
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure R−C(=O)−R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group −C(=O)−. The simplest ketone is acetone, with the formula (CH3)2CO. Many ketones are of great importance in biology and in industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, and the solvent acetone.
Methylation, in the chemical sciences, is the addition of a methyl group on a substrate, or the substitution of an atom by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replacing a hydrogen atom. These terms are commonly used in chemistry, biochemistry, soil science, and biology.

In organic chemistry, an imine is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond. The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bonds. Imines are common in synthetic and naturally occurring compounds and they participate in many reactions.

Anthraquinone, also called anthracenedione or dioxoanthracene, is an aromatic organic compound with formula C
14H
8O
2. Isomers include various quinone derivatives. The term anthraquinone however refers to the isomer, 9,10-anthraquinone wherein the keto groups are located on the central ring. It is a building block of many dyes and is used in bleaching pulp for papermaking. It is a yellow, highly crystalline solid, poorly soluble in water but soluble in hot organic solvents. It is almost completely insoluble in ethanol near room temperature but 2.25 g will dissolve in 100 g of boiling ethanol. It is found in nature as the rare mineral hoelite.
Cyclohexene is a hydrocarbon with the formula (CH2)4C2H2. It is a colorless liquid with a sharp odor. Although it is one of the simplest cycloalkene, it has few applications.

Anisole, or methoxybenzene, is an organic compound with the formula CH3OC6H5. It is a colorless liquid with a smell reminiscent of anise seed, and in fact many of its derivatives are found in natural and artificial fragrances. The compound is mainly made synthetically and is a precursor to other synthetic compounds. Structurally, it is an ether with a methyl and phenyl group attached. Anisole is a standard reagent of both practical and pedagogical value.

Trimethylaluminium is one of the simplest examples of an organoaluminium compound. Despite its name it has the formula Al2(CH3)6 (abbreviated as Al2Me6 or TMA), as it exists as a dimer. This colorless liquid is pyrophoric. It is an industrially important compound, closely related to triethylaluminium.

Raney nickel, also called spongy nickel, is a fine-grained solid composed mostly of nickel derived from a nickel–aluminium alloy. Several grades are known, of which most are gray solids. Some are pyrophoric, but most are used as air-stable slurries. Raney nickel is used as a reagent and as a catalyst in organic chemistry. It was developed in 1926 by American engineer Murray Raney for the hydrogenation of vegetable oils. Raney is a registered trademark of W. R. Grace and Company. Other major producers are Evonik and Johnson Matthey.

Amidines are organic compounds with the functional group RC(NR)NR2, where the R groups can be the same or different. They are the imine derivatives of amides (RC(O)NR2). The simplest amidine is formamidine, HC(=NH)NH2.

o-Phenylenediamine (OPD) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(NH2)2. This aromatic diamine is an important precursor to many heterocyclic compounds. OPD is a white compound although samples appear darker owing to oxidation by air. It is isomeric with m-phenylenediamine and p-phenylenediamine.

1,4-Benzoquinone, commonly known as para-quinone, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H4O2. In a pure state, it forms bright-yellow crystals with a characteristic irritating odor, resembling that of chlorine, bleach, and hot plastic or formaldehyde. This six-membered ring compound is the oxidized derivative of 1,4-hydroquinone. The molecule is multifunctional: it exhibits properties of a ketone, being able to form oximes; an oxidant, forming the dihydroxy derivative; and an alkene, undergoing addition reactions, especially those typical for α,β-unsaturated ketones. 1,4-Benzoquinone is sensitive toward both strong mineral acids and alkali, which cause condensation and decomposition of the compound.
Tetrahydropyran (THP) is the organic compound consisting of a saturated six-membered ring containing five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. It is named by reference to pyran, which contains two double bonds, and may be produced from it by adding four hydrogens. In 2013, its preferred IUPAC name was established as oxane. The compound is a colourless volatile liquid. Derivatives of tetrahydropyran are, however, more common. 2-Tetrahydropyranyl (THP-) ethers derived from the reaction of alcohols and 3,4-dihydropyran are commonly used as protecting groups in organic synthesis. Furthermore, a tetrahydropyran ring system, i.e., five carbon atoms and an oxygen, is the core of pyranose sugars, such as glucose.
The reduction of nitro compounds are chemical reactions of wide interest in organic chemistry. The conversion can be effected by many reagents. The nitro group was one of the first functional groups to be reduced. Alkyl and aryl nitro compounds behave differently. Most useful is the reduction of aryl nitro compounds.

Sulfolene, or butadiene sulfone is a cyclic organic chemical with a sulfone functional group. It is a white, odorless, crystalline, indefinitely storable solid, which dissolves in water and many organic solvents. The compound is used as a source of butadiene.
The Glaser coupling is a type of coupling reaction. It is by far the oldest acetylenic coupling and is based on cuprous salts like copper(I) chloride or copper(I) bromide and an additional oxidant like oxygen. The base in its original scope is ammonia. The solvent is water or an alcohol. The reaction was first reported by Carl Andreas Glaser in 1869. He suggested the following process for his way to diphenylbutadiyne:

Benzyl cyanide (abbreviated BnCN) is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH2CN. This colorless oily aromatic liquid is an important precursor to numerous compounds in organic chemistry. It is also an important pheromone in certain species.

Cyclohexenone is an organic compound which is a versatile intermediate used in the synthesis of a variety of chemical products such as pharmaceuticals and fragrances. It is colorless liquid, but commercial samples are often yellow.

2-Naphthol, or β-naphthol, is a fluorescent colorless (or occasionally yellow) crystalline solid with the formula C10H7OH. It is an isomer of 1-naphthol, differing by the location of the hydroxyl group on the naphthalene ring. The naphthols are naphthalene homologues of phenol, but more reactive. Both isomers are soluble in simple alcohols, ethers, and chloroform. 2-Naphthol is a widely used intermediate for the production of dyes and other compounds.
1-Naphthol, or α-naphthol, is a organic compound with the formula C10H7OH. It is a fluorescent white solid. 1-Naphthol differs from its isomer 2-naphthol by the location of the hydroxyl group on the naphthalene ring. The naphthols are naphthalene homologues of phenol. Both isomers are soluble in simple organic solvents. They are precursors to a variety of useful compounds.
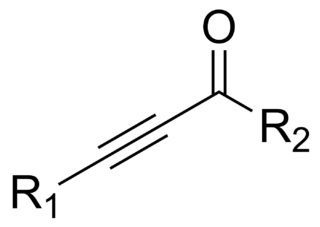
In organic chemistry, an ynone is an organic compound containing a ketone functional group and a C≡C triple bond. Many ynones are α,β-ynones, where the carbonyl and alkyne groups are conjugated. Capillin is a naturally occurring example. Some ynones are not conjugated.













