
Ujung Kulon National Park is a national park at the westernmost tip of Java, located in Sumur District of Pandeglang Regency, part of Banten province in Indonesia. It once included the volcanic island group of Krakatoa in Lampung province, although current maps has suggested the Krakatoa island group as its own protected area, the Pulau Anak Krakatau Marine Nature Reserve.

The Sundaland heath forests, also known as Kerangas forest, is a type of tropical moist forest found on the island of Borneo, which is divided between Brunei, Indonesia, and Malaysia, as well as on the Indonesian islands of Belitung and Bangka, which lie to the west of Borneo.

Tesso Nilo National Park is a national park in Riau Province, Sumatra, Indonesia. It was declared a national park by the Indonesian government in 2004. The original area of the park was 385.76 km2, but the decision has been made to expand it to 1000 km2. Tesso Nilo National Park houses some of the largest coherent lowland rainforests remaining on Sumatra. The Center for Biodiversity Management has surveyed over 1,800 plots in tropical forests around the world. They found that no other plot has as many vascular plants as in Tesso Nilo. Indonesian Institute of Sciences (LIPI) surveyed forests throughout Sumatra, and also found that Tesso Nilo housed by far the most species.

Gunung Leuser National Park is a national park covering 7,927 km2 in northern Sumatra, Indonesia, straddling the border of Aceh and North Sumatra provinces, a fourth portion and three-fourths portion, respectively. The national park, settled in the Barisan mountain range, is named after Mount Leuser (3,119 m), and protects a wide range of ecosystems. An orangutan sanctuary at Bukit Lawang is located within the park. Together with Bukit Barisan Selatan and Kerinci Seblat National Parks, it forms a World Heritage Site, the Tropical Rainforest Heritage of Sumatra.

Kerinci Seblat National Park is the largest national park on the island of Sumatra, Indonesia. It has a total area of 13,791 km2 and spans four provinces: West Sumatra, Jambi, Bengkulu, and South Sumatra.
The Tropical Rainforest Heritage of Sumatra site was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2004. It comprises three Indonesian national parks on the island of Sumatra: Gunung Leuser National Park, Kerinci Seblat National Park and the Bukit Barisan Selatan National Park. The site is listed under Criteria vii - outstanding scenic beauty; ix- an outstanding example representing significant on-going ecological and biological processes; and x- contains the most important and significant natural habitats for in-situ conservation. The Tropical Rainforest Heritage of Sumatra has been placed on the Danger List since 2011 to help overcome threats posed by poaching, illegal logging, agricultural encroachment, and plans to build roads through the site.

Bukit Barisan Selatan National Park is a national park in Sumatra, Indonesia. The park located along the Bukit Barisan mountain range, has a total area of 3,568 km2, and spans three provinces: Lampung, Bengkulu, and South Sumatra. Together with Gunung Leuser and Kerinci Seblat national parks it forms a World Heritage Site, Tropical Rainforest Heritage of Sumatra.

Betung Kerihun National Park is a national park located in the Indonesian province of West Kalimantan, on the island of Borneo. The park was established in 1995, and has a total area of 8,000 km2 (3,100 sq mi) or about 5.5 percent of West Kalimantan Province area. Together with the 2,000 km2 (800 sq mi) Lanjak Entimau Wildlife Sanctuary in Malaysia, it has been proposed to form a World Heritage Site named the "Transborder Rainforest Heritage of Borneo".

The Borneo lowland rain forests is an ecoregion, within the tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests biome, of the large island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. It supports approximately 15,000 plant species, 380 bird species and several mammal species. The Borneo lowland rain forests is diminishing due to logging, hunting and conversion to commercial land use.
Under UNESCO's Man and Biosphere Reserve Programme, there are 142 biosphere reserves recognized as part of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves in Asia and the Pacific as of April 2016. These are distributed across 24 countries in the region.

Batang Gadis is a national park covering 1,080 km2 in North Sumatra province, Indonesia extending between 300 and 2,145 metres altitude. It is named after the Batang Gadis river that flows through the park. Signs of the endangered Sumatran tiger and the threatened Asian golden cat, leopard cat and clouded leopard were seen in the park. The protection of Batang Gadis as a national park is part of a plan to create the Northern Sumatra biodiversity conservation corridor, which would be connected, via a series of protected areas and forests, to Gunung Leuser National Park in the north of the island.

Taka Bonerate National Park is a marine park which includes the Takabonerate atoll islands, located in the Flores Sea, south of Sulawesi island of Indonesia.

Wakatobi National Park is a marine national park in Southeast Sulawesi, Indonesia. The name of Wakatobi is a portmanteau of the four main Tukangbesi Islands: Wangi-wangi, Kaledupa, Tomia, and Binongko. Since 2005 the park is listed as a tentative World Heritage Site.

The Borneo montane rain forests is an ecoregion on the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. It includes montane tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, also known as a cloud forests. The ecoregion is partly in East Malaysia and Indonesia (Kalimantan).
Lanjak Entimau Wildlife Sanctuary is a 1,870 km2 (1,870 km2) large protected area on the island of Borneo in Sarawak, Malaysia. It is significant for orangutan conservation. Together with Batang Ai National Park these protected areas host an estimated 1,400 orangutans. Hunting and illegal logging are only minor problems in these areas, but could become serious if not monitored, especially because the areas are contiguous with Indonesia, where illegal logging is rampant.
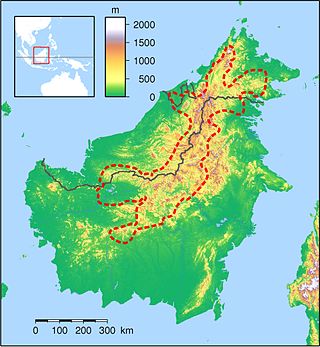
The Heart of Borneo is a conservation agreement initiated by the World Wide Fund for Nature to protect a 220,000 km² forested region on Borneo island. The agreement was signed by the governments of Brunei, Indonesia and Malaysia in Bali on 12 February 2007 to support the initiative. The region provides habitat to 10 endemic species of primates, more than 350 birds, 150 reptiles and amphibians and 10,000 plants. From 2007 to 2010 a total of 123 new species have been recorded in the region. A status report from 2012 found that the lowland rain forest within the area is deteriorating and under threat. The Bornean rhinoceros was the most threatened fauna, in 2015 three captive individuals remained in Sabah.




































