyclic ring system. Prothipendyl is said to not possess antipsychotic effects, and in accordance, appears to be a weaker dopamine receptor antagonist than other phenothiazines.

Bolasterone, also known as 7α,17α-dimethyltestosterone, is a 17α-alkylated androgen/anabolic steroid (AAS) which is used in veterinary medicine. It has close structural similarity to testosterone, and like methyltestosterone has a methyl group at C17α in order to increase oral bioavailability. In addition, it is also 7α-methylated, similar to its 7β-methylated isomer calusterone. The medication has a low to moderate ratio of anabolic to androgenic activity, similar to that of fluoxymesterone.

Oxymesterone, also known as methandrostenediolone, as well as 4-hydroxy-17α-methyltestosterone or 17α-methylandrost-4-en-4,17β-diol-3-one, is an orally active anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS). It was known by 1960.

Trioxifene (INN), or as the salt trioxifene mesylate (USAN), is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) with competitive binding activity against estradiol for the ERα and antagonistic activity against ERα-mediated gene expression, that was under preclinical and clinical development by Eli Lilly and Company for breast cancer and prostate cancer, but was abandoned.

Chloral betaine, also known as cloral betaine (INN), is a sedative-hypnotic drug. It was introduced by Mead Johnson in the United States in 1963. It is a betaine complex with chloral hydrate, which acts as an extended-acting formulation of chloral hydrate which is then metabolized into trichloroethanol, which is responsible for most or all of its effects.

Testosterone phenylpropionate, or testosterone phenpropionate, also known as testosterone hydrocinnamate, is a synthetic anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) and an androgen ester – specifically, the C17β phenylpropionate ester of testosterone – which was formerly marketed in Romania. It was first synthesized in 1951 and was first described in the literature by 1953. The medication was an ingredient of several isolated AAS commercial products, but was never widely used. Testosterone phenylpropionate was also notably a component of Sustanon and Omnadren.

Butidrine (INN), or butedrine or butydrine, also known as hydrobutamine or idrobutamine, is a beta blocker related to pronethalol and propranolol that was developed in the 1960s. Similarly to certain other beta blockers, butidrine also possesses local anesthetic properties.
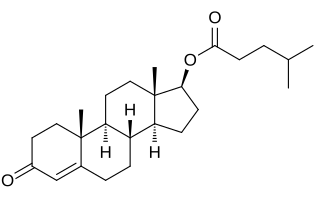
Testosterone isocaproate, sold under the brand names Sustanon 100, Sustanon 250, and Omnadren 250, is an androgen and anabolic steroid medication and a testosterone ester which has been used as a component of mixed testosterone ester preparations.

Testosterone caproate (TCa), also known as testosterone hexanoate, is an androgen and anabolic steroid and a testosterone ester that is no longer marketed. It was formerly available as a component of Omnadren 250, along with testosterone isocaproate, testosterone phenylpropionate, and testosterone propionate, but this formulation has since been discontinued.

Doisynolic acid is a synthetic, nonsteroidal, orally active estrogen that was never marketed. The reaction of estradiol or estrone with potassium hydroxide, a strong base, results in doisynolic acid as a degradation product, which retains high estrogenic activity, and this reaction was how the drug was discovered, in the late 1930s. The drug is a highly active and potent estrogen by the oral or subcutaneous route. The reaction of equilenin or dihydroequilenin with potassium hydroxide was also found to produce bisdehydrodoisynolic acid, the levorotatory isomer of which is an estrogen with an "astonishingly" high degree of potency, while the dextrorotatory isomer is inactive. Doisynolic acid was named after Edward Adelbert Doisy, a pioneer in the field of estrogen research and one of the discoverers of estrone.

Testosterone furoate is an androgen and anabolic steroid and a testosterone ester.

Testosterone hexahydrobenzylcarbonate, or testosterone cyclohexylmethylcarbonate, is an androgen and anabolic steroid and a testosterone ester.

Testosterone hexyloxyphenylpropionate is an androgen and anabolic steroid and a testosterone ester.

Droloxifene, also known as 3-hydroxytamoxifen, is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group that was developed originally in Germany and later in Japan for the treatment of breast cancer, osteoporosis in men and postmenopausal women, and cardiovascular disorders but was abandoned and never marketed. It reached phase II and phase III clinical trials for these indications before development was discontinued in 2000. The drug was found to be significantly less effective than tamoxifen in the treatment of breast cancer in two phase III clinical trials.
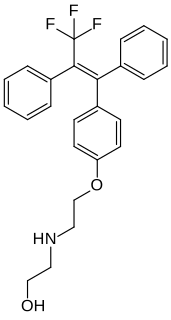
Panomifene (INN) is a nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group related to tamoxifen that was under development as an antineoplastic agent by Egis Pharmaceuticals and IVAX Drug Research Institute in the 1990s for the treatment of breast cancer but was not marketed. It reached phase II clinical trials before development was terminated. The drug was described in 1981.

Pirenperone (INN, USAN, BAN; developmental code names R-47456, R-50656) is a serotonin receptor antagonist described as an antipsychotic and tranquilizer which was never marketed. It is a relatively selective antagonist of the serotonin 5-HT2 receptors and has been used in scientific research to study the serotonin system. In the 1980s, the drug was found to block the effects of the lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) in animals, and along with ketanserin, led to the elucidation of the 5-HT2A receptor as the biological mediator of the effects of serotonergic psychedelics.

Pinoxepin is an antipsychotic of the tricyclic group with a dibenzoxepin ring system which was developed in the 1960s but was never marketed. It was found in clinical trials to have effectiveness in the treatment of schizophrenia similar to that of chlorpromazine and thioridazine. The drug has marked sedative effects but causes relatively mild extrapyramidal symptoms.




















