| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1994 Timeline of Eritrean history | ||||
Events in the year 1994 in Eritrea .
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1994 Timeline of Eritrean history | ||||
Events in the year 1994 in Eritrea .

The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa. Located on the easternmost part of the African mainland, it is the fourth largest peninsula in the world. It is composed of Ethiopia, Eritrea, Somalia and Djibouti; broader definitions also include parts or all of Kenya, Sudan, South Sudan, and Uganda. The term Greater Horn Region (GHR) can additionally include Burundi, Rwanda, and Tanzania. It lies along the southern boundary of the Red Sea and extends hundreds of kilometres into the Guardafui Channel, Gulf of Aden, and Indian Ocean and shares a maritime border with the Arabian Peninsula of Western Asia.

Isaias Afwerki is an Eritrean political leader and partisan who has been the president of Eritrea since shortly after he led the Eritrean People's Liberation Front (EPLF) to victory in May 1991, ending the 30-year-old war for independence from Ethiopia.
"Eritrea, Eritrea, Eritrea" is the national anthem of Eritrea. Adopted in 1993 shortly after independence, it was written by Solomon Tsehaye Beraki and composed by Isaac Abraham Meharezghi and Aron Tekle Tesfatsion.
The Saho language is an Afro-Asiatic language spoken in Eritrea, Sudan and Ethiopia. It belongs to the family's Cushitic branch.

The Eritrean People's Liberation Front (EPLF), colloquially known as Shabia, was an armed Marxist–Leninist organization that fought for the independence of Eritrea from Ethiopia. It emerged in 1970 as a far-left to left-wing nationalist group that split from the Eritrean Liberation Front (ELF). After achieving Eritrean independence in 1991, it transformed into the People's Front for Democracy and Justice (PFDJ), which serves as Eritrea's sole legal political party.

The Eritrean–Ethiopian War, also known as the Badme War, was a major armed conflict between Ethiopia and Eritrea that took place from May 1998 to June 2000. The war has its origins in a territorial dispute between the two states. After Eritrea gained independence from Ethiopia, relations were initially friendly. However, disagreements about where the newly created international border should be caused relations to deteriorate significantly, eventually leading to full scale war. According to a 2005 ruling by an international commission, Eritrea broke international law and triggered the war by invading Ethiopia. By 2000, Ethiopia held all of the disputed territory and had advanced into Eritrea. The war officially came to an end with the signing of the Algiers Agreement in 12 December 2000; however, the ensuing border conflict would continue on for nearly two decades.

Nakfa, Tigrinya: ናቕፋ, is a town in the Northern Red Sea region of Eritrea. It is also the name of a sub region of Eritrea.
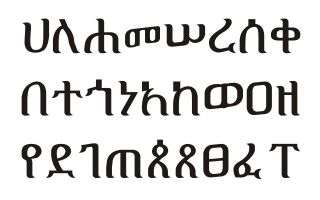
Geʽez is a script used as an abugida (alphasyllabary) for several Afro-Asiatic and Nilo-Saharan languages of Ethiopia and Eritrea in the Horn of Africa. It originated as an abjad and was first used to write the Geʽez language, now the liturgical language of the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church, the Eritrean Orthodox Tewahedo Church, the Eritrean Catholic Church, the Ethiopian Catholic Church, and Haymanot Judaism of the Beta Israel Jewish community in Ethiopia. In the languages Amharic and Tigrinya, the script is often called fidäl (ፊደል), meaning “script” or “letter”. Under the Unicode Standard and ISO 15924, it is defined as Ethiopic text.

The Eritrean War of Independence was a war for independence which Eritrean independence fighters waged against successive Ethiopian governments from 1 September 1961 to 24 May 1991.
The Tigre people are an ethnic group indigenous to Eritrea. They mainly inhabit the lowlands and northern highlands of Eritrea.
Articles related to Eritrea include:
Ruth Simon is an Eritrean journalist.

Eritrea, officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city at Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia in the south, Sudan in the west, and Djibouti in the southeast. The northeastern and eastern parts of Eritrea have an extensive coastline along the Red Sea. The nation has a total area of approximately 117,600 km2 (45,406 sq mi), and includes the Dahlak Archipelago and several of the Hanish Islands.

Djibouti–Eritrea relations refers to the current and historical relationship between neighboring states Djibouti and Eritrea.
Eritrean Canadians are a hyphenated ethnicity of Canadians who are of full or partial Eritrean national origin, heritage and/or ancestry, Canadian citizens of Eritrean descent, or an Eritrea-born person who resides in Canada. According to the 2016 Canadian census, 25,255 people reported Eritrean ancestry.
Eritrean nationalism is centered on the fact that the Eritreans share a common history, and as such constitute a nation unto themselves. Even though there is a natural basis for Eritrean nationalism, there is still diversity within Eritrean demographics. Eritrea has nine major ethnic groups, each with their own language and culture and is split between two major religions, even though there is 70% Christianity in Eritrea. However the Eritrean government seeks to foster Eritrean nationalism through programs such as national service programs, the promotion of liberal nationalism and the Formation of the YPFDJ and curbing foreign influences.

The history of cinema in Eritrea dates back to the country's colonial rule under the Kingdom of Italy. In connection with the growth of Italian cinema in the 1930s, so too did the rise of cinema occur in Asmara, Eritrea. In 1937, Asmara's Opera was converted into a dual-use theatre and cinema. By the following year, Asmara had a total of nine movie theatres.
The Tigray War was an armed conflict that lasted from 3 November 2020 to 3 November 2022. The war was primarily fought in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia between the Ethiopian federal government and Eritrea on one side, and the Tigray People's Liberation Front (TPLF) on the other.

Eritreans in Italy are residents of Italy who were born in Eritrea or are of Eritrean descent. According to the United Nations, there were 13,592 Eritrean migrants in Italy in 2015.
The US Embassy in Asmara is diplomatic mission of the United States to Eritrea.