 |
|---|
| Constitution |
Parliamentary elections were held in Abkhazia on 23 November 1996, with a second round on 7 December. [1] There was also a simultaneous referendum held amongst Abkhazian Refugees.
 |
|---|
| Constitution |
Parliamentary elections were held in Abkhazia on 23 November 1996, with a second round on 7 December. [1] There was also a simultaneous referendum held amongst Abkhazian Refugees.
The election was held to replace the former Abkhaz Autonomous Republic's Supreme Soviet which had split during the Georgian-Abkhazian conflict in 1993 with 28 deputies continuing in Abkhazia as the Abkhaz Supreme Soviet. The remaining 24 formed a parliament in exile in Georgia. [2]
However, international organisations and the most important international political leaders declared that the election would be invalid. [2]
The elections were held using the two-round system; candidates had to receive over 50% of the vote in the first round to be elected, otherwise a second round would be held.
Voters could choose by crossing off all the names on the list of candidates that they didn't want to be the elected, except for the one they preferred. [3]
The number of registered candidates contesting the 35 seats was initially reported to be 85, three of whom being Georgian, [4] later there were only 78 with 2 Georgians. [5] All candidates ran as independents. [6]
Of the 35 seats, 30 were filled already in the first round. These 30 MPs elected included 19 Abkhazians, four Russians, three Armenians, two Georgians, one Greek and one Kabardian. [6] Voter turnout was reported to be 81%.
In response to the elections, Georgia organised a referendum among refugees from Abkhazia, with polling stations opened in Moscow, St Petersburg, Podolsk and Sochi in Russia, Kyiv in Ukraine, Trabzon in Turkey, Minsk in Belarus, Yerevan in Armenia, as well as in Greece and Israel. [3] The Georgian government stated that over 99% of refugees agreed that the elections were invalid until refugees were allowed to return and its political status as part of Georgia was agreed. [2] [3]

Vladislav Ardzinba was the first de facto President of Abkhazia. A historian by education, Ardzinba led Abkhazia to de facto independence in the 1992–1993 War with Georgia, but its de jure independence from Georgia remained internationally unrecognised during Ardzinba's two terms as President from 1994 to 2005.

Raul Jumkovich Khajimba is an Abkhazian politician, and served as President of Abkhazia from 25 September 2014 until 12 January 2020. He was also Chairman of the Forum for the National Unity of Abkhazia from 2010 to 2015. Khajimba previously held the offices of Vice President (2005–2009), Prime Minister (2003–2004) and Defence Minister (2002–2003). He unsuccessfully ran for President in 2004, 2009 and 2011. He resigned the presidency in 2020 due to protests against him.

Sergei Uasyl-ipa Bagapsh was an Abkhaz politician who served as the second President of Abkhazia from 12 February 2005 until his death on 29 May 2011. He previously served as Prime Minister of Abkhazia from 1997 to 1999. He was re-elected in the 2009 presidential election. Bagapsh's term as Prime Minister included the 1998 war with Georgia, while he oversaw both the recognition of Abkhazia by Russia and the Russo-Georgian War during his presidency.

Konstantin Ozgan was a leading politician in Abkhazia serving i.a. as Supreme Soviet Chairman, Foreign Minister, Economy Minister, First Vice Premier and as Chairman of the Council of Elders of Abkhazia

Politics in Abkhazia is dominated by its conflict with Georgia. Abkhazia became de facto independent from Georgia after the 1992–1993 war, but its de jure independence has only been recognised by a few other countries. Abkhazia is a presidential representative democratic republic with a multi-party system, wherein the President is both head of state and head of government. Executive power is exercised by the government of the Republic of Abkhazia. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the People's Assembly of Abkhazia.

The Abkhaz–Georgian conflict involves ethnic conflict between Georgians and the Abkhaz people in Abkhazia, a de facto independent, partially recognized republic. In a broader sense, one can view the Georgian–Abkhaz conflict as part of a geopolitical conflict in the Caucasus region, intensified at the end of the 20th century with the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991.

Abkhazians, or Abkhazes, are a Northwest Caucasian ethnic group, mainly living in Abkhazia, a disputed region on the northeastern coast of the Black Sea. A large Abkhaz diaspora population resides in Turkey, the origins of which lie in the population movements from the Caucasus in the late 19th century. Many Abkhaz also live in other parts of the former Soviet Union, particularly in Russia and Ukraine.

Aleksandr Zolotinskovich Ankvab is an Abkhaz politician and businessman who was president of Abkhazia from 29 May 2011, until his resignation on 1 June 2014. Under president Sergei Bagapsh, he previously served as prime minister from 2005 to 2010 and vice-president from 2010 to 2011. He was appointed prime minister again on 23 April 2020.

