| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1988 List of years in Armenia | ||||
The following lists events that happened during 1988 in Armenia .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1988 List of years in Armenia | ||||
The following lists events that happened during 1988 in Armenia .


Nagorno-Karabakh is a region in Azerbaijan, covering the southeastern stretch of the Lesser Caucasus mountain range. Part of the greater region of Karabakh, it spans the area between Lower Karabakh and Syunik. Its terrain mostly consists of mountains and forestland.

Stepanakert or Khankendi is a ghost city in the Nagorno-Karabakh region of Azerbaijan. The city was under the control and the capital city of the breakaway Republic of Artsakh prior to the 2023 Azerbaijani offensive in the region. The city is located in a valley on the eastern slopes of the Karabakh mountain range, on the left bank of the Qarqarçay (Karkar) river.

Artsakh, officially the Republic of Artsakh or the Republic of Nagorno-Karabakh, was a breakaway state in the South Caucasus whose territory was internationally recognised as part of Azerbaijan. Between 1991 and 2023, Artsakh controlled parts of the former Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast of the Azerbaijani Soviet Socialist Republic, including its capital Stepanakert. It had been an enclave within Azerbaijan from the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war until the 2023 Azerbaijani offensive, when the Azerbaijani military took control over the remaining territory controlled by Artsakh. Its only overland access route to Armenia after the 2020 war was via the five kilometres (3.1 mi)–wide Lachin corridor, which was placed under the supervision of Russian peacekeeping forces.
The 1988 Armenian earthquake, also known as the Spitak earthquake, occurred on December 7 at 11:41 local time with a surface wave magnitude of 6.8 and a maximum MSK intensity of X (Devastating). The shock occurred in the northern region of Armenia which is vulnerable to large and destructive earthquakes and is part of a larger active seismic belt that stretches from the Alps to the Himalayas. Activity in the area is associated with tectonic plate boundary interaction and the source of the event was slip on a thrust fault just to the north of Spitak. The complex incident ruptured multiple faults, with a strike-slip event occurring shortly after the initiation of the mainshock. Between 25,000 and 50,000 were killed and up to 130,000 were injured.

The First Nagorno-Karabakh War was an ethnic and territorial conflict that took place from February 1988 to May 1994, in the enclave of Nagorno-Karabakh in southwestern Azerbaijan, between the majority ethnic Armenians of Nagorno-Karabakh backed by Armenia, and the Republic of Azerbaijan with support from Turkey. As the war progressed, Armenia and Azerbaijan, both former Soviet republics, entangled themselves in protracted, undeclared mountain warfare in the mountainous heights of Karabakh as Azerbaijan attempted to curb the secessionist movement in Nagorno-Karabakh.

The Nagorno-Karabakh conflict is an ethnic and territorial conflict between Armenia and Azerbaijan over the region of Nagorno-Karabakh, inhabited mostly by ethnic Armenians until 2023, and seven surrounding districts, inhabited mostly by Azerbaijanis until their expulsion during the 1990s. The Nagorno-Karabakh region was entirely claimed by and partially controlled by the breakaway Republic of Artsakh, but was recognized internationally as part of Azerbaijan. Azerbaijan gradually re-established control over Nagorno-Karabakh region and the seven surrounding districts.
Nagorno-Karabakh is located in the southern part of the Lesser Caucasus range, at the eastern edge of the Armenian Highlands, encompassing the highland part of the wider geographical region known as Karabakh. Under Russian and Soviet rule, the region came to be known as Nagorno-Karabakh, meaning "Mountainous Karabakh" in Russian. The name Karabakh itself was first encountered in Georgian and Persian sources from the 13th and 14th centuries to refer to lowlands between the Kura and Aras rivers and the adjacent mountainous territory.
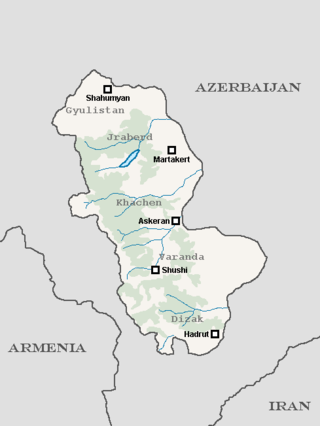
The Karabakh Council was the unrecognised government over Mountainous Karabakh (Nagorno-Karabakh) in eastern Armenia between 1918 and 1920. The council's body was elected by the assembly of Mountainous Karabakh—the representative body of the people of Nagorno-Karabakh—on 27 July 1918. Initially it was called the People's Government of Karabakh, but in September 1918 it was renamed into the Karabakh Council. The Karabakh Council's control throughout 1918–1920 did not exceed the ethnic Armenian locales of Karabakh which were subordinate to them. The council's statehood related to the historical Artsakh province and the modern-day self-proclaimed Republic of Artsakh founded in 1991. Its capital was the city of Shushi (Shusha).

