| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
This article lists events that occurred during 1925 in Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
This article lists events that occurred during 1925 in Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes .

The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was a country in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 to 1929, it was officially called the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, but the term "Yugoslavia" was its colloquial name due to its origins. The official name of the state was changed to "Kingdom of Yugoslavia" by King Alexander I on 3 October 1929.
The Treaty of Rome was agreed on 27 January 1924, when Italy and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes agreed that Fiume would be annexed to Italy as the Province of Fiume, and the town of Sušak would be part of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes.
The Treaty of Rapallo was an agreement between the Kingdom of Italy and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes in the aftermath of the First World War. It was intended to settle the Adriatic question, i.e. Italian claims over territories promised to the country, in return for its entry into the war, against Austria-Hungary; claims that were made on the basis of the 1915 Treaty of London. The wartime pact promised Italy large areas of the eastern Adriatic. The treaty, signed on 12 November 1920 in Rapallo, Italy, generally redeemed the promises of territorial gains in the former Austrian Littoral by awarding Italy territories generally corresponding to the peninsula of Istria and the former Princely County of Gorizia and Gradisca, with the addition of the Snežnik Plateau, in addition to what was promised by the London treaty. The articles regarding Dalmatia were largely ignored. There Italy received the city of Zadar and several islands. Other provisions of the treaty contained safeguards for the rights of Italian nationals remaining in the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, and provisions for commissions to demarcate the new border, and facilitate economic and educational cooperation. The treaty also established the Free State of Fiume, the city-state consisting of the former Austro-Hungarian Corpus Separatum that consisted of Rijeka and a strip of coast giving the new state a land border with Italy at Istria.

The State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs was a political entity that was constituted in October 1918, at the end of World War I, by Slovenes, Croats and Serbs (Prečani) residing in what were the southernmost parts of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Although internationally unrecognised, this was the first incarnation of a Yugoslav state founded on the Pan-Slavic ideology. Thirty-three days after it was proclaimed, the state joined the Kingdom of Serbia and the Kingdom of Montenegro to form the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes.

The State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs became merged with the Kingdom of Serbia and the Kingdom of Montenegro to form the nation of Yugoslavia in 1918. The formation of Yugoslavia began with the formation of the Yugoslav Committee, a collection of mostly Croats, then Serbs and later Slovenes, whose goal was to form a single south Slavic state. In October 1918 the Croatian Parliament declared the Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia as an independent state, which, in December that same year, incorporated into the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs, merged with Kingdom of Serbia and Kingdom of Montenegro and created the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. The kingdom would be renamed to Yugoslavia in 1929, and ruled by Serbian Karađorđević dynasty till Second World War. After the formation of Yugoslavia, Serbia attempted to create a "Greater Serbia" by using police intimidation and vote rigging to establish a Serbian controlled Yugoslavia. From 1929-1941 Serbian controlled Yugoslavia established control over Croatia through Royal Yugoslav police force brutality and assassinations of important Croatians.

The Yugoslavia national football team represented Yugoslavia in international association football.
The Yugoslav Cup, officially known between 1923 and 1940 as the King Alexander Cup (Serbian: Куп краља Александра; Croatian: Kup kralja Aleksandra, and between 1947 and 1991 as the Marshal Tito Cup, was one of two major football competitions in Yugoslavia, the other one being the Yugoslav League Championship. The Yugoslav Cup took place after the league championships when every competitive league in Yugoslavia had finished, in order to determine which teams are ranked as their corresponding seeds. The Marshal Tito Cup trophy was based on a design by Branko Šotra.
The 1923 National Championship held in the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes was the first nationwide domestic football competition. At this point there was no league championship in the modern sense as the competition was held in a single-legged cup format, with participating clubs qualifying via regional playoffs organised by the existing 6 regional football subfederations.
The 1924 National Championship held in the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes was the second nationwide domestic football competition. At this point there was no league championship in the modern sense as the competition was held in a single-legged cup format, with participating clubs qualifying via regional playoffs organised by regional football subfederations.
The 1925 National Championship was a football competition in the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. It was the second straight year that the club from Belgrade, Jugoslavija, has taken the championships.
The 1926 National Championship was a football competition held within the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes. The two dominant teams of pre-World War II Yugoslav football, Jugoslavija and Građanski, began laying the foundations of the next seven decades of a deeply rooted rivalry between Zagreb and Belgrade. Both teams dominated the competition with comfortable margins, but were quite evenly matched in the finals.
The 1939–40 Yugoslav Football Championship was the 17th, and last, season of Kingdom of Yugoslavia's premier football competition. The season lasted from May 2 to June 19, 1940.
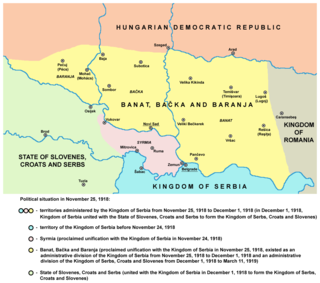
Banat, Bačka and Baranya was a province of the Kingdom of Serbia and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes between November 1918 and 1922. It included the geographical regions of Banat, Bačka, and Baranya and its administrative center was Novi Sad. They were later separated from the country to become SAP Vojvodina in 1945 with the creation of Federal Yugoslavia; smaller parts of Baranya were incorporated into Croatia or ceded to Kingdom of Hungary, while a portion of Banat was ceded to Kingdom of Romania.

The prime minister of Yugoslavia was the head of government of the Yugoslav state, from the creation of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes in 1918 until the breakup of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia in 1992.
The Croatian Bloc or the Croatian National Representation was the name held by the wide coalition of Croatian political parties in the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes from 1921 to 1929's 6th of January Dictatorship and within the Kingdom of Yugoslavia from 1935 to 1941.

Yugoslavia was a state concept among the South Slavic intelligentsia and later popular masses from the 19th to early 20th centuries that culminated in its realization after the 1918 collapse of Austria-Hungary at the end of World War I and the formation of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. However, the kingdom was better known colloquially as Yugoslavia ; in 1929 it was formally renamed the "Kingdom of Yugoslavia".

Dušan Zinaja was a Croatian and Yugoslav cross-country skier and football striker and coach.
The Party of Rights was a Croatian nationalist political party in Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia and later in Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes.

Srđan Budisavljević was a politician and lawyer born in Požega. Budisavljević studied law in Zagreb and Berlin before being elected to the Sabor of the Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia in 1908 as a representative of the Croat-Serb Coalition led by Frano Supilo and Svetozar Pribičević. Budisavljević was appointed the interior minister of the new the government of Croatia-Slavonia. In 1918, Budisavljević was among founders and the secretary of the National Council of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs – a body composed of political representatives of the South Slavs living in Austria-Hungary tasked with achieving independence of South Slavic lands from the empire. In the same year he launched the Glas Slovenaca, Hrvata i Srba journal. Budisavljević was elected to the Parliament of Yugoslavia on the Democratic Party ticket in 1920 and 1923 before switching his allegiance to Pribičević-led Independent Democratic Party (SDS) in 1925. He was a member of the parliament representing the SDS, and the president of the SDS in 1939–1945. In the same period he held several ministerial positions in Yugoslav governments including the government-in-exile during the World War II. Following the Tito–Šubašić Agreements, King Peter II of Yugoslavia appointed Budisavljević a member of three-person regency council to represent him in the Democratic Federal Yugoslavia. In 1945, Budisavljević returned to Yugoslavia and lived in Zagreb until his death. In 1958, he published Stvaranje države Srba, Hrvata i Slovenaca.