
The chalcogens are the chemical elements in group 16 of the periodic table. This group is also known as the oxygen family. Group 16 consists of the elements oxygen (O), sulfur (S), selenium (Se), tellurium (Te), and the radioactive elements polonium (Po) and livermorium (Lv). Often, oxygen is treated separately from the other chalcogens, sometimes even excluded from the scope of the term "chalcogen" altogether, due to its very different chemical behavior from sulfur, selenium, tellurium, and polonium. The word "chalcogen" is derived from a combination of the Greek word khalkόs (χαλκός) principally meaning copper, and the Latinized Greek word genēs, meaning born or produced.

Polonium is a chemical element; it has symbol Po and atomic number 84. A rare and highly radioactive metal with no stable isotopes, polonium is a chalcogen and chemically similar to selenium and tellurium, though its metallic character resembles that of its horizontal neighbors in the periodic table: thallium, lead, and bismuth. Due to the short half-life of all its isotopes, its natural occurrence is limited to tiny traces of the fleeting polonium-210 in uranium ores, as it is the penultimate daughter of natural uranium-238. Though longer-lived isotopes exist, such as the 124 years half-life of polonium-209, they are much more difficult to produce. Today, polonium is usually produced in milligram quantities by the neutron irradiation of bismuth. Due to its intense radioactivity, which results in the radiolysis of chemical bonds and radioactive self-heating, its chemistry has mostly been investigated on the trace scale only.
Livermorium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Lv and atomic number 116. It is an extremely radioactive element that has only been created in a laboratory setting and has not been observed in nature. The element is named after the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in the United States, which collaborated with the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR) in Dubna, Russia, to discover livermorium during experiments conducted between 2000 and 2006. The name of the laboratory refers to the city of Livermore, California, where it is located, which in turn was named after the rancher and landowner Robert Livermore. The name was adopted by IUPAC on May 30, 2012. Five isotopes of livermorium are known, with mass numbers of 288 and 290–293 inclusive; the longest-lived among them is livermorium-293 with a half-life of about 60 milliseconds. A sixth possible isotope with mass number 294 has been reported but not yet confirmed.

The carbon group is a periodic table group consisting of carbon (C), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), tin (Sn), lead (Pb), and flerovium (Fl). It lies within the p-block.
A period 6 element is one of the chemical elements in the sixth row (or period) of the periodic table of the chemical elements, including the lanthanides. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behaviour of the elements as their atomic number increases: a new row is begun when chemical behaviour begins to repeat, meaning that elements with similar behaviour fall into the same vertical columns. The sixth period contains 32 elements, tied for the most with period 7, beginning with caesium and ending with radon. Lead is currently the last stable element; all subsequent elements are radioactive. For bismuth, however, its only primordial isotope, 209Bi, has a half-life of more than 1019 years, over a billion times longer than the current age of the universe. As a rule, period 6 elements fill their 6s shells first, then their 4f, 5d, and 6p shells, in that order; however, there are exceptions, such as gold.
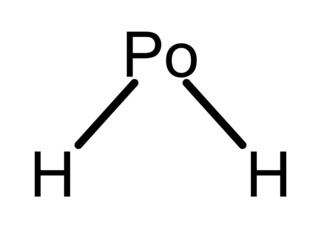
Polonium hydride (also known as polonium dihydride, hydrogen polonide, or polane) is a chemical compound with the formula PoH2. It is a liquid at room temperature, the second hydrogen chalcogenide with this property after water. It is very unstable chemically and tends to decompose into elemental polonium and hydrogen. It is a volatile and very labile compound, from which many polonides can be derived. Additionally, it is radioactive.

Lithium polonide is a chemical compound with the formula Li2Po. It is a polonide, a set of very chemically stable compounds of polonium.

Sodium polonide is a radioactive chemical compound with the formula Na2Po. This salt is a polonide, a set of very chemically stable compounds of polonium. Due to the difference in electronegativity (ΔEN) between sodium and polonium and the slight non-metallic character of polonium, it is intermediate between intermetallic phases and ionic compounds.

Potassium polonide is a chemical compound with the formula K2Po. It is a polonide, a set of very chemically stable compounds of polonium.
Hydrogen chalcogenides are binary compounds of hydrogen with chalcogen atoms. Water, the first chemical compound in this series, contains one oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms, and is the most common compound on the Earth's surface.

Samarium(II) bromide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula SmBr
2. It is a brown solid that is insoluble in most solvents but degrades readily in air.
Organopolonium chemistry describes the synthesis and properties of chemical compounds containing a carbon to polonium chemical bond.
Samarium(III) iodide is an inorganic compound, a salt of samarium and hydroiodic acid with the chemical formula SmI
3.
Polonium tetranitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of polonium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Po(NO3)4. The compound is radioactive, forms white crystals.
Polonium sulfide is an inorganic compound of polonium and sulfur with the chemical formula PoS. The compound is radioactive and forms black crystals.
Polonium tetraiodide is a binary inorganic compound of polonium and iodine with the chemical formula PoI
4. The compound forms volatile black crystals.
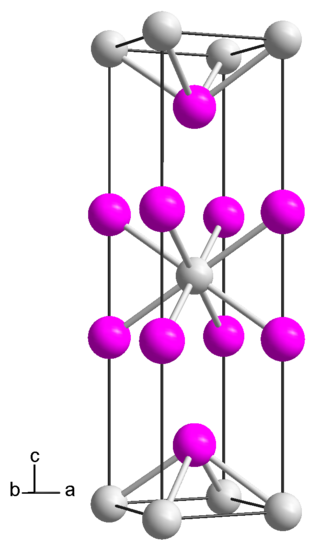
Praseodymium diiodide is a chemical compound with the empirical formula of PrI2, consisting of praseodymium and iodine. It is an electride, with the ionic formula of Pr3+(I−)2e−, and therefore not a true praseodymium(II) compound.

Disulfur diiodide is an unstable inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula S2I2. It is a red-brown solid that decomposes above −30 °C to elemental sulfur and iodine.
Californium(II) iodide is a binary inorganic compound of californium and iodine with the formula CfI
2.
Einsteinium(II) iodide is a binary inorganic chemical compound of einsteinium and iodide with the chemical formula EsI2.







