| Kelimutu National Park | |
|---|---|
| Taman Nasional Kelimutu | |
IUCN category II (national park) | |
Kelimutu lakes Tiwu Nuwa Muri Ko'o Fai and Tiwu Ata Polo | |
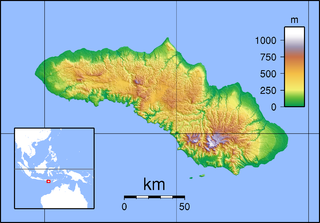
| Location | Flores, East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia |
| Coordinates | 8°45′30″S121°50′41″E / 8.75833°S 121.84472°E Coordinates: 8°45′30″S121°50′41″E / 8.75833°S 121.84472°E |
| Area | 50 km2 |
| Established | 1992 |
| Visitors | 12,507(in 2007 [1] ) |
| Governing body | Ministry of Environment and Forestry |
Kelimutu National Park (Indonesian: Taman Nasional Kelimutu) is located on the island of Flores, East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. It consists of a region with hills and mountains, with Mount Kelibara (1,731 m) as its highest peak. Mount Kelimutu, which has the three coloured lakes, is also located in this national park. This natural attraction is a destination for tourists.

Flores is one of the Lesser Sunda Islands, a group of islands in the eastern half of Indonesia. The population was 1,831,000 in the 2010 census and the largest town is Maumere. The name Flores is derived from the Portuguese for "flowers".

East Nusa Tenggara is the southernmost province of Indonesia. It compires the eastern portion of the Lesser Sunda Islands, facing the Indian Ocean in the south and the Flores Sea in the north. It consists of more than 500 islands, with the largest ones being Sumba, Flores, and the western part of Timor; the latter shares a land border with the separate nation of East Timor. The province was sub-divided into 21 regencies and the regency-level city of Kupang, which is the capital and largest city.

Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia, between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It is the world's largest island country, with more than seventeen thousand islands, and at 1,904,569 square kilometres, the 14th largest by land area and the 7th largest in combined sea and land area. With over 261 million people, it is the world's 4th most populous country as well as the most populous Muslim-majority country. Java, the world's most populous island, is home to more than half of the country's population.
Contents
Some endangered plant species are protected in this national park, such as: Toona spp., Anthocephalus cadamba, Canarium spp., Diospyros ferra, Alstonis scholaris, Schleichera oleosa, Casuarina equisetifolia and Anaphalis javanica. Some endangered animals can also be found here, such as: Javan rusa, wild boar sp., red junglefowl, Elanus sp. and drongo sp. ( Dicrurus sulphurea ).

Toona, commonly known as redcedar, toon or toona, is a genus in the mahogany family, Meliaceae, native from Afghanistan south to India, and east to North Korea, Papua New Guinea and eastern Australia. In older texts, the genus was often incorporated within a wider circumscription of the related genus Cedrela, but that genus is now restricted to species from the Americas.

Canarium is a genus of about 100 species of tropical and subtropical trees, in the family Burseraceae. They grow naturally across tropical Africa, south and southeast Asia, Indochina, Malesia, Australia and western Pacific Islands; including from southern Nigeria east to Madagascar, Mauritius, Sri Lanka and India; from Burma, Malaysia and Thailand through the Malay Peninsula and Vietnam to south China, Taiwan and the Philippines; through Borneo, Indonesia, Timor and New Guinea, through to the Solomon Islands, New Caledonia, Fiji, Samoa, Tonga and Palau.

Casuarina equisetifolia, or Australian pine tree, is a she-oak species of the genus Casuarina. The native range extends throughout Southeast Asia, Northern Australia and the Pacific Islands; including Thailand, Burma, Vietnam, Malaysia, Brunei, Indonesia, Timor-Leste, and the Philippines, east to Papua New Guinea, French Polynesia, New Caledonia, and Vanuatu, and south to Australia. Populations are also found in Madagascar, but it is doubtful if this is within the native range of the species. The species has been introduced to the Southern United States and West Africa. It is an invasive species in Florida, South Africa and Brazil
The four endemic mammals in the park include two montane rodents: Bunomys naso and Hainald's rat (Rattus hainaldi). [2]

Endemism is the ecological state of a species being unique to a defined geographic location, such as an island, nation, country or other defined zone, or habitat type; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. The extreme opposite of endemism is cosmopolitan distribution. An alternative term for a species that is endemic is precinctive, which applies to species that are restricted to a defined geographical area.

Rodents are mammals of the order Rodentia, which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents ; they are found in vast numbers on all continents except Antarctica. They are the most diversified mammalian order and live in a variety of terrestrial habitats, including human-made environments.
Hainald's rat is a species of rodent in the family Muridae. It is found only on Flores Island in Indonesia, including on Mount Ranaka. Part of its habitat is protected within the Kelimutu National Park.
In this area, there is also an arboretum, a mini jungle (4,5 ha) represent flora biodiversity of Kelimutu National Park. The arboterum consists of 78 types of tree plants which are grouped into 36 families. Some of the Kelimutu's endemic flora collections are uta onga (Begonia kelimutuensis), turuwara (Rhododendron renschianum), and arngoni (Vaccinium varingiaefolium). [3]

An arboretum in a general sense is a botanical collection composed exclusively of trees. More commonly a modern arboretum is a botanical garden containing living collections of woody plants and is intended at least in part for scientific study.

Biodiversity refers to the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is typically a measure of variation at the genetic, species, and ecosystem level. Terrestrial biodiversity is usually greater near the equator, which is the result of the warm climate and high primary productivity. Biodiversity is not distributed evenly on Earth, and is richest in the tropics. These tropical forest ecosystems cover less than 10 percent of earth's surface, and contain about 90 percent of the world's species. Marine biodiversity is usually highest along coasts in the Western Pacific, where sea surface temperature is highest, and in the mid-latitudinal band in all oceans. There are latitudinal gradients in species diversity. Biodiversity generally tends to cluster in hotspots, and has been increasing through time, but will be likely to slow in the future.