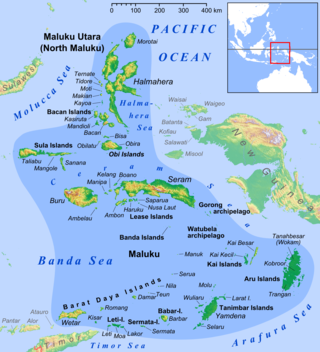
The Maluku Islands or the Moluccas are an archipelago in the east of Indonesia. Tectonically they are located on the Halmahera Plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone. Geographically they are located east of Sulawesi, west of New Guinea, and north and east of Timor. Lying within Wallacea, the Maluku Islands have been considered as a geographical and cultural intersection of Asia and Oceania.

Makian, known to local people as Mount Kie Besi, is a volcanic island, one of the Maluku Islands within the province of North Maluku in Indonesia. It lies near the southern end of a chain of volcanic islands off the western coast of the province's major island, Halmahera, and lies between the islands of Moti and Tidore to the north and Kayoa and the Bacan Group to the south. The island, which forms two districts within South Halmahera Regency of North Maluku Province, covers an area of 84.36 sq.km, and had a population of 12,394 at the 2010 Census, which rose to 14,000 at the 2020 Census.

Ambon Island is part of the Maluku Islands of Indonesia. The island has an area of 743.37 km2 (287.02 sq mi) and is mountainous, well watered, and fertile. Ambon Island consists of two territories: the city of Ambon to the south and various districts (kecamatan) of the Central Maluku Regency to the north. The main city and seaport is Ambon, which is also the capital of Maluku province, while those districts of Maluku Tengah Regency situated on Ambon Island had a 2020 Census population of 128,069. Ambon has an airport and is home to the Pattimura University and Open University, state universities, and a few private universities, which include Darussalam University and Universitas Kristen Indonesia Maluku (UKIM).

North Maluku is a province of Indonesia. It covers the northern part of the Maluku Islands, bordering the Pacific Ocean to the north, the Halmahera Sea to the east, the Molucca Sea to the west, and the Seram Sea to the south. The provincial capital is Sofifi on the largest island of Halmahera, while the largest city is the island city of Ternate. The population of North Maluku was 1,038,087 in the 2010 census, making it one of the least-populous provinces in Indonesia, but by the 2020 Census the population had risen to 1,282,937, and the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 1,319,338.

Seram is the largest and main island of Maluku province of Indonesia, despite Ambon Island's historical importance. It is located just north of the smaller Ambon Island and a few other adjacent islands, such as Saparua, Haruku, Nusa Laut and the Banda Islands.

Saparua is an island east of Ambon Island in the Indonesian province of Maluku; the island of Haruku lies between Saparua and Ambon. The main port is in the south at Kota Saparua. The island of Maolana is located near its southwestern side and Nusa Laut off its southeastern tip.

Halmahera, formerly known as Jilolo, Gilolo, or Jailolo, is the largest island in the Maluku Islands. It is part of the North Maluku province of Indonesia, and Sofifi, the capital of the province, is located on the west coast of the island.

Kelang Island is an island in West Seram Regency, Maluku Province, Indonesia. It is a mountainous island located off the western tip of Seram Island, just east of Manipa. Sole, located on the northeastern side, and Tahalupu are the two principal villages. Tono, the highest point in the island, is an old volcano.
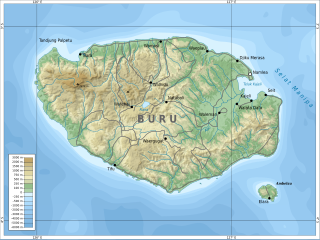
Buru is the third largest island within the Maluku Islands of Indonesia. It lies between the Banda Sea to the south and Seram Sea to the north, west of Ambon and Seram islands. The island belongs to Maluku province and includes the Buru and South Buru regencies. Their administrative centers, Namlea and Namrole, respectively, have ports and are the largest towns of the island, served by Namlea Airport and Namrole Airport.
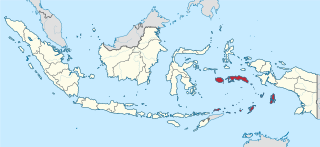
Maluku is a province of Indonesia. It comprises the central and southern regions of the Maluku Islands. The main city and capital of Maluku province is Ambon on the small Ambon Island. The land area is 46,150.92 km2, and the total population of this province at the 2010 census was 1,533,506 people, rising to 1,848,923 at the 2020 census. The official estimate as at mid 2022 was 1,881,727. Maluku is located in Eastern Indonesia. It is directly adjacent to North Maluku, Southwest Papua, and West Papua in the north, Central Sulawesi, and Southeast Sulawesi in the west, Banda Sea, East Timor and East Nusa Tenggara in the south and Arafura Sea, Central Papua and South Papua in the east.

Wetar is a tropical island which belongs to the Indonesian province of Maluku and is the largest island of the Maluku Barat Daya Islands of the Maluku Islands. It lies east of the Lesser Sunda Islands, which include nearby Alor and Timor, but it is politically part of the Maluku Islands. To the south, across the Wetar Strait, lies the island of Timor; at its closest it is 50 km away. To the west, across the Ombai Strait, lies the island of Alor. To the southwest is the very small island of Liran, which is also part of Wetar district (kecamatan) and, further southwest, the small East Timorese island of Atauro. To the north is the Banda Sea and to the east lie Romang and Damar Islands, while to the southeast lie the other principal islands of the Barat Daya Islands. Including Liran, Wetar has an area of 2,651.9 km2, and had a population of 7,916 at the 2010 Census.

Manuk is an uninhabited volcanic island located in the Banda Sea, Indonesia. Administratively it is part of the Maluku Tengah Regency, Maluku Province.

Raja Ampat, or the Four Kings, is an archipelago located off the northwest tip of Bird's Head Peninsula on the island of New Guinea, in Indonesia's Southwest Papua province. It comprises over 1,500 small islands, cays, and shoals surrounding the four main islands of Misool, Salawati, Batanta, and Waigeo, and the smaller island of Kofiau.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Indonesia:
The Timoric languages are a group of Austronesian languages spoken on the islands of Timor, neighboring Wetar, and Southwest Maluku to the east.

Ambelau or Ambalau is a volcanic island in the Banda Sea within Maluku Islands of Indonesia. The island forms an administrative district which is part of the South Buru Regency of Maluku province, Indonesia. It has a land area of 201.7 km2, and had a population of 6,846 at the 2010 Census. The administrative center is Wailua, a settlement located at the south of the island. About half of the island's population is composed of indigenous Ambelau people who speak the Ambelau language; the other half are mostly immigrants from the nearby Maluku Islands and Java.

Central Maluku Regency is a regency of Maluku Province of Indonesia. The Regency covers an area of 11,595.57 km2, and had a population of 361,698 at the 2010 Census, and 423,094 at the 2020 Census. The official estimate as at mid 2021 was 424,730. The principal town lies at Masohi, on Seram Island. The regency (kebupaten) is composed of the central part of the island of Seram, the Banda Islands, and the Lease Islands, together with those parts of Ambon Island which are outside the City of Ambon.
Teun is an Austronesian language originally spoken on Teun Island and Nila Island in Maluku, Indonesia. Speakers were relocated to Seram due to volcanic activity on Teun.
Serua is an almost extinct Austronesian language originally spoken on Serua Island in Maluku, Indonesia. Speakers were relocated to Seram due to volcanic activity on Serua. The language continues in communities in Waipia in Seram, where the islanders were resettled, along with those also from Nila and Teun. Here, the older generation retain the island language as a strong form of identity.














