A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposes in some nations. The term is derived from the Old French comté denoting a jurisdiction under the sovereignty of a count (earl) or a viscount. Literal equivalents in other languages, derived from the equivalent of "count", are now seldom used officially, including comté, contea, contado, comtat, condado, Grafschaft, graafschap, and zhupa in Slavic languages; terms equivalent to 'commune' or 'community' are now often instead used.
An independent city or independent town is a city or town that does not form part of another general-purpose local government entity.

Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of governance or public administration within a particular sovereign state.

Taiwan Province is a de jure administrative division of the Republic of China (ROC). Provinces remain a titular division as a part of the Constitution of the Republic of China, but are no longer considered to have any administrative function practically.
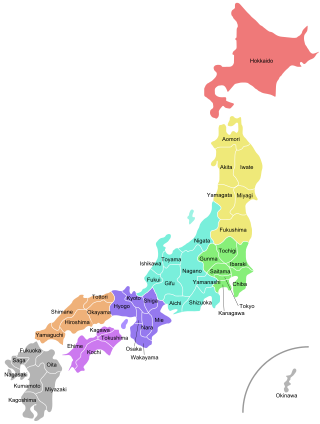
Japan is divided into 47 prefectures, which rank immediately below the national government and form the country's first level of jurisdiction and administrative division. They include 43 prefectures proper, two urban prefectures, one regional prefecture and one metropolis. In 1868, the Meiji Fuhanken sanchisei administration created the first prefectures to replace the urban and rural administrators in the parts of the country previously controlled directly by the shogunate and a few territories of rebels/shogunate loyalists who had not submitted to the new government such as Aizu/Wakamatsu. In 1871, all remaining feudal domains (han) were also transformed into prefectures, so that prefectures subdivided the whole country. In several waves of territorial consolidation, today's 47 prefectures were formed by the turn of the century. In many instances, these are contiguous with the ancient ritsuryō provinces of Japan.

A district is a type of administrative division that in some countries is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions of municipalities, school district, or political district.
Taiwan is divided into multi-layered statutory subdivisions. Due to the complex political status of Taiwan, there is a significant difference in the de jure system set out in the original constitution and the de facto system in use today.
A federal district is a type of administrative division of a federation, usually under the direct control of a federal government and organized sometimes with a single municipal body. Federal districts often include capital districts, and they exist in various federations worldwide.
The district of Aachen is a district in the west of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Neighboring districts are Heinsberg, Düren, Euskirchen, and also the Netherlands province of Limburg and the Belgian province of Liège. Its administrative body is the Städteregionsparlament, headed by the Städteregionspräsident or "region president".

An unincorporated area is a region that is not governed by a local municipal corporation. There are many unincorporated communities and areas in the United States and Canada.

Zamboanga Peninsula is an administrative region in the Philippines, designated as Region IX. It consists of three provinces including four cities and the highly urbanized Zamboanga City. The region was previously known as Western Mindanao before the signing of Executive Order No. 36 of 2001. The city of Zamboanga was designated as the regional center until Pagadian was designated as its new regional center, although Zamboanga City remains the region's cultural, commercial, economic, and educational center.

Basilan, officially the Province of Basilan, is an island province of the Philippines located primarily in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region. Basilan Island is the largest and northernmost of the major islands of the Sulu Archipelago. It is just off the southern coast of the geographic Zamboanga Peninsula.

Cotabato or North Cotabato, officially the Province of Cotabato, is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the Soccsksargen region in Mindanao. Its capital is the city of Kidapawan. Some of its municipalities are under the jurisdiction of the nearby Bangsamoro Autonomous Region.

Isabela, officially the City of Isabela, is a 4th class component city (separate) and de facto capital of the province of Basilan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 130,379 people.
Local government is the third-level of government in Australia, administered with limited autonomy under the states and territories, and in turn beneath the federal government. Local government is not mentioned in the Constitution of Australia, and two referendums in 1974 and 1988 to alter the Constitution relating to local government were unsuccessful. Every state/territory government recognises local government in its own respective constitution. Unlike the two-tier local government system in Canada or the United States, there is only one tier of local government in each Australian state/territory, with no distinction between counties and cities.
A capital district, capital region, or capital territory is normally a specially designated administrative division where a country's seat of government is located. As such, in a federal model of government, no state or territory has any political or economic advantage relative to the others because of the national capital lying within its borders. A capital territory can be a specific form of federal district.

An administrative centre is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune is located.
An unorganized area or unorganized territory is any geographic region in Canada that does not form part of a municipality or Indian reserve. In these areas, the lowest level of government is provincial or territorial. In some of these areas, local service agencies may have some of the responsibilities that would otherwise be covered by municipalities.

The 2019 Bangsamoro autonomy plebiscite was a two-part plebiscite held in Mindanao, Philippines, that ratified the Bangsamoro Organic Law (BOL) and replaced the Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (ARMM) with the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM), as well as the scope of the said region.










