
The Cree are a North American Indigenous people. They live primarily in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations.

Fort Vancouver was a 19th century fur trading post that was the headquarters of the Hudson's Bay Company's Columbia Department, located in the Pacific Northwest. Named for Captain George Vancouver, the fort was located on the northern bank of the Columbia River in present-day Vancouver, Washington. The fort was a major center of the regional fur trading. Every year trade goods and supplies from London arrived either via ships sailing to the Pacific Ocean or overland from Hudson Bay via the York Factory Express. Supplies and trade goods were exchanged with a plethora of Indigenous cultures for fur pelts. Furs from Fort Vancouver were often shipped to the Chinese port of Guangzhou where they were traded for Chinese manufactured goods for sale in the United Kingdom. At its pinnacle, Fort Vancouver watched over 34 outposts, 24 ports, six ships, and 600 employees. Today, a full-scale replica of the fort, with internal buildings, has been constructed and is open to the public as Fort Vancouver National Historic Site.

The North West Company was a fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in the regions that later became Western Canada and Northwestern Ontario. With great wealth at stake, tensions between the companies increased to the point where several minor armed skirmishes broke out, and the two companies were forced by the British government to merge.

The Beaver Wars, also known as the Iroquois Wars or the French and Iroquois Wars were a series of conflicts fought intermittently during the 17th century in North America throughout the Saint Lawrence River valley in Canada and the Great Lakes region which pitted the Iroquois against the Hurons, northern Algonquians and their French allies. As a result of this conflict, the Iroquois destroyed several confederacies and tribes through warfare: the Hurons or Wendat, Erie, Neutral, Wenro, Petun, Susquehannock, Mohican and northern Algonquins whom they defeated and dispersed, some fleeing to neighbouring peoples and others assimilated, routed, or killed.

The Chipewyan are a Dene Indigenous Canadian people of the Athabaskan language family, whose ancestors are identified with the Taltheilei Shale archaeological tradition. They are part of the Northern Athabascan group of peoples, and hail from what is now Western Canada.
Peter Pond was an American explorer, cartographer, merchant and soldier who was a founding member of the North West Company and the Beaver Club. Though he was born and died in Milford, Connecticut, most of his life was spent in northwestern North America, on the upper Mississippi and in western Canada.

Winnipeg River is a Canadian river that flows roughly northwest from Lake of the Woods in the province of Ontario to Lake Winnipeg in Manitoba. This river is 235 kilometres (146 mi) long from the Norman Dam in Kenora to its mouth at Lake Winnipeg. Its watershed is 106,500 square kilometres (41,100 sq mi) in area, mainly in Canada. About 29,000 square kilometres (11,000 sq mi) of the watershed is in northern Minnesota, United States.
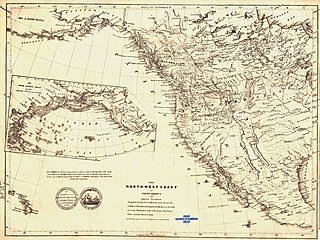
New Caledonia was a fur-trading district of the Hudson's Bay Company that comprised the territory of the north-central portions of present-day British Columbia, Canada. Though not a British colony, New Caledonia was part of the British claim to North America. Its administrative centre was Fort St. James. The rest of what is now mainland British Columbia was called the Columbia Department by the British, and the Oregon Country by the Americans. Even before the partition of the Columbia Department by the Oregon Treaty in 1846, New Caledonia was often used to describe anywhere on the mainland not in the Columbia Department, such as Fort Langley in the Fraser Valley.

Peter Skene Ogden was a British-Canadian fur trader and an early explorer of what is now British Columbia and the Western United States. During his many expeditions, he explored parts of Oregon, Washington, Nevada, California, Utah, Idaho, and Wyoming. Despite early confrontations with the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) while working for the North West Company, he later became a senior official in the operations of the HBC's Columbia Department, serving as manager of Fort Simpson and similar posts.
Spokane House was a fur-trading post founded in 1810 by the British-Canadian North West Company, located on a peninsula where the Spokane River and Little Spokane River meet. When established, the North West Company's farthest outpost in the Columbia River region was the first ever non-Indigenous settlement in the Pacific Northwest. An American rival of the NWC, the Pacific Fur Company opened a station adjacent to Spokane House, called Fort Spokane. The War of 1812 and ongoing supply issues caused the collapse of the PFC, with its posts now under the control of the NWC. The original Spokane House was abandoned in favor of Fort Spokane, though the latter location was still called Spokane House. The second Spokane House saw use as a major post in the interior Oregon Country until the NWC was absorbed by the Hudson's Bay Company in 1821. During a general tour of the Pacific Northwest, Spokane House was abandoned by George Simpson in 1825, in favor of a new post that became Fort Colvile. The site of Spokane House is in Spokane County in the U.S. state of Washington, just northwest of the city of Spokane.

The trade center Fort Colvile was built by the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) at Kettle Falls on the Columbia River in 1825 and operated in the Columbia fur district of the company. Named for Andrew Colvile, a London governor of the HBC, the fort was a few miles west of the present site of Colville, Washington. It was an important stop on the York Factory Express trade route to London via the Hudson Bay. The HBC for some time considered Fort Colvile second in importance only to Fort Vancouver, near the mouth of the Columbia, until the foundation of Fort Victoria.
Fort Nassau was the first Dutch settlement in North America, located beside the "North River" within present-day Albany, New York, in the United States. The factorij was a small fortification which served as a trading post and warehouse.

The Red River Trails were a network of ox cart routes connecting the Red River Colony and Fort Garry in British North America with the head of navigation on the Mississippi River in the United States. These trade routes ran from the location of present-day Winnipeg in the Canadian province of Manitoba across the Canada–United States border, and thence by a variety of routes through what is now the eastern part of North Dakota and western and central Minnesota to Mendota and Saint Paul, Minnesota on the Mississippi.
Lac la Nonne is a lake in northern Alberta, Canada. It is located between Lac Ste. Anne County and the County of Barrhead No. 11, 85 km north-west from Edmonton, east of the Grizzly Trail.

The history of Albany, New York prior to 1664 begins with the native inhabitants of the area and ends in 1664, with the English takeover of New Netherland. The area was originally inhabited by Algonquian Indian tribes and was given different names by the various peoples. The Mohican called it Pempotowwuthut-Muhhcanneuw, meaning "the fireplace of the Mohican nation", while the Iroquois called it Sche-negh-ta-da, or "through the pine woods". Albany's first European structure was a primitive fort on Castle Island built by French traders in 1540. It was destroyed by flooding soon after construction.

This article covers the water based Canadian canoe routes used by early explorers of Canada with special emphasis on the fur trade.

Voyageurs were 18th- and 19th-century French Canadians who transported furs by canoe at the peak of the North American fur trade. The emblematic meaning of the term applies to places and times where that transportation was over long distances. The voyageurs' strength and endurance was regarded as legendary. They were celebrated in folklore and music. For reasons of promised celebrity status and wealth, this position was coveted.

The Pemmican War was a series of armed confrontations during the North American fur trade between the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) and the North West Company (NWC) in the years following the establishment of the Red River Colony in 1812 by Lord Selkirk. It ended in 1821 when the NWC merged with the HBC.

Fort Albany was a Hudson's Bay Company trading post established in 1679 near the site of the present day Fort Albany First Nation. The fort was one of the oldest and most important of the Hudson's Bay Company's posts. It was also involved in Anglo-French tensions leading to the Battle of Fort Albany in 1688.














