Regular elections in Croatia are mandated by the Constitution and legislation enacted by Parliament. The presidency, Parliament, county prefects and assemblies, city and town mayors, and city and municipal councils are all elective offices. Since 1990, seven presidential elections have been held. During the same period, ten parliamentary elections were also held. In addition, there were nine nationwide local elections. Croatia has also held three elections to elect members of the European Parliament following its accession to the EU on 1 July 2013.

At the national level, the Republic of Cyprus holds elections for its head of state, the President of Cyprus, and for its legislature, the House of Representatives.

Elections in Kenya take place within the framework of a multi-party democracy and a presidential system. The President, Senate and National Assembly are directly elected by voters, with elections organised by the Independent Electoral and Boundaries Commission (IEBC).
Elections in Hungary are held at two levels: general elections to elect the members of the National Assembly and local elections to elect local authorities. European Parliament elections are also held every 5 years.

Elections in Lithuania are held to select members of the parliament, the president, members of the municipal councils and mayors, as well as delegates to the European Parliament. Lithuanian citizens can also vote in mandatory or consultative referendums.

Elections in Togo take place within the framework of a presidential system. Both the President and the National Assembly are directly elected by voters. Togo is a one party dominant state with the Union for the Republic in power.

The Legislature of Liberia is the bicameral legislature of the government of Liberia. It consists of a Senate – the upper house, and a House of Representatives – the lower house, modeled after the United States Congress. Sessions are held at the Capitol Building in Monrovia. Legislature of Liberia is considered one of the three branches of government based on the Article III of the Constitution of Liberia that stipulates all three branches ought to be equal and coordinated based on the Principle of checks and balances.

Legislative elections were held in the Soviet Union on 26 March 1989 to elect members of the Congress of People's Deputies, with run-offs on 2, 9 and 20 April and 14 and 23 May. They were the first partially free nationwide elections held in the Soviet Union and were the last national elections prior to the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. The elections were followed by regional elections in 1990, the last regional elections to take place in the country.
Early parliamentary elections were held in Egypt on 27 October 1971, with a second round for 141 seats taking place on 3 November, following the adoption of a new constitution in September 1971. At the time the country was a one-party state and all candidates had to be members of the Arab Socialist Union (ASU). Two candidates were elected from each of the 175 constituencies, with a second round of voting required if one or both of the candidates failed to win over 50% of the vote in the first round, or neither of the candidates with over 50% were classed as a worker or farmer. In total, 1,661 candidates contested the elections.
Parliamentary elections were held in Egypt on 28 October 1976, with a second round in four constituencies on 4 November. While the Arab Socialist Union remained the sole legal party in the country, as in previous elections, these elections were unique in having three distinct political factions of the party compete against each other, along with 208 independents. This electoral experiment would lead, in 1979, to Egypt's first multi-party elections since 1952.
Early parliamentary elections were held in Egypt on 7 June 1979, with a second round for 147 seats being held on 14 June. Following the experimental 1976 elections, in which three different factions of the Arab Socialist Union had competed against each other, the country had returned to multi-party politics. This was confirmed in a referendum on the formation of new parties held in April.

Parliamentary elections were held in Mauritania on 23 November. The opposition has vowed to boycott the election unless the president steps down beforehand. A total of 1,096 candidates have registered to compete for the leadership of 218 local councils across Mauritania, whilst 438 candidates are contesting for the 146 parliamentary seats. Some 1.2 million Mauritanians were eligible to vote in the election. The first round results yielded a landslide victory for the ruling UPR winning 56 seats and their 14 coalition partners winning 34 seats. The Islamist Tewassoul party won 12 seats. The remaining seats were contested in a runoff on 21 December 2013. The UPR won the majority with 75 seats in the Assembly.
Parliamentary elections were held in the United Arab Republic on 10 March 1964, with a second round on 19 March. At the time the country was a one-party state and all candidates had to be members of the Arab Socialist Union (ASU). A total of 1,750 candidates contested the 350 elected seats. A further ten members were appointed by President Gamal Abdel Nasser.

Shura Council elections were held in Egypt between 29 January and 22 February 2012. The Freedom and Justice Party emerged as the largest party in the council, winning 105 of the 180 elected seats.

General elections were held in Dominican Republic on 15 May 2016 to elect a president, vice-president and the Congress, as well as 20 deputies to the Central American Parliament, municipal councils, mayors and vice mayors. On 15 May 2015 Roberto Rosario, president of the Central Electoral Board, said that there would be about 4,300 seats up for election in the "most complex elections in history".

Parliamentary elections were held in Cuba on 11 March 2018 to elect members of the National Assembly of People's Power. Prior to the elections, President Raúl Castro declared he would not be seeking a new term, and a new President of the Council of State will be elected by the National Assembly. His deputy, Miguel Díaz-Canel, was subsequently elected as the new president. However, Castro remained the First Secretary of the Communist Party of Cuba, the most senior position in the country.
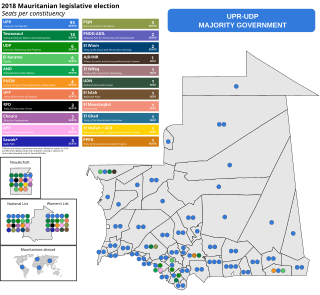
Parliamentary elections were held in Mauritania in September 2018; the first round took place on 1 September, with a second round held on 15 September. At the national level, elections were held in 157 constituencies, each electing one member to the National Assembly. Elections were also held in 13 regional councils and 219 municipalities.

Parliamentary elections were held in Cuba on 26 March 2023 to elect members of the National Assembly of People's Power.
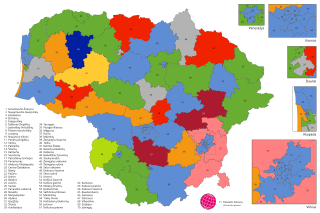
Parliamentary elections were held in Lithuania on 11 and 25 October 2020 to elect the 141 members of the Seimas. 71 were elected in single-member constituencies using the two-round system, and the remaining 70 in a single nationwide constituency using proportional representation. The first round was held on 11 October and the second round on 25 October.

General elections were held in Seychelles on 22–24 October 2020 to elect the President and members of the National Assembly. The National Assembly elections had been due in 2021, but in July 2020 were brought forward by President Danny Faure in order to hold them together with the presidential elections, a proposal supported by opposition parties.














