
The United Arab Republic was a sovereign state in the Middle East from 1958 until 1961. It was initially a short-lived political union between Egypt and Syria from 1958 until Syria seceded from the union following the 1961 Syrian coup d'état. Egypt continued to be known officially as the United Arab Republic until it was formally dissolved by Anwar Sadat in September 1971.

The president of the Arab Republic of Egypt is the executive head of state of Egypt and the de facto appointer of the official head of government under the Egyptian Constitution of 2014. Under the various iterations of the Constitution of Egypt following the Egyptian Revolution of 1952, the president is also the supreme commander of the Armed Forces, and head of the executive branch of the Egyptian government.
According to most scholars the history of modern Egypt dates from the start of the rule of Muhammad Ali in 1805 and his launching of Egypt's modernization project that involved building a new army and suggesting a new map for the country, though the definition of Egypt's modern history has varied in accordance with different definitions of modernity. Some scholars date it as far back as 1516 with the Ottomans' defeat of the Mamlūks in 1516–17.

The Arab Islamic Republic was a proposed unification of Tunisia and Libya in 1974, agreed upon by Libyan head of state Muammar Gaddafi and Tunisian President Habib Bourguiba. Additional countries—Morocco and Algeria—were later included in the proposal, which was never implemented.

Elections in Egypt are held for the president and a bicameral legislature. The president of Egypt is elected for a six-year term by popular vote after draft amendments to the 2013 constitution altered the presidential term limits from the original four years to six years.

The Federation of Arab Republics was an unsuccessful attempt by Muammar Gaddafi to merge Libya, Egypt and Syria in order to create a unified Arab state. Although approved by a referendum in each country on 1 September 1971, the three countries disagreed on the specific terms of the merger. The federation lasted from 1 January 1972 to 19 November 1977.

The Senate is the upper house of the bicameral Parliament of Egypt since its introduction in the 2019 Egyptian constitutional referendum and the subsequent 2020 Egyptian Senate election. The current president of the Senate is Abdel-Wahab Abdel-Razeq.

The Constitution of Egypt has passed over a long period of evolution from the liberal constitution of 1923 to the contemporary constitution.
The Arab Games, formerly called the Pan-Arab Games, are a regional multi-sport event held between nations from the Arab world. They are organized by the Union of Arab National Olympic Committees. The first Games took place in 1953 in Alexandria, Egypt. Intended to be held every four years since, political turmoil and financial difficulties have made the event an unstable one. Women first competed in 1985.

This timeline lists the dates of the first women's suffrage in Muslim majority countries. Dates for the right to vote, suffrage, as distinct from the right to stand for election and hold office, are listed.

The vice-president of the Arab Republic of Egypt is a senior official within the Egyptian government.
The History of Republican Egypt spans the period of modern Egyptian history from the Egyptian Revolution of 1952 to the present day, which saw the toppling of the monarchy of Egypt and Sudan, the establishment of a presidential republic, and a period of profound economic, and political change in Egypt, and throughout the Arab world. The abolition of a monarchy and aristocracy viewed widely as sympathetic to Western interests, particularly since the ousting of Khedive Isma'il Pasha, over seven decades earlier, helped strengthen the authentically Egyptian character of the republic in the eyes of its supporters.
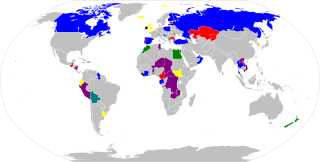
This national electoral calendar for 2011 lists the national/federal elections held in 2011 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.

A referendum on the Federation of Arab Republics was held in Libya on 1 September 1971, alongside simultaneous referendums in Egypt and Syria. The referendum was an attempt by Muammar Gaddafi to merge Libya, Egypt and Syria into a unified Arab state.

A constitutional referendum was held in Egypt on 19 March 2011, following the 2011 Egyptian revolution. More than 14 million (77%) were in favour, while around 4 million (23%) opposed the changes; 41% of 45 million eligible voters turned out to vote.

This national electoral calendar for 2012 lists the national/federal elections held in 2012 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.
The Constitution of 1956 was the constitution of Egypt from 1956 to 1958. It was promulgated on 19 January 1956 was implemented by referendum on 23 June, with Gamal Abdel Nasser being elected president simultaneously. It replaced a 1953 provisional constitution which in turn had replaced the Constitution of 1923 following the revolution of 1952. With the 1958 political union of Egypt and the Syrian Republic as the United Arab Republic, the 1956 Constitution was superseded by the Provisional Constitution of the United Arab Republic.

A referendum on the Federation of Arab Republics was held in Syria on 1 September 1971, alongside simultaneous referendums in Egypt and Libya. It was approved by 96.4% of voters, with a turnout of 89.7%.

The Constitution of the Arab Republic of Egypt is the fundamental law of Egypt.












