
In microelectronics, a dual in-line package is an electronic component package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins. The package may be through-hole mounted to a printed circuit board (PCB) or inserted in a socket. The dual-inline format was invented by Don Forbes, Rex Rice and Bryant Rogers at Fairchild R&D in 1964, when the restricted number of leads available on circular transistor-style packages became a limitation in the use of integrated circuits. Increasingly complex circuits required more signal and power supply leads ; eventually microprocessors and similar complex devices required more leads than could be put on a DIP package, leading to development of higher-density chip carriers. Furthermore, square and rectangular packages made it easier to route printed-circuit traces beneath the packages.

The 7400 series is a popular logic family of transistor–transistor logic (TTL) integrated circuits (ICs).
Pro Electron or EECA is the European type designation and registration system for active components.

A small outline integrated circuit (SOIC) is a surface-mounted integrated circuit (IC) package which occupies an area about 30–50% less than an equivalent dual in-line package (DIP), with a typical thickness being 70% less. They are generally available in the same pin-outs as their counterpart DIP ICs. The convention for naming the package is SOIC or SO followed by the number of pins. For example, a 14-pin 4011 would be housed in an SOIC-14 or SO-14 package.
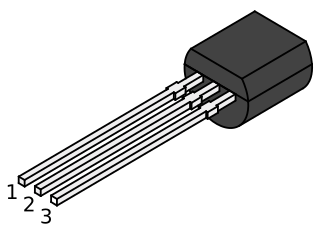
The TO-92 is a widely used style of semiconductor package mainly used for transistors. The case is often made of epoxy or plastic, and offers compact size at a very low cost.

The TO-220 is a style of electronic package used for high-powered, through-hole components with 0.1 inches (2.54 mm) pin spacing. The "TO" designation stands for "transistor outline". TO-220 packages have three leads. Similar packages with two, four, five or seven leads are also manufactured. A notable characteristic is a metal tab with a hole, used to mount the case to a heatsink, allowing the component to dissipate more heat than one constructed in a TO-92 case. Common TO-220-packaged components include discrete semiconductors such as transistors and silicon-controlled rectifiers, as well as integrated circuits.

The 2N3055 is a silicon NPN power transistor intended for general purpose applications. It was introduced in the early 1960s by RCA using a hometaxial power transistor process, transitioned to an epitaxial base in the mid-1970s. Its numbering follows the JEDEC standard. It is a transistor type of enduring popularity.
Open collector, open drain, open emitter, and open source refer to integrated circuit (IC) output pin configurations that process the IC's internal function through a transistor with an exposed terminal that is internally unconnected. One of the IC's internal high or low voltage rails typically connects to another terminal of that transistor. When the transistor is off, the output is internally disconnected from any internal power rail, a state called "high-impedance" (Hi-Z). Open outputs configurations thus differ from push–pull outputs, which use a pair of transistors to output a specific voltage or current.
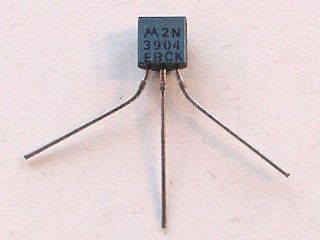
The 2N3904 is a common NPN bipolar junction transistor used for general-purpose low-power amplifying or switching applications. It is designed for low current and power, medium voltage, and can operate at moderately high speeds. It is complementary to the 2N3906 PNP transistor. Both types were registered by Motorola Semiconductor in the mid-1960s.

The 2N2222 is a common NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) used for general purpose low-power amplifying or switching applications. It is designed for low to medium current, low power, medium voltage, and can operate at moderately high speeds. It was originally made in the TO-18 metal can as shown in the picture.

The BC548 is a general-purpose NPN bipolar junction transistor commonly used in European and American electronic equipment. It is notably often the first type of bipolar transistor hobbyists encounter and is often featured in designs in hobby electronics magazines where a general-purpose transistor is required. The BC548 is low in cost and widely available.
A semiconductor package is a metal, plastic, glass, or ceramic casing containing one or more discrete semiconductor devices or integrated circuits. Individual components are fabricated on semiconductor wafers before being diced into die, tested, and packaged. The package provides a means for connecting it to the external environment, such as printed circuit board, via leads such as lands, balls, or pins; and protection against threats such as mechanical impact, chemical contamination, and light exposure. Additionally, it helps dissipate heat produced by the device, with or without the aid of a heat spreader. There are thousands of package types in use. Some are defined by international, national, or industry standards, while others are particular to an individual manufacturer.

In electronics, TO-18 is a designation for a style of transistor metal case. The case is more expensive than the similarly sized plastic TO-92 package. The name is from JEDEC, signifying Transistor Outline Package, Case Style 18.

DO-204 is a family of diode semiconductor packages defined by JEDEC. This family comprises lead-mounted axial devices with round leads. Generally a diode will have a line painted near the cathode end.

In electronics, a chip carrier is one of several kinds of surface-mount technology packages for integrated circuits. Connections are made on all four edges of a square package; compared to the internal cavity for mounting the integrated circuit, the package overall size is large.

In electronics, TO-5 is a designation for a standardized metal semiconductor package used for transistors and some integrated circuits. The TO element stands for "transistor outline" and refers to a series of technical drawings produced by JEDEC. The first commercial silicon transistors, the 2N696 and 2N697 from Fairchild Semiconductor, came in a TO-5 package.

TO-126 is a type of semiconductor package for devices with three pins, such as transistors. The package is rectangular with a hole in the middle to allow for easy mounting to a board or a heat sink. On one side of the package typically a metal sheet is exposed, with the transistor die bonded to the other side of the metal sheet inside the package. This allows for an efficient heat transfer from the transistor die to an external heat sink but also implies that the metal sheet is electrically connected to the die.

TO-66 is a type of semiconductor package for devices with three connections, such as transistors. The shape is similar to the TO-3 package, but the size is smaller. The TO-66 package is made entirely of metal and is commonly used by silicon controlled rectifiers and power transistors. In Europe, it was popularly used by the complementary germanium power transistors AD161/AD162.

In electronics, TO-8 is a designation for a standardized metal semiconductor package. TO in TO-8 stands for "transistor outline" and refers to a series of technical drawings produced by JEDEC. The TO-8 package is noticeably larger than the more common TO-5 package. While originally designed for medium power transistors such as the 2N1483 series or the AD136, it is more commonly used for integrated circuits and sensors.




