Irakli Alasania is a Georgian politician, soldier and former diplomat who served as the Minister of Defense of Georgia from 2012 to 2014. He was Georgia's Ambassador to the United Nations from September 11, 2006, until December 4, 2008. His previous assignments include Chairman of the Government of Abkhazia(-in-exile) and the President of Georgia's aide in the Georgian-Abkhaz talks. Soon after his resignation, Alasania withdrew into opposition to the Mikheil Saakashvili administration, setting up the Our Georgia – Free Democrats party in July 2009. In 2012 Alasania was appointed Minister of Defense, a position he held until 2014.

The ethnic cleansing of Georgians in Abkhazia, also known in Georgia as the genocide of Georgians in Abkhazia, refers to the ethnic cleansing, massacres, and forced mass expulsion of thousands of ethnic Georgians living in Abkhazia during the Georgian-Abkhaz conflict of 1992–1993 and 1998 at the hands of Abkhaz separatists and their allies. Armenians, Greeks, Russians, and opposing Abkhazians were also killed.

The history of Abkhazia, a region in the South Caucasus, spans more than 5,000 years from its settlement by the lower-paleolithic hunter-gatherers to its present status as a partially recognized state.

The Abkhaz Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic, abbreviated as Abkhaz ASSR, was an autonomous republic of the Soviet Union within the Georgian SSR. It came into existence in February 1931, when the Socialist Soviet Republic of Abkhazia, originally created in March 1921, was transformed to the status of Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic within the Georgian SSR.

Parliamentary elections were held in Abkhazia on 4 March 2007, with a second round in seventeen constituencies on 18 March.
The War in Abkhazia was fought between Georgian government forces for the most part and Abkhaz separatist forces, Russian government armed forces and North Caucasian militants between 1992 and 1993. Ethnic Georgians who lived in Abkhazia fought largely on the side of Georgian government forces. Ethnic Armenians and Russians within Abkhazia's population largely supported the Abkhazians and many fought on their side. The separatists received support from thousands of North Caucasus and Cossack militants and from the Russian Federation forces stationed in and near Abkhazia.

Sokrat Rachevich Jinjolia was the second Prime Minister and the second foreign minister of the internationally unrecognised Republic of Abkhazia from 1993 to 1994. He has also been the speaker of the People's Assembly of Abkhazia from 1996 until he lost his seat in the 2002 parliamentary elections to Anatoly Khashba, and was succeeded by Nugzar Ashuba. He graduated from the Department of Russian Language and Literature Faculty of Philology of Sukhumi Pedagogical Institute. In 1956–1959 he served in the Soviet Army. After transferring to the Army reserve, he worked on Tkvarcheli power plant, and in 1967 was elected secretary to the Tkvarcheli City Council. Between 1985 and 1988 he worked on the Tkvarcheli Party Committee, becoming head of the Department of Agitation and Propaganda. In 1988–1992 – chief editor of "Tkvarchalsky Miner." In 1991, he was elected to the Supreme Council, and in 1992 he became deputy chairman of the Abkhazian armed forces. In 1993 he was appointed Prime Minister. He headed the official delegation from Abkhazia for the peace talks in Geneva. He was elected speaker of the new parliament – the National Assembly – the first and second convocations. He is married. He has two children. During the 2004 presidential elections, Jinjolia was head of opposition candidate Sergei Bagapsh's election team. He has since become the head of the Sukhumi branch of the Caucasian Institute for Democracy. Recently, Jinjolia became a member of the newly founded Public Chamber of Abkhazia.

Parliamentary elections were held in Abkhazia on 2 March 2002 to elect the third convocation of the People's Assembly. The elections had originally been scheduled for 24 November 2001, but had to be postponed due to the October 2001 Chechen incursion into the lower Kodori Valley. Candidates supporting President Vladislav Ardzinba won all 35 seats.

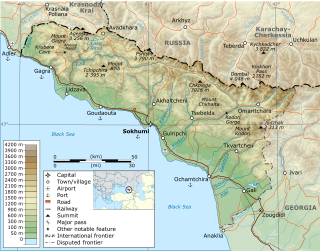
Abkhazia, officially the Republic of Abkhazia, is a partially recognised state in the South Caucasus, at the intersection of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It lies on the eastern coast of the Black Sea in northwestern Georgia. It is recognised by most countries as part of the latter. It covers 8,665 square kilometres (3,346 sq mi) and has a population of around 245,000. Its capital and largest city is Sukhumi.

The elections for the 5th convocation of the People's Assembly of Abkhazia were held in two rounds on 10 and 24 March 2012.
This is an alphabetical list of Abkhazia-related articles.

Parliamentary elections were held in Abkhazia on 12 March 2022, with a second round taking place on 26 March.