
Tabernaemontana is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae. It has a pan-tropical distribution, found in Asia, Africa, Australia, North America, South America, and a wide assortment of oceanic islands. These plants are evergreen shrubs and small trees growing to 1–15 m tall. The leaves are opposite, 3–25 cm long, with milky sap; hence it is one of the diverse plant genera commonly called "milkwood". The flowers are fragrant, white, 1–5 cm in diameter.

Voacangine is an alkaloid found predominantly in the root bark of the Voacanga africana tree, as well as in other plants such as Tabernanthe iboga, Tabernaemontana africana, Trachelospermum jasminoides, Tabernaemontana divaricata and Ervatamia yunnanensis. It is an iboga alkaloid which commonly serves as a precursor for the semi-synthesis of ibogaine. It has been demonstrated in animals to have similar anti-addictive properties to ibogaine itself. It also potentiates the effects of barbiturates. Under UV-A and UV-B light its crystals fluoresce blue-green, and it is soluble in ethanol.

Indole alkaloids are a class of alkaloids containing a structural moiety of indole; many indole alkaloids also include isoprene groups and are thus called terpene indole or secologanin tryptamine alkaloids. Containing more than 4100 known different compounds, it is one of the largest classes of alkaloids. Many of them possess significant physiological activity and some of them are used in medicine. The amino acid tryptophan is the biochemical precursor of indole alkaloids.

Tabernaemontana corymbosa is a species of plant in the family Apocynaceae. It is found in Brunei, China, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam. Glossy green leaves and faintly sweet scented flower. Flowers continuously all year. Frost tolerant. Grows to about 2metres. Likes full sun to part shade. A number of cultivars are available.
In enzymology, a secologanin synthase (EC 1.14.19.62, was wrongly classified as EC 1.3.3.9 in the past) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Ibogamine is an anti-convulsant, anti-addictive, CNS stimulant alkaloid found in Tabernanthe iboga and Crepe Jasmine. Basic research related to how addiction affects the brain has used this chemical.

Conolidine is an indole alkaloid. Preliminary reports suggest that it could provide analgesic effects with few of the detrimental side-effects associated with opioids such as morphine, though at present it has only been evaluated in mouse models.

Affinine is a monoterpenoid indole alkaloid which can be isolated from plants of the genus Tabernaemontana. Structurally it can be considered a member of the vobasine alkaloid family and may be synthesized from tryptophan. Limited pharmacological testing has indicated that it may be an effective inhibitor of both acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase.

Conodurine is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitor isolated from Tabernaemontana.
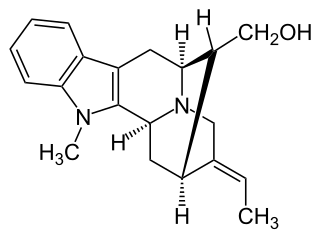
Affinisine is a monoterpenoid indole alkaloid which can be isolated from plants of the genus Tabernaemontana. Structurally, it can be considered a member of the sarpagine alkaloid family and may be synthesized from tryptophan via a Pictet-Spengler reaction.

Stemmadenine is a terpene indole alkaloid. Stemmadenine is believed to be formed from preakuammicine by a carbon-carbon bond cleavage. Cleavage of a second carbon-carbon bond is thought to form dehydrosecodine. The enzymes forming stemmadenine and using it as a substrate remain unknown to date. It is thought to be intermediate compound in many different biosynthetic pathways such as in Aspidosperma species. Many alkaloids are proposed to be produced through intermediate stemmadenine. Some of them are:

Apparicine is a monoterpenoid indole alkaloid. It is named after Apparicio Duarte, a Brazilian botanist who studied the Aspidosperma species from which apparicine was first isolated. It was the first member of the vallesamine group of alkaloids to be isolated and have its structure established, which was first published in 1965. It has also been known by the synonyms gomezine, pericalline, and tabernoschizine.
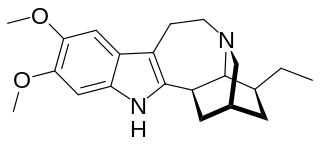
Ibogaline is an alkaloid found in Tabernanthe iboga along with the related chemical compounds ibogaine, ibogamine, and other minor alkaloids. It is a relatively smaller component of Tabernanthe iboga root bark total alkaloids (TA) content. It is also present in Tabernaemontana species such as Tabernaemontana australis which shares similar ibogan-biosynthetic pathways. The percentage of ibogaline in T. iboga root bark is up to 15% TA with ibogaine constituting 80% of the alkaloids and ibogamine up to 5%.

Tabernaemontanine is a naturally occurring monoterpene indole alkaloid found in several species in the genus Tabernaemontana including Tabernaemontana divaricata.

Dregamine is a naturally occurring monoterpene indole alkaloid found in several species in the genus Tabernaemontana including Ervatamia hirta and Tabernaemontana divaricata.

Conophylline is a autophagy inducing vinca alkaloid found in several species of Tabernaemontana including Ervatamia microphylla and Tabernaemontana divaricata. Among its many functional groups is an epoxide: the compound where that ring is replaced with a double bond is called conophyllidine and this co-occurs in the same plants.

Ervaticine is a 2-acylindole alkaloid. It occurs in Ervatamia coronaria and Tabernaemontana divaricata.

Vobasine is a naturally occurring monoterpene indole alkaloid found in several species in the genus Tabernaemontana including Tabernaemontana divaricata.

Voacristine is a indole alkaloid occurring in Voacanga and Tabernaemontana genus. It is also an iboga type alkaloid.
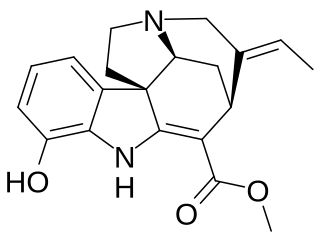
Vinervine is a monoterpene indole alkaloid of the Vinca sub-group. It is a derivative of akuammicine, with one additional hydroxy (OH) group in the indole portion, hence it is also known as 12-hydroxyakuammicine.



















