
Elections in Antigua and Barbuda take place in the framework of a parliamentary democracy.

Elections in the Bahamas take place in the framework of a parliamentary democracy. Since independence, voter turnout has been generally high in national elections, with a low of 87.9% in 1987 and a high of 98.5% in 1997. The current Prime Minister is The Hon. Philip Davis. The electorate is less than half of citizenry.

Elections in Botswana take place within the framework of a multi-party democracy and a parliamentary system. The National Assembly is mostly directly elected, and in turn elects the President and some of its own members. The Ntlo ya Dikgosi is a mixture of appointed, hereditary and indirectly elected members.

Elections in Guyana take place within the framework of a multi-party representative democracy and a presidential system. The National Assembly is directly elected, with the nominee of the party or alliance that receives the most votes becoming President.

Elections in Rwanda are manipulated in various ways, which include banning opposition parties, arresting or assassinating critics, and electoral fraud. According to its constitution, Rwanda is a multi-party democracy with a presidential system. In practice, it functions as a one-party state ruled by the Rwandan Patriotic Front and its leader Paul Kagame. The President and majority of members of the Chamber of Deputies are directly elected, whilst the Senate is indirectly elected and partly appointed.

Elections in Yemen take place within the framework of a presidential system, with both the President and House of Representatives elected by the public. Due to political instability, elections have not been held regularly since the early 2000s.

Parliamentary elections were held in Russia on 12 December 1993. They were the first parliamentary elections in post-Soviet Russia and the only time to the Federation Council, with future members appointed by provincial legislatures and governors.

Direct presidential elections were held in Yemen for the first time on 23 September 1999. Candidates had to be approved by at least 10% of the 301 members of the House of Representatives; however, in practice this meant that only two parties, the ruling General People's Congress (GPC) and Al-Islah had enough seats to nominate their candidates. However, al-Islah backed the GPC candidate, incumbent President Ali Abdullah Saleh rather than running a candidate of their own.

Parliamentary elections were held in the Republic of the Congo in 1992, along with a presidential election, marking the end of the transition to multiparty politics. The election was held in two rounds, the first on 24 June 1992 and the second on 19 July 1992. The Pan-African Union for Social Democracy (UPADS)—led by Pascal Lissouba, who won the presidential election—won a plurality of seats (39), while the Congolese Movement for Democracy and Integral Development (MCDDI) of second place presidential candidate Bernard Kolélas won the second highest number of seats (29). Following in third place was the Congolese Labor Party (PCT), which had been the ruling party during single-party rule.
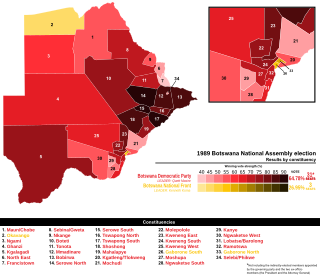
General elections were held in Botswana on 7 October 1989, alongside local elections. The result was the sixth straight landslide victory for the Botswana Democratic Party (BDP), which won 31 of the 34 elected seats.

General elections were held in Kenya on 29 December 1997 to elect the President and the members of the National Assembly. The result was a victory for the ruling Kenya African National Union, which won 107 of the 210 seats in the National Assembly, and whose candidate Daniel arap Moi won the presidential election. Following the election, Moi appointed a further 12 members to the Assembly.

Parliamentary elections were held in Yemen on 27 April 1997. The governing General People's Congress of President Ali Abdullah Saleh won a landslide victory, taking 187 of the 301 seats, although several opposition parties including the Yemeni Socialist Party boycotted the election alleging that the government had harassed and arrested their party workers. The main opposition party, al-Islah, attacked the government for not carrying out economic reforms and for corruption. Voter turnout was 61.0%.

General elections were held in Zambia on 19 December 1968 to elect the National Assembly and President. The first post-independence polls saw incumbent Kenneth Kaunda retain his post as president, whilst his United National Independence Party, the only party to field candidates in all 105 constituencies, won 81 of the 105 seats in the National Assembly. Voter turnout was 82.5% in the parliamentary election, but 87.1% in the presidential election.

General elections were held in Zambia on 12 December 1978. At the time, the country was a one-party state with the United National Independence Party (UNIP) as the sole legal party. UNIP leader Kenneth Kaunda was automatically elected to a fourth five-year term as President, with 80.7% of voters voting to confirm him in office. UNIP also won all 125 seats in the National Assembly. Voter turnout was around 65% in the parliamentary election, but 66.7% in the presidential election.

General elections were held in Zambia on 27 October 1983. At the time, the country was a one-party state, with the United National Independence Party (UNIP) as the only legally permitted party. Its leader, Kenneth Kaunda was automatically re-elected for a fifth term as President, and was confirmed in office with over 95% of the vote. UNIP also won all 125 seats in the National Assembly. Voter turnout was around 63% in the parliamentary election, but 65.5% in the presidential election.

General elections were held in Zambia on 26 October 1988. At the time, the country was a one-party state with the United National Independence Party (UNIP) as the sole legal party. UNIP leader Kenneth Kaunda was automatically re-elected for a sixth five-year term as President with 95.5% of the vote, whilst UNIP also won all 125 seats in the National Assembly. Voter turnout was around 60% in the parliamentary elections, but 58.8% in the presidential elections.

Parliamentary elections were held in South Yemen between 28 and 30 October 1986, having originally been scheduled for 1983, but later postponed. A total of 181 candidates contested the 111 seats of the Supreme People's Council. Although the country was a one-party state at the time, with the Yemeni Socialist Party as the sole legal party, independents were also able to run as candidates.

Parliamentary elections were held in the Yemen Arab Republic in February and March 1971. As political parties were banned, all candidates ran as independents.

Parliamentary elections were held in Cyprus in 1960. The House of Representatives was elected on 31 July 1960. The Communal Chambers were also elected on 7 August. In the House of Representatives 35 seats were elected by Greek Cypriots and 15 by Turkish Cypriots. The result was a victory for the Patriotic Front, which won 30 of the 50 seats. In the Communal Chambers, the Patriotic Front won the majority of seats in the Greek Chamber, whilst the Cyprus Turkish National Union won all seats in the Turkish Chamber.
Parliamentary elections were held in Hungary on 25 April 1971. The Hungarian Socialist Workers' Party was the only party to contest the elections, and won 224 of the 352 seats, with the remaining 128 going to independents selected by the party.
