The Armenian-Azerbaijani war (1918–1920) was a conflict that took place in the South Caucasus in regions with a mixed Armenian-Azerbaijani population, broadly encompassing what are now modern-day Azerbaijan and Armenia. It began during the final months of World War I and ended with the establishment of Soviet rule.

There are no diplomatic relations between Armenia and Azerbaijan. The two neighboring states had formal governmental relations between 1918 and 1921, during their brief independence from the collapsed Russian Empire, as the First Republic of Armenia and the Democratic Republic of Azerbaijan; these relations existed from the period after the Russian Revolution until they were occupied and annexed by the Soviet Union, becoming the constituent republics of Soviet Armenia and Soviet Azerbaijan. Due to the five wars waged by the countries in the past century—one from 1918 to 1921, another from 1988 to 1994, and the most recent in 2016, 2020 and 2023—the two have had strained relations. In the wake of hostilities, social memory of Soviet-era cohabitation is widely repressed through censorship and stigmatization.
Armenians in Azerbaijan are the Armenians who lived in great numbers in the modern state of Azerbaijan and its precursor, Soviet Azerbaijan. According to the statistics, about 500,000 Armenians lived in Soviet Azerbaijan prior to the outbreak of the First Nagorno-Karabakh War in 1988. Most of the Armenians in Azerbaijan had to flee the republic, like Azerbaijanis in Armenia, in the events leading up to the First Nagorno-Karabakh War, a result of the ongoing Armenian-Azerbaijani conflict. Atrocities directed against the Armenian population took place in Sumgait, Ganja and Baku. Armenians continued to live in large numbers in the region of Nagorno-Karabakh, which was controlled by the break-away state known as the Nagorno-Karabakh Republic from 1991 until the region was forcibly retaken by Azerbaijan in 2023. After the Azerbaijani takeover, almost all Armenians living in Nagorno-Karabakh left the region.
The Baku pogrom was a pogrom directed against the ethnic Armenian inhabitants of Baku, Azerbaijan SSR. From January 12, 1990, a seven-day pogrom broke out against the Armenian civilian population in Baku during which Armenians were beaten, murdered, and expelled from the city. There were also many raids on apartments, robberies and arsons. According to the Human Rights Watch reporter Robert Kushen, "the action was not entirely spontaneous, as the attackers had lists of Armenians and their addresses". The pogrom of Armenians in Baku was one of the acts of ethnic violence in the context of the First Nagorno-Karabakh War, directed against the demands of the Nagorno-Karabakh Armenians to secede from Azerbaijan and unify with Armenia.

The Law on Abolishment of Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast was a motion passed by the Supreme Soviet of the Republic of Azerbaijan and signed into law by the President of Azerbaijan Ayaz Mutalibov on November 26, 1991. The law had been prompted by a vote in the National Assembly of the Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast in favor of uniting itself with the Armenian SSR on 20 February 1988. The vote was followed by an independence referendum in 1991 which was boycotted by the Azerbaijani population of the Oblast; most voted in favor of independence. While these votes and elections had mainly been conducted in a relatively peaceful manner, in the following months, as the Soviet Union disintegrated, it gradually grew into an increasingly violent conflict between ethnic Armenians and ethnic Azerbaijanis. Both sides claimed that ethnic cleansing was being carried out. The declaration of secession from Azerbaijan was the final result of a territorial conflict regarding the land.

The Karabakh movement, also known as the Artsakh movement, was a national mass movement in Armenia and Nagorno-Karabakh from 1988 to 1991 that advocated for the transfer of the mainly Armenian-populated Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast of neighboring Azerbaijan to the jurisdiction of Armenia.

Simon Achikgyozyan was one of the earliest Armenian military commanders during the First Nagorno-Karabakh War. He is considered a hero in Armenia.
The Zvartnots Airport clash occurred on 5 July 1988 between Armenian protesters and the Soviet troops at the Zvartnots International Airport at the outskirts of Yerevan.

The 1988 violence in Shusha and Stepanakert was the expulsion of the ethnic Armenian population of Shusha and the ethnic Azerbaijani population of Stepanakert, in the Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast in the Azerbaijani SSR, Soviet Union, from September 18 to 20, 1988. During the violence, 33 Armenians and 16 Azerbaijanis were wounded, more than 30 houses hed been set on fire, and a 61-year-old Armenian was killed. At the end of the violence, 3,117 ethnic Azerbaijanis were forced to leave Stepanakert.
The Gugark pogrom was a pogrom directed against the Azerbaijani minority of the Gugark District in the Armenian SSR, then part of the Soviet Union.