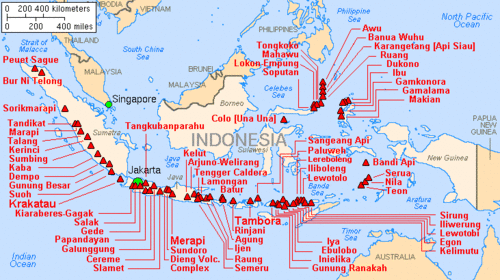
The geography of Indonesia is dominated by volcanoes that are formed due to subduction zones between the Eurasian plate and the Indo-Australian plate. Some of the volcanoes are notable for their eruptions, for instance, Krakatoa for its global effects in 1883, [1] the Lake Toba Caldera for its supervolcanic eruption estimated to have occurred 74,000 years before present which was responsible for six years of volcanic winter, [2] and Mount Tambora for the most violent eruption in recorded history in 1815 and the resulting "Year Without a Summer". [3]
Contents
- Scope
- Geographical groups
- Sumatra
- Sunda Strait and Java
- Lesser Sunda Islands
- Banda Sea
- Sulawesi and Sangihe Islands
- Halmahera
- Major eruptions
- See also
- References
- Notes
- Sources
- External links
Volcanoes in Indonesia are part of the alpida belt and Pacific Ring of Fire. The 150 entries in the list below are grouped into six geographical regions, four of which belong to the volcanoes of the Sunda Arc trench system. The remaining two groups are volcanoes of Halmahera, including its surrounding volcanic islands, and volcanoes of Sulawesi and the Sangihe Islands. The latter group is in one volcanic arc together with the Philippine volcanoes.
The most active volcano is Mount Merapi on Java. Since AD 1000, Kelut has erupted more than 30 times, of which the largest eruption was at scale 5 on the volcanic explosivity index (VEI), [4] while Mount Merapi has erupted more than 80 times. [5] The International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior has named Mount Merapi as a Decade Volcano since 1995 because of its high volcanic activity.
As of 2012, Indonesia has 127 active volcanoes and about 5 million people live within the danger zones. It has been conjectured that the earthquake and tsunami event of 26 December 2004 could trigger eruptions, with Mount Sinabung (dormant since the 1600s) erupting in 2010 as a possible example. [6]
The word for Mount in Indonesian and many regional languages of the country is Gunung. Thus, Mount Merapi may be referred to as Gunung Merapi.