
Mosquitoes are approximately 3,600 species of small flies comprising the family Culicidae. The word "mosquito" is Spanish for "little fly". Mosquitoes have a slender segmented body, one pair of wings, three pairs of long hair-like legs, and specialized piercing-sucking mouthparts. Evolutionary biologists view mosquitoes as micropredators, small animals that parasitise larger ones by drinking their blood without immediately killing them. Medical parasitologists view mosquitoes instead as vectors of disease, carrying protozoan parasites or bacterial or viral pathogens from one host to another.

Mahogany is a straight-grained, reddish-brown timber of three tropical hardwood species of the genus Swietenia, indigenous to the Americas and part of the pantropical chinaberry family, Meliaceae. Mahogany is used commercially for a wide variety of goods, due to its coloring and durable nature. It is naturally found within the Americas, but has also been imported to plantations across Asia and Oceania. The mahogany trade may have begun as early as the 16th century and flourished in the 17th and 18th centuries. In certain countries, mahogany is considered an invasive species.

Meliaceae, the mahogany family, is a flowering plant family of mostly trees and shrubs in the order Sapindales.

Aedes albopictus, from the mosquito (Culicidae) family, also known as the (Asian) tiger mosquito or forest mosquito, is a mosquito native to the tropical and subtropical areas of Southeast Asia. In the past few centuries, however, this species has spread to many countries through the transport of goods and international travel. It is characterized by the white bands on its legs and body.

Wolbachia is a genus of intracellular bacteria that infects mainly arthropod species, including a high proportion of insects, and also some nematodes. It is one of the most common parasitic microbes, and is possibly the most common reproductive parasite in the biosphere. Its interactions with its hosts are often complex, and in some cases have evolved to be mutualistic rather than parasitic. Some host species cannot reproduce, or even survive, without Wolbachia colonisation. One study concluded that more than 16% of neotropical insect species carry bacteria of this genus, and as many as 25 to 70% of all insect species are estimated to be potential hosts.
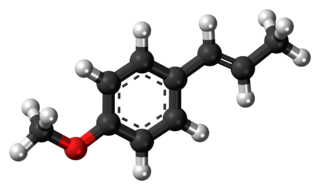
Anethole is an organic compound that is widely used as a flavoring substance. It is a derivative of the aromatic compound allylbenzene and occurs widely in plants in essential oils. It is in the class of phenylpropanoid organic compounds. It contributes a large component of the odor and flavor of anise and fennel, anise myrtle (Myrtaceae), liquorice (Fabaceae), magnolia blossoms, and star anise (Schisandraceae). Closely related to anethole is its isomer estragole, which is abundant in tarragon (Asteraceae) and basil (Lamiaceae), and has a flavor reminiscent of anise. It is a colorless, fragrant, mildly volatile liquid. Anethole is only slightly soluble in water but exhibits high solubility in ethanol. This trait causes certain anise-flavored liqueurs to become opaque when diluted with water; this is called the ouzo effect.

An insect repellent is a substance applied to the skin, clothing, or other surfaces to discourage insects from landing or climbing on that surface. Insect repellents help prevent and control the outbreak of insect-borne diseases such as malaria, Lyme disease, dengue fever, bubonic plague, river blindness, and West Nile fever. Pest animals commonly serving as vectors for disease include insects such as flea, fly, and mosquito; and ticks (arachnids).

Carapa is a genus of flowering plants in the mahogany family, Meliaceae. These are trees up to 30 meters tall occurring in tropical South America, Central America, and Africa. Common names include andiroba and crabwood.

Shorea is a genus of about 196 species of mainly rainforest trees in the family Dipterocarpaceae. The genus is named after Sir John Shore, the governor-general of the British East India Company, 1793–1798. The timber of trees of the genus is sold under the common names lauan, luan, lawaan, meranti, seraya, balau, bangkirai, and Philippine mahogany.

