
Lumber, also known as timber, is wood that has been processed into beams and planks, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for structural purposes but has many other uses as well.

Joinery is a part of woodworking that involves joining pieces of wood, engineered lumber, or synthetic substitutes, to produce more complex items. Some woodworking joints employ mechanical fasteners, bindings, or adhesives, while others use only wood elements.

A chisel is a tool with a characteristically shaped cutting edge of blade on its end, for carving or cutting a hard material such as wood, stone, or metal by hand, struck with a mallet, or mechanical power. The handle and blade of some types of chisel are made of metal or of wood with a sharp edge in it.

A mortiseand tenon joint connects two pieces of wood or other material. Woodworkers around the world have used it for thousands of years to join pieces of wood, mainly when the adjoining pieces connect at right angles.

Engineered wood, also called mass timber, composite wood, man-made wood, or manufactured board, includes a range of derivative wood products which are manufactured by binding or fixing the strands, particles, fibres, or veneers or boards of wood, together with adhesives, or other methods of fixation to form composite material. The panels vary in size but can range upwards of 64 by 8 feet and in the case of cross-laminated timber (CLT) can be of any thickness from a few inches to 16 inches (410 mm) or more. These products are engineered to precise design specifications, which are tested to meet national or international standards and provide uniformity and predictability in their structural performance. Engineered wood products are used in a variety of applications, from home construction to commercial buildings to industrial products. The products can be used for joists and beams that replace steel in many building projects. The term mass timber describes a group of building materials that can replace concrete assemblies. Broad-base adoption of mass timber and their substitution for steel and concrete in new mid-rise construction projects over the next couple decades could help mitigate climate change.

A hand plane is a tool for shaping wood using muscle power to force the cutting blade over the wood surface. Some rotary power planers are motorized power tools used for the same types of larger tasks, but are unsuitable for fine-scale planing, where a miniature hand plane is used.

A lap joint or overlap joint is a joint in which the members overlap. Lap joints can be used to join wood, plastic, or metal. A lap joint can be used in woodworking for joining wood together.

A dovetail joint or simply dovetail is a joinery technique most commonly used in woodworking joinery (carpentry), including furniture, cabinets, log buildings, and traditional timber framing. Noted for its resistance to being pulled apart, the dovetail joint is commonly used to join the sides of a drawer to the front. A series of 'pins' cut to extend from the end of one board interlock with a series of 'tails' cut into the end of another board. The pins and tails have a trapezoidal shape. Once glued, a wooden dovetail joint requires no mechanical fasteners.

A log house, or log building, is a structure built with horizontal logs interlocked at the corners by notching. Logs may be round, squared or hewn to other shapes, either handcrafted or milled. The term "log cabin" generally refers to a smaller, more rustic log house, such as a hunting cabin in the woods, that may or may not have electricity or plumbing.

The steel square is a tool used in carpentry. Carpenters use various tools to lay out structures that are square, many of which are made of steel, but the name steel square refers to a specific long-armed square that has additional uses for measurement, especially of various angles. It consists of a long, wider arm and a shorter, narrower arm, which meet at an angle of 90 degrees. Today the steel square is more commonly referred to as the framing square or carpenter's square, and such squares are no longer invariably made of steel ; they can also be made of aluminum or polymers, which are light and resistant to rust.
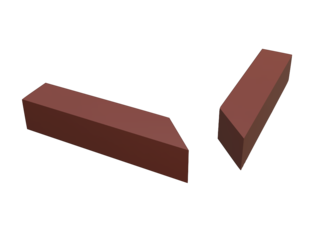
A mitre joint is a joint made by cutting each of two parts to be joined, across the main surface, usually at a 45° angle, to form a corner, usually to form a 90° angle, though it can comprise any angle greater than 0 degrees. It is called beveling when the angled cut is done on the side, although the resulting joint is still a mitre joint.

Clapboard, also called bevel siding, lap siding, and weatherboard, with regional variation in the definition of these terms, is wooden siding of a building in the form of horizontal boards, often overlapping.

A scarf joint is a method of joining two members end to end in woodworking or metalworking. The scarf joint is used when the material being joined is not available in the length required. It is an alternative to other joints such as the butt joint and the splice joint and is often favored over these in joinery because it yields a barely visible glue line.

A finger joint, also known as a comb joint, is a woodworking joint made by cutting a set of complementary, interlocking profiles in two pieces of wood, which are then glued. The cross-section of the joint resembles the interlocking of fingers between two hands, hence the name "finger joint". The sides of each profile increases the surface area for gluing, resulting in a strong bond, stronger than a butt joint but not very visually appealing. Finger joints are regularly confused with box joints, which are used for corners of boxes or box-like constructions.

Japanese carpentry is carpentry in Japan.
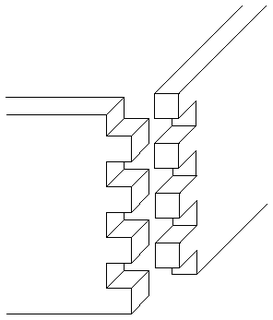
A box joint is a woodworking joint made by cutting a set of complementary, interlocking profiles in two pieces of wood, which are then joined (usually) at right angles, usually glued. The glued box joint has a high glued surface area resulting in a strong bond, on a similar principle to a finger joint. Box joints are used for corners of boxes or box-like constructions, hence the name. The joint does not have the same interlocking properties as a dovetail joint, but is much simpler to make, and can be mass-produced fairly easily.

A butt joint is a technique in which two pieces of material are joined by simply placing their ends together without any special shaping. The name "butt joint" comes from the way the material is joined together. The butt joint is the simplest joint to make since it merely involves cutting the material to the appropriate length and butting them together. It is also the weakest because unless some form of reinforcement is used, it relies upon glue or welding alone to hold it together. Because the orientation of the material usually presents only one end to a long gluing or welding surface, the resulting joint is inherently weak.

A bridle joint is a woodworking joint, similar to a mortise and tenon, in that a tenon is cut on the end of one member and a mortise is cut into the other to accept it. The distinguishing feature is that the tenon and the mortise are cut to the full width of the tenon member.
This glossary of woodworking lists a number of specialized terms and concepts used in woodworking, carpentry, and related disciplines.

Butt welding is when two pieces of metal are placed end-to-end without overlap and then welded along the joint. Importantly, in a butt joint, the surfaces of the workpieces being joined are on the same plane and the weld metal remains within the planes of the surfaces.




















