A saw is a tool consisting of a tough blade, wire, or chain with a hard toothed edge. It is used to cut through material, very often wood, though sometimes metal or stone. The cut is made by placing the toothed edge against the material and moving it forcefully forth and less vigorously back or continuously forward. This force may be applied by hand, or powered by steam, water, electricity or other power source. An abrasive saw has a powered circular blade designed to cut through metal or ceramic.

A mortiseand tenon joint connects two pieces of wood or other material. Woodworkers around the world have used it for thousands of years to join pieces of wood, mainly when the adjoining pieces connect at right angles.

A hand plane is a tool for shaping wood using muscle power to force the cutting blade over the wood surface. Some rotary power planers are motorized power tools used for the same types of larger tasks, but are unsuitable for fine-scale planing, where a miniature hand plane is used.

A lap joint or overlap joint is a joint in which the members overlap. Lap joints can be used to join wood, plastic, or metal. A lap joint can be used in woodworking for joining wood together.

A file is a tool used to remove fine amounts of material from a workpiece. It is common in woodworking, metalworking, and other similar trade and hobby tasks. Most are hand tools, made of a case hardened steel bar of rectangular, square, triangular, or round cross-section, with one or more surfaces cut with sharp, generally parallel teeth. A narrow, pointed tang is common at one end, to which a handle may be fitted.
A reamer is a type of rotary cutting tool used in metalworking. Precision reamers are designed to enlarge the size of a previously formed hole by a small amount but with a high degree of accuracy to leave smooth sides. There are also non-precision reamers which are used for more basic enlargement of holes or for removing burrs. The process of enlarging the hole is called reaming. There are many different types of reamer and they may be designed for use as a hand tool or in a machine tool, such as a milling machine or drill press.

A biscuit joiner or biscuit jointer is a woodworking tool used to join two pieces of wood together. A biscuit joiner uses a small circular saw blade to cut a crescent-shaped hole in the opposite edges of two pieces of wood or wood composite panels. An oval-shaped, highly dried and compressed wooden biscuit is covered with glue, or glue is applied in the slot. The biscuit is immediately placed in the slot, and the two boards are clamped together. The wet glue expands the biscuit, further improving the bond.
A rabbet or rebate is a recess or groove cut into the edge of a piece of machinable material, usually wood. When viewed in cross-section, a rabbet is two-sided and open to the edge or end of the surface into which it is cut.

A flat or coulisse is a flat piece of theatrical scenery which is painted and positioned on stage so as to give the appearance of buildings or other background.

A coping saw is a type of bow saw used to cut intricate external shapes and interior cut-outs in woodworking or carpentry. It is widely used to cut moldings to create coped rather than mitre joints. It is occasionally used to create fretwork though it is not able to match a fretsaw in intricacy of cut, particularly in thin materials. Coping saw blades are always thicker and much coarser cutting than typical fretsaw blades and many others of its family members. Coping saws can however cut slight bends in the work, allowing circles to be cut if used carefully.

A jointer or in some configurations, a jointer-planer is a woodworking machine used to produce a flat surface along a board's length. As a jointer, the machine operates on the narrow edge of boards, preparing them for use as butt joint or gluing into panels. A planer-jointer setup has the width that enables smoothing ('surface planing') and leveling the faces (widths) of boards small enough to fit the tables.

A butt joint is a technique in which two pieces of material are joined by simply placing their ends together without any special shaping. The name "butt joint" comes from the way the material is joined. The butt joint is the simplest joint to make since it merely involves cutting the material to the appropriate length and butting them together. It is also the weakest because unless some form of reinforcement is used, it relies upon glue or welding alone to hold it together. Because the orientation of the material usually presents only one end to a long gluing or welding surface, the resulting joint is inherently weak.
A splice joint is a method of joining two members end to end in woodworking. The splice joint is used when the material being joined is not available in the length required. It is an alternative to other joints such as the butt joint and the scarf joint. Splice joints are stronger than unenforced butt joints and have the potential to be stronger than a scarf joint.
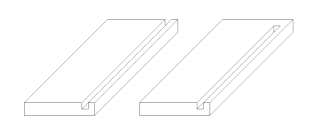
In joinery, a groove is a slot or trench cut into a member which runs parallel to the grain. A groove is thus differentiated from a dado, which runs across the grain.

A countertop, also counter top, counter, benchtop, worktop or kitchen bench, bunker is a raised, firm, flat, and horizontal surface. They are built for work in kitchens or other food preparation areas, bathrooms or lavatories, and workrooms in general. The surface is frequently installed upon and supported by cabinets, positioned at an ergonomic height for the user and the particular task for which it is designed. A countertop may be constructed of various materials with different attributes of functionality, durability and aesthetics, and may have built-in appliances, or accessory items relative to the intended application.

A bridle joint is a woodworking joint, similar to a mortise and tenon, in that a tenon is cut on the end of one member and a mortise is cut into the other to accept it. The distinguishing feature is that the tenon and the mortise are cut to the full width of the tenon member.
This glossary of woodworking lists a number of specialized terms and concepts used in woodworking, carpentry, and related disciplines.
Rift-sawing is a woodworking process that aims to produce lumber that is less vulnerable to distortion than flat sawn lumber. Rift-sawing may be done strictly along a log's radials—perpendicular to the annular growth ring orientation or wood grain—or as part of the quarter sawing process.

In sewing, a seam is the join where two or more layers of fabric, leather, or other materials are held together with stitches. Prior to the invention of the sewing machine, all sewing was done by hand. Seams in modern mass-produced household textiles, sporting goods, and ready-to-wear clothing are sewn by computerized machines, while home shoemaking, dressmaking, quilting, crafts, haute couture and tailoring may use a combination of hand and machine sewing.
The splitting band knife is a kind of knife used in several fields including: tannery, EVA/rubber, foam, cork, shoe and leather goods, paper, carpet and other soft sheet materials. It is a power tool which is very similar in operation to a band saw, with an endless loop blade; the material to be cut is supported by a flat table.













