
Timor is an island at the southern end of Maritime Southeast Asia, in the north of the Timor Sea. The island is divided between the sovereign states of East Timor on the eastern part and Indonesia on the western part. The Indonesian part, known as West Timor, constitutes part of the province of East Nusa Tenggara. Within West Timor lies an exclave of East Timor called Oecusse District. The island covers an area of 30,777 square kilometres. The name is a variant of timur, Malay for "east"; it is so called because it lies at the eastern end of the Lesser Sunda Islands. Mainland Australia is less than 500 km away, separated by the Timor Sea.

Alor is the largest island in the Alor Archipelago and is one of the 92 officially listed outlying islands of Indonesia. It is located at the eastern Lesser Sunda Islands that runs through southeastern Indonesia, which from the west include such islands as Bali, Lombok, Sumbawa, Komodo, and Flores.
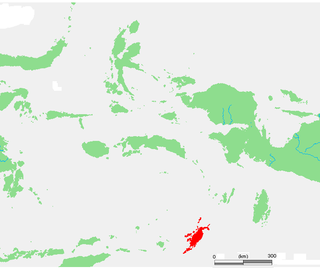
The Tanimbar Islands, also called Timur Laut, are a group of about 65 islands in the Maluku province of Indonesia. The largest and most central of the islands is Yamdena; others include Selaru to the southwest of Yamdena, Larat and Fordata to the northeast, Maru and Molu to the north, and Seira, Wuliaru, Selu, Wotap and Makasar to the west. The Indonesian phrase timur laut means "east of the sea" or "northeast".

The Barat Daya Islands are a group of islands in the Maluku province of Indonesia. The Indonesian phrase barat daya means 'south-west'.

The Banda Sea is one of four seas that surround the Maluku Islands of Indonesia, connected to the Pacific Ocean, but surrounded by hundreds of islands, including Timor, as well as the Halmahera and Ceram Seas. It is about 1000 km (600 mi) east to west, and about 500 km (300 mi) north to south.

The Alor Archipelago is located at the eastern Lesser Sunda Islands.
The Babar Islands(Indonesian: Kepulauan Babar) are located in Maluku Province, Indonesia between latitudes 7 degrees 31 minutes South to 8 degrees 13 minutes South and from longitudes 129 degrees 30 minutes East to 130 degrees 05 minutes East. The group now constitutes five districts (kecamatan) within the Maluku Barat Daya Regency of Maluku province.
Wetarese is an Austronesian language of Wetar, an island in the south Maluku, Indonesia, and of the nearby islands Liran and Atauro, the latter island separate from the mainland of East Timor, north of Dili.

Liran is a small island off the southwest coast of Wetar Island, Indonesia. Administratively it is part of West Wetar District within the Southwest Maluku Regency. The East Timorese island Atauro is 12 km to the southwest. Liran is the westernmost of the Barat Daya Islands in the province of Maluku. It covers an area of 39.14 km2 and had 841 inhabitants in 2019.

The Letti Islands of Indonesia are part of the Maluku Islands, in southwest Maluku Province. They are also called the "Lemola" Archipelago, from the initial two letters of each of the three main islands, Letti, Moa and Lakor; each of the three islands now constitutes a separate administrative district (kecamatan) within the Maluku Barat Daya Regency

Romang is an island, part of the Barat Daya Islands in Indonesia, located at 7.5833333°S 127.4333333°E, east of Wetar Island. Alternate names in use are Roma, Romonu and Fataluku. The group includes neighbouring smaller islands including Nyata to the west, Mitan to the south, and Maopora, Tellang, Laut, Limtutu and Djuha Islands to the east. Together they form the Kepulauan Roma District within the Barat Daya Islands Regency of the Maluku Province. The district covers a land area of 194.30 km2 and had a population of 4,430 in mid 2023.

Southwest Aceh Regency is a regency in the Aceh Province of Indonesia. The regency was created on 10 April 2002 from the northwestern districts of South Aceh Regency. It is located on the west side of the island of Sumatra. The regency covers an area of 1,882.99 square kilometres and according to the 2010 census had a population of 126,036; this rose to 140,366 at the 2015 Census, and to 150,775 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 156,990. The seat of the regency government is the town of Blangpidie.

Alor Regency is a regency (kabupaten) in East Nusa Tenggara (NTT) province of Indonesia. Established in 1958, Alor Regency administers the Alor Archipelago with its seat (capital) in Kalabahi on Alor Island.
South Halmahera Regency is a regency of North Maluku Province, Indonesia. It lies partly on Halmahera Island and partly on smaller islands to the west and south of Halmahera. It covers a land area of 8,779.32 km2, and at the 2010 Census it had a population of 198,911 people, while the 2020 Census showed that this had risen to 248,395 and the official estimate in mid 2022 was 253,331. The capital lies at the town of Labuha on Bacan Island.

Southeast Maluku Regency is a regency of Maluku, Indonesia. It is coincident with the Kei Islands, except that the city of Tual, although within the Kei Islands geographically and the seat of the Regency's administration, is since 17 July 2007 technically independent of the Regency. The land area of the Regency is 1,031.01 km2, while the sea area administered by the Regency was 3,181 km2; it had a population of 96,442 at the 2010 Census; this increased to 121,511 at the 2020 Census, and the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 129,034.

Southwest Maluku Regency is a regency of Maluku Province, Indonesia. Geographically it forms the most eastern portion of the Lesser Sunda Islands, although it has never been administratively included with them, and politically has always comprised a part of the Maluku Province. It comprises a number of islands and island groups in the south of the province, including Lirang Island, Wetar Island, Kisar Island, Romang Island, the Letti Islands, the Damer Islands, the Sermata Islands and the Babar Islands. The total land area is 4,581.06 km2, and the population was 70,714 at the 2010 Census and 81,928 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 93,766.

Tanimbar Islands Regency is a regency of Maluku province, Indonesia, consisting primarily of the Tanimbar Islands. The Regency covers a land area of 10,102 km2, and it had a population of 105,341 at the 2010 Census and 123,572 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 124,787. The principal town and administrative centre lies at Saumlaki in Tanimbar Selatan District.

Damer, or Damar,, also called Kenli Island, is a small volcanic island in the Barat Daya Islands group in Indonesia's Maluku province, on the southern side of the Banda Sea. It is flanked by four smaller uninhabited islands - one to the east (Layeni), one to the west and two to the south. Together they are called the Damar Islands, and constitute one administrative district within the Maluku Barat Daya Regency. The district has a land area of 201.80 km2 and had a population of 5,718 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 6,362, all on Damer Island itself.


















