
A tsunami is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explosions above or below water all have the potential to generate a tsunami. Unlike normal ocean waves, which are generated by wind, or tides, which are in turn generated by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun, a tsunami is generated by the displacement of water from a large event.

The Ring of Fire is a tectonic belt, about 40,000 km (25,000 mi) long and up to about 500 km (310 mi) wide, which circumscribes the Pacific Ocean. It contains between 750 and 915 volcanoes, around two-thirds of the world total, and 90% of the world's earthquakes, including 81% of its largest, take place within the belt.

A megatsunami is a very large wave created by a large, sudden displacement of material into a body of water.

Pico do Fogo is an active stratovolcano located on the island of Fogo, Cape Verde, rising to 2,829 metres (9,281 ft) above sea level. The main cone last erupted in 1680, causing mass emigration from the island. A subsidiary vent erupted in 1995. The only deadly eruption was in 1847 when earthquakes killed several people.

Anak Krakatoa is a volcanic island in Indonesia. On 29 December 1927, Anak Krakatoa first emerged from the caldera formed in 1883 by the explosive volcanic eruption that destroyed the island of Krakatoa. There has been sporadic eruptive activity at the site since the late 20th century, culminating with a large underwater collapse of the volcano that caused a deadly tsunami in December 2018. There has been subsequent activity since. Due to its young age, the island is one of several in the area that are of interest to, and the subject of extensive study by, volcanologists.

Ruang is the southernmost stratovolcano in the Sangihe Islands arc. It comprises an island 4 × 5 km wide. The summit contains a partial lava dome, and reaches some 725 meters (2,379 ft) in altitude. From its summit, Klabat's peak in the south, that of Siau to the north, and Ternate to the east can all be seen.
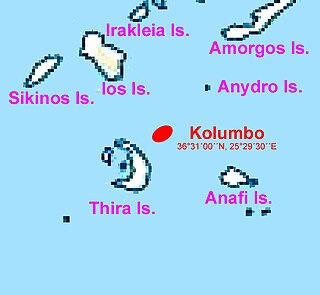
Kolumbo is an active submarine volcano in the Aegean Sea in Greece, about 8 km northeast of Cape Kolumbo, Santorini island. The largest of a line of about twenty submarine volcanic cones extending to the northeast from Santorini, it is about 3 km in diameter with a crater 1.5 km across. It was "discovered" when it breached the sea surface in 1649-50, but its explosion was not to be compared to the well-known Thera explosion and caldera collapse, currently dated ca. 1630 BCE, with its devastating consequences for Minoan civilization. The Smithsonian Institution's Global Volcanism Program treats it as part of the Santorini volcano, though at least one source maintains that it is a separate magmatic system.

Ōshima is an uninhabited island in the Sea of Japan, 50 kilometers (31 mi) to the west from Matsumae town and therefore the westernmost point of Hokkaido. It is part of the town of Matsumae in Oshima Subprefecture in Hokkaido, Japan. To distinguish Ōshima from other islands with the same name, it is sometimes known as Oshima Ōshima (渡島大島) or Matsumae Ōshima (松前大島).

Hunga Tonga–Hunga Haʻapai is a submarine volcano in the South Pacific located about 30 km (19 mi) south of the submarine volcano of Fonuafoʻou and 65 km (40 mi) north of Tongatapu, Tonga's main island. It is part of the highly active Kermadec-Tonga subduction zone and its associated volcanic arc, which extends from New Zealand north-northeast to Fiji, and is formed by the subduction of the Pacific Plate under the Indo-Australian Plate. It lies about 100 km (62 mi) above a very active seismic zone.

The 1792 Unzen landslide and tsunami resulted from the volcanic activities of Mount Unzen on 21 May. This caused the collapse of the southern flank of the Mayuyama dome in front of Mount Unzen, resulting in a tremendous tsunami, killing 15,000 people altogether. It was also called Shimabara erupted, Higo affected (島原大変肥後迷惑), since many people were killed by this tsunami in Higo.
On the morning of March 13, 1888, an explosion took place on Ritter Island, a small volcanic island in the Bismarck and Solomon Seas, between New Britain and Umboi Island. The explosion resulted in the collapse of most of the island and generated a tsunami with runups of up to 15 meters (49 ft) that caused damage more than 700 kilometers (430 mi) away and killed anywhere between 500 and 3,000 on neighbouring islands, including scientists and explorers. This event is the largest volcanic island sector collapse in recent history.

