Bromine is a chemical element; it has symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured vapour. Its properties are intermediate between those of chlorine and iodine. Isolated independently by two chemists, Carl Jacob Löwig and Antoine Jérôme Balard, its name was derived from the Ancient Greek βρῶμος (bromos) meaning "stench", referring to its sharp and pungent smell.

Iodine is a chemical element; it has symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists at standard conditions as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid that melts to form a deep violet liquid at 114 °C (237 °F), and boils to a violet gas at 184 °C (363 °F). The element was discovered by the French chemist Bernard Courtois in 1811 and was named two years later by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, after the Ancient Greek Ιώδης, meaning 'violet'.

Titration is a common laboratory method of quantitative chemical analysis to determine the concentration of an identified analyte. A reagent, termed the titrant or titrator, is prepared as a standard solution of known concentration and volume. The titrant reacts with a solution of analyte to determine the analyte's concentration. The volume of titrant that reacted with the analyte is termed the titration volume.
An iodide ion is the ion I−. Compounds with iodine in formal oxidation state −1 are called iodides. In everyday life, iodide is most commonly encountered as a component of iodized salt, which many governments mandate. Worldwide, iodine deficiency affects two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disability.
In chemistry, an interhalogen compound is a molecule which contains two or more different halogen atoms and no atoms of elements from any other group.
In chemistry, the iodine value is the mass of iodine in grams that is consumed by 100 grams of a chemical substance. Iodine numbers are often used to determine the degree of unsaturation in fats, oils and waxes. In fatty acids, unsaturation occurs mainly as double bonds which are very reactive towards halogens, the iodine in this case. Thus, the higher the iodine value, the more unsaturations are present in the fat. It can be seen from the table that coconut oil is very saturated, which means it is good for making soap. On the other hand, linseed oil is highly unsaturated, which makes it a drying oil, well suited for making oil paints.
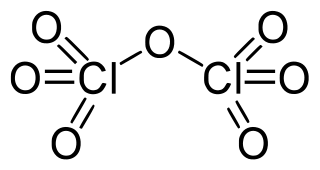
Dichlorine heptoxide is the chemical compound with the formula Cl2O7. This chlorine oxide is the anhydride of perchloric acid. It is produced by the careful distillation of perchloric acid in the presence of the dehydrating agent phosphorus pentoxide:

Periodic acid is the highest oxoacid of iodine, in which the iodine exists in oxidation state +7. It can exist in two forms: orthoperiodic acid, with the chemical formula H5IO6, and metaperiodic acid, which has the formula HIO4.

The iodine clock reaction is a classical chemical clock demonstration experiment to display chemical kinetics in action; it was discovered by Hans Heinrich Landolt in 1886. The iodine clock reaction exists in several variations, which each involve iodine species and redox reagents in the presence of starch. Two colourless solutions are mixed and at first there is no visible reaction. After a short time delay, the liquid suddenly turns to a shade of dark blue due to the formation of a triiodide–starch complex. In some variations, the solution will repeatedly cycle from colorless to blue and back to colorless, until the reagents are depleted.
Glycol cleavage is a specific type of organic chemistry oxidation. The carbon–carbon bond in a vicinal diol (glycol) is cleaved and instead the two oxygen atoms become double-bonded to their respective carbon atoms. Depending on the substitution pattern in the diol, these carbonyls will be ketones and/or aldehydes.
Bromine compounds are compounds containing the element bromine (Br). These compounds usually form the -1, +1, +3 and +5 oxidation states. Bromine is intermediate in reactivity between chlorine and iodine, and is one of the most reactive elements. Bond energies to bromine tend to be lower than those to chlorine but higher than those to iodine, and bromine is a weaker oxidising agent than chlorine but a stronger one than iodine. This can be seen from the standard electrode potentials of the X2/X− couples (F, +2.866 V; Cl, +1.395 V; Br, +1.087 V; I, +0.615 V; At, approximately +0.3 V). Bromination often leads to higher oxidation states than iodination but lower or equal oxidation states to chlorination. Bromine tends to react with compounds including M–M, M–H, or M–C bonds to form M–Br bonds.
Iodine compounds are compounds containing the element iodine. Iodine can form compounds using multiple oxidation states. Iodine is quite reactive, but it is much less reactive than the other halogens. For example, while chlorine gas will halogenate carbon monoxide, nitric oxide, and sulfur dioxide, iodine will not do so. Furthermore, iodination of metals tends to result in lower oxidation states than chlorination or bromination; for example, rhenium metal reacts with chlorine to form rhenium hexachloride, but with bromine it forms only rhenium pentabromide and iodine can achieve only rhenium tetraiodide. By the same token, however, since iodine has the lowest ionisation energy among the halogens and is the most easily oxidised of them, it has a more significant cationic chemistry and its higher oxidation states are rather more stable than those of bromine and chlorine, for example in iodine heptafluoride.

Hypoiodous acid is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula HOI.It forms when an aqueous solution of iodine is treated with mercuric or silver salts. It rapidly decomposes by disproportionation:

Thiocyanogen, (SCN)2, is a pseudohalogen derived from the pseudohalide thiocyanate, [SCN]−, with behavior intermediate between dibromine and diiodine. This hexatomic compound exhibits C2 point group symmetry and has the connectivity NCS-SCN.

Iodine oxides are chemical compounds of oxygen and iodine. Iodine has only two stable oxides which are isolatable in bulk, iodine tetroxide and iodine pentoxide, but a number of other oxides are formed in trace quantities or have been hypothesized to exist. The chemistry of these compounds is complicated with only a few having been well characterized. Many have been detected in the atmosphere and are believed to be particularly important in the marine boundary layer.
Unlike its lighter congeners, the halogen iodine forms a number of stable organic compounds, in which iodine exhibits higher formal oxidation states than -1 or coordination number exceeding 1. These are the hypervalent organoiodines, often called iodanes after the IUPAC rule used to name them.
Carbonyl oxidation with hypervalent iodine reagents involves the functionalization of the α position of carbonyl compounds through the intermediacy of a hypervalent iodine(III) enolate species. This electrophilic intermediate may be attacked by a variety of nucleophiles or undergo rearrangement or elimination.
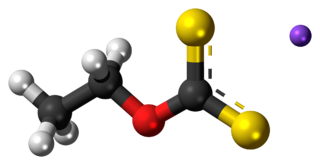
Sodium ethyl xanthate (SEX) is an organosulfur compound with the chemical formula CH3CH2OCS2Na. It is a pale yellow powder, which is usually obtained as the dihydrate. Sodium ethyl xanthate is used in the mining industry as a flotation agent. A closely related potassium ethyl xanthate (KEX) is obtained as the anhydrous salt.
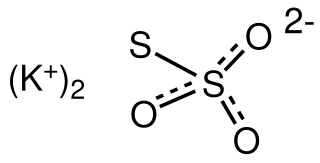
Potassium thiosulfate, commonly abbreviated KTS, is an inorganic compound with the formula K2S2O3. This salt can form multiple hydrates, such as the monohydrate, dihydrate, and the pentahydrate, all of which are white or colorless solids. It is used as a fertilizer.

Tetraiodine nonoxide is an iodine oxide with the chemical formula I4O9.