Aedes aegypti, the yellow fever mosquito, is a mosquito that can spread dengue fever, chikungunya, Zika fever, Mayaro and yellow fever viruses, and other disease agents. The mosquito can be recognized by black and white markings on its legs and a marking in the form of a lyre on the upper surface of its thorax. This mosquito originated in Africa, but is now found in tropical, subtropical and temperate regions throughout the world.
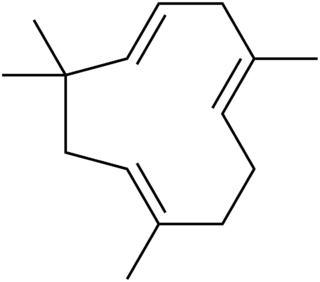
Humulene, also known as α-humulene or α-caryophyllene, is a naturally occurring monocyclic sesquiterpene (C15H24), containing an 11-membered ring and consisting of 3 isoprene units containing three nonconjugated C=C double bonds, two of them being triply substituted and one being doubly substituted. It was first found in the essential oils of Humulus lupulus (hops), from which it derives its name. Humulene is an isomer of β-caryophyllene, and the two are often found together as a mixture in many aromatic plants.

Calophyllum brasiliense (guanandi) is a species of plant in the family Calophyllaceae. It is native to subtropical and tropical regions of Mexico, Central America, South America and the Caribbean.

Swietenia macrophylla, commonly known as mahogany, Honduran mahogany, Honduras mahogany, or big-leaf mahogany is a species of plant in the Meliaceae family. It is one of three species that yields genuine mahogany timber (Swietenia), the others being Swietenia mahagoni and Swietenia humilis. It is native to South America, Mexico and Central America, but naturalized in the Philippines, Singapore, Malaysia and Hawaii, and cultivated in plantations and wind-breaks elsewhere.
Bagassa guianensis is a tree in the plant family Moraceae which is native to the Guianas and Brazil. It is valued as a timber tree and as a food tree for wildlife. The juvenile leaves are distinctly different in appearance from the mature leaves, and were once thought to belong to different species.

Pentaclethra macroloba is a large and common leguminous tree in the genus Pentaclethra native to the wet tropical areas of the northern Neotropics, which can form monocultural stands in some seasonally flooded habitats. It has giant, bipinnate leaves shaped like feathers. It uses seed dispersal by water to establish itself in new areas, having floating seeds that are left behind after the waters recede after floods or tides. It has hard timber which is not very resistant to rot in the tropics, but it can be treated, has a pretty pink-red colour when dry, and has a number of uses. Oil used in cosmetics is extracted from the large seeds. In the northern Amazon region the bark is used in herbal medicine as an antivenom, and in the Guianas the bark has been used as a fish poison. Despite their toxicity, the seeds are eaten by variegated squirrels, parrots and macaws, and serve as the nurseries of the larvae of the moth Carmenta surinamensis.

Lecythis ampla is a species of woody plant in the family Lecythidaceae, which also includes the Brazil nut. Common names include coco, olla de mono, jicaro and salero. It is found in Central and South America. It has been considered an endangered species in Costa Rica.

Piper marginatum, the cake bush, Anesi wiwiri, marigold pepper, Ti Bombé in Creole or Hinojo, is a plant species in the genus Piper found in moist, shady spots in the Amazon rainforest in Surinam, French Guiana and Brazil.
Oxitec is a UK-based, US-owned biotechnology company that develops genetically modified insects in order to improve public health and food security through insect control. The insects act as biological insecticides. Insects are controlled without the use of chemical insecticides. Instead, the insects are genetically engineered to be unable to produce offspring. The company claims that this technology is more effective than insecticides and more environmentally friendly.
Aedes africanus is a species of mosquito that is found on the continent of Africa with the exclusion of Madagascar. Aedes aegypti and Aedes africanus are the two main yellow fever vector species in Zambia. Aedes africanus is mainly found in tropical forests not near wetlands.

