The devastating eruption of Oshima–Ōshima began on 18 August 1741 and ended on 1 May the next year. Eleven days into the eruption, the Kampo tsunami with estimated maximum heights of over 90 meters swept across neighboring islands in Japan and the Korean Peninsula.

A volcanic tsunami, also called a volcanogenic tsunami, is a tsunami produced by volcanic phenomena. About 20–25% of all fatalities at volcanoes during the past 250 years have been caused by volcanic tsunamis. The most devastating volcanic tsunami in recorded history was that produced by the 1883 eruption of Krakatoa. The waves reached heights of 40 m (130 ft) and killed 36,000 people.
The 1852 Banda Sea earthquake struck on 26 November at 07:40 local time, affecting coastal communities on the Banda Islands. It caused violent shaking lasting five minutes, and was assigned XI on the Modified Mercalli intensity scale in the Maluku Islands. A tsunami measuring up to 8 m (26 ft) slammed into the islands of Banda Neira, Saparua, Haruku and Ceram. The tsunami caused major damage, washing away many villages, ships and residents. At least 60 people were killed in the earthquake and tsunami. The earthquake had an estimated moment magnitude of 7.5 or 8.4–8.8, according to various academic studies.
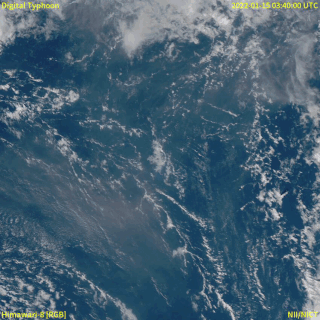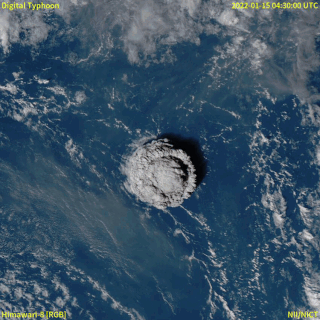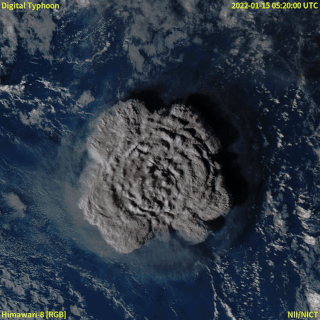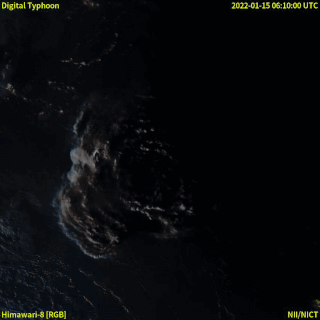
In December 2021, an eruption began on Hunga Tonga–Hunga Haʻapai, a submarine volcano in the Tongan archipelago in the southern Pacific Ocean. The eruption reached a very large and powerful climax nearly four weeks later, on 15 January 2022. Hunga Tonga–Hunga Haʻapai is 65 kilometres (40 mi) north of Tongatapu, the country's main island, and is part of the highly active Tonga–Kermadec Islands volcanic arc, a subduction zone extending from New Zealand to Fiji. On the Volcanic Explosivity Index scale, the eruption was rated at least a VEI-5. Described by scientists as a "magma hammer", the volcano at its height produced a series of four underwater thrusts, displaced 10 cubic kilometres (2.4 cu mi) of rock, ash and sediment, and generated the largest atmospheric explosion recorded by modern instrumentation.
The 1843 Nias earthquake off the northern coast of Sumatra, Indonesia caused severe damage when it triggered a tsunami along the coastline. The earthquake with a moment magnitude (Mw ) of 7.8 lasted nine minutes, collapsing many homes in Sumatra and Nias. It was assigned a maximum modified Mercalli intensity of XI (Extreme).

The 1867 Keelung earthquake occurred off the northern coast of Taiwan on the morning of December 18 with a magnitude of 7.0. It produced strong shaking that seriously damaged the cities of Keelung and Taipei. A tsunami, thought to be the only confirmed destructive of its kind in Taiwan, drowned hundreds and had a run-up exceeding 15 m (49 ft). The total death toll was estimated to be 580 while more than 100 were injured. It was followed by aftershocks that were felt on average ten times a day.













