
Central America is a subregion of North America. Its political boundaries are defined as bordering Mexico to the north, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. Central America is usually defined as consisting of seven countries: Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Panama. Within Central America is the Mesoamerican biodiversity hotspot, which extends from southern Mexico to southeastern Panama. Due to the presence of several active geologic faults and the Central America Volcanic Arc, there is a high amount of seismic activity in the region, such as volcanic eruptions and earthquakes, which has resulted in death, injury, and property damage.

Izabal is one of the 22 departments of Guatemala. Its coastal areas form part of the homeland of the Garifuna people.

The Caribbean plate is a mostly oceanic tectonic plate underlying Central America and the Caribbean Sea off the northern coast of South America.

On 13 January 2001, at 11:33 CTZ, a Mw 7.7 earthquake struck off the coast of Usulután Department, El Salvador, at a depth of 60 km (37 mi). At least 952 people were killed; 944 in El Salvador and 8 in Guatemala, over 5,500 were injured and nearly 200 were left missing due to the earthquake; every single department in the country reported casualties and severe damage, and damage from the earthquake was reported in five countries throughout Central America.

The 1976 Guatemala earthquake struck on February 4 at with a moment magnitude of 7.5. The shock was centered on the Motagua Fault, about 160 km northeast of Guatemala City at a depth of 5 kilometers (3.1 mi) near the town of Los Amates in the department of Izabal.

The Motagua Fault is a major, active left lateral-moving transform fault which cuts across Guatemala. It forms part of the tectonic boundary between the North American plate and the Caribbean plate. It is considered the onshore continuation of the Swan Islands Transform Fault and Cayman trench, which run under the Caribbean Sea. Its western end appears not to continue further than its surface trace, where it is covered by Cenozoic volcanics.
The 1972 Nicaragua earthquake occurred at 12:29:44 a.m. local time on December 23 near Managua, the capital of Nicaragua. It had a moment magnitude of 6.3 and a maximum MSK intensity of IX (Destructive). The epicenter was 28 km (17 mi) northeast of the city centre and a depth of about 10 km (6.2 mi). The earthquake caused widespread casualties among Managua's residents: 4,000–11,000 were killed, 20,000 were injured and over 300,000 were left homeless.
The 2009 Swan Islands earthquake occurred on May 28 at with a moment magnitude of 7.3 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VII. The epicenter was located in the Caribbean Sea, 64 kilometres (40 mi) northeast of the island of Roatán, 19 miles northeast of Port Royal, Isla de Bahias, 15 miles northwest of Isla Barbaretta, and 130 kilometres (81 mi) north-northeast of La Ceiba. Three aftershocks followed the earthquake within magnitude 4 range.
The 1982 El Salvador earthquake occurred southeast of San Salvador on 19 June at 00:21 local time. This undersea earthquake struck offshore in the Pacific Ocean and had a surface wave magnitude of 7.3 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VII. Occurring adjacent to a subduction zone at the Middle America Trench, this normal-slip shock left at least 16 and as many as 43 people dead, and many injured, and also inflicted $5 million in damage.
The 1932 Jalisco earthquakes began on June 3 at 10:36 UTC with a megathrust event that registered 8.1 on the moment magnitude scale. With a maximum perceived intensity of X (Extreme) on the Mercalli intensity scale, at least 400 deaths were caused in Mexico and neighboring Guatemala. It was the first of a series of seismic events that affected parts of western Mexico during the month of June 1932, all reaching magnitude 7 or greater.
The February 2001 El Salvador earthquake occurred with a moment magnitude of 6.6 on 13 February at 14:22:05 UTC. The epicentre was 15 miles (30 km) E of San Salvador, El Salvador, at a depth of 10 km (6.2 mi). At least 315 people were killed, 3,399 were injured, and extensive damage affected the area. Another 16,752 homes were damaged and 44,759 destroyed. The most severe damage occurred in the San Juan Tepezontes-San Vicente-Cojutepeque area, though it was felt throughout the country and in neighboring Guatemala and Honduras. Landslides occurred in many areas of El Salvador.
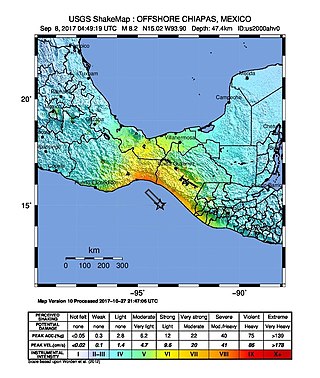
The 2017 Chiapas earthquake struck at 23:49 CDT on 7 September in the Gulf of Tehuantepec off the southern coast of Mexico near the state of Chiapas, approximately 87 kilometres (54 mi) southwest of Pijijiapan, with a Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent). The moment magnitude was estimated to be 8.2.

On 9 January 2018, at approximately 8:51 p.m. local time, a magnitude 7.5 earthquake struck in the Yucatán Basin of the Caribbean Sea, 44 kilometres (27 mi) east of Great Swan Island off the coast of Honduras. The earthquake was felt across Central America, and rattled windows in Tegucigalpa. The earthquake was also felt in the Cayman Islands.

At 02:10 PM local time (UTC-5) on 28 January 2020, an earthquake with a magnitude of 7.7 struck the north side of the Cayman Trough, north of Jamaica and west of the southern tip of Cuba, with the epicenter being 80 miles (130 km) east-southeast of Cayman Brac, Cayman Islands, and 83 miles (134 km) north of Montego Bay, Jamaica. Schools in Jamaica, as well as corporate and public buildings in Miami, were evacuated after shaking was experienced in parts of the U.S. state of Florida, a region not typically thought of in-relation to seismic activity. Light shaking was also reported on the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico. The quake was the largest seismic event in the Caribbean since 1946. A tsunami warning for the Caribbean Sea was initially issued by the Pacific Tsunami Warning Center, later being withdrawn.
An earthquake struck the Mexican state of Oaxaca at 10:29 local time on June 23, 2020, with a magnitude of 7.4 . The epicenter was 19 miles (31 km) from San Miguel del Puerto and 7.5 miles (12.1 km) south-southwest of Santa María Zapotitlán. The quake was felt by an estimated 49 million people in Mexico and Guatemala, with some tremors felt as far away as 640 kilometers (400 mi). Thousands of houses in Oaxaca were damaged and 10 deaths were reported. A tsunami warning was issued for southern Mexico, El Salvador, Guatemala, and Honduras.

On November 29, 1978, a moment magnitude 7.7–7.8 earthquake struck off the coast of the southern Mexican state Oaxaca. The thrust-faulting event caused severe damage in Oaxaca and Mexico City.

The 2017 Guatemala earthquake struck near the city of Malacatán in the San Marcos Department, near the Guatemala–Mexico border at 1:29 am local time (UTC−06:00) on June 14. The earthquake killed five people, and caused 30 injuries, 11 of which were from Chiapas, Mexico across the border. No tsunami warning was issued.
The 2022 Guatemala earthquake occurred on the early morning of February 16, 2022 in the southern regions of Guatemala. The quake measured a moment magnitude of 6.2 and reached a peak intensity of VI (Strong) on the Modified Mercalli Intensity scale. Damage was widespread but light in and around the capital, Guatemala City, resulting mostly in cracked walls and rockslides.
On 6 May 1951 EL Salvador was struck by an earthquake with a magnitude of 5.9–6.2 at 23:03 UTC. This was the first in a sequence that affected the area around Jucuapa over a period of a few days. The maximum felt intensity was VIII (Severe) on the Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale and it led to between 400 and 1,100 deaths.












