
In chemistry, an ester is a functional group derived from an acid in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group of that acid is replaced by an organyl group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well, but not according to the IUPAC.

In organic chemistry, a ketene is an organic compound of the form RR'C=C=O, where R and R' are two arbitrary monovalent chemical groups. The name may also refer to the specific compound ethenone H2C=C=O, the simplest ketene.
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters. They are derived from the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids by esterification. They can be saturated or unsaturated. Some contain heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring.
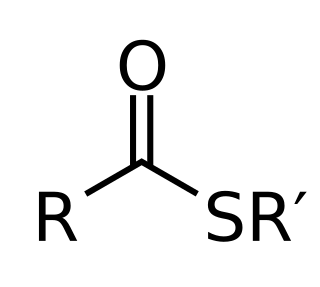
In organic chemistry, thioesters are organosulfur compounds with the molecular structure R−C(=O)−S−R’. They are analogous to carboxylate esters with the sulfur in the thioester replacing oxygen in the carboxylate ester, as implied by the thio- prefix. They are the product of esterification of a carboxylic acid with a thiol. In biochemistry, the best-known thioesters are derivatives of coenzyme A, e.g., acetyl-CoA. The R and R' represent organyl groups, or H in the case of R.

Fischer esterification or Fischer–Speier esterification is a special type of esterification by refluxing a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst. The reaction was first described by Emil Fischer and Arthur Speier in 1895. Most carboxylic acids are suitable for the reaction, but the alcohol should generally be primary or secondary. Tertiary alcohols are prone to elimination. Contrary to common misconception found in organic chemistry textbooks, phenols can also be esterified to give good to near quantitative yield of products. Commonly used catalysts for a Fischer esterification include sulfuric acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid, and Lewis acids such as scandium(III) triflate. For more valuable or sensitive substrates other, milder procedures such as Steglich esterification are used. The reaction is often carried out without a solvent or in a non-polar solvent that can facilitate Dean–Stark distillation to remove the water byproduct. Typical reaction times vary from 1–10 hours at temperatures of 60–110 °C.
In organic chemistry, an acyl chloride is an organic compound with the functional group −C(=O)Cl. Their formula is usually written R−COCl, where R is a side chain. They are reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids. A specific example of an acyl chloride is acetyl chloride, CH3COCl. Acyl chlorides are the most important subset of acyl halides.

1,1'-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) is an organic compound with the molecular formula (C3H3N2)2CO. It is a white crystalline solid. It is often used for the coupling of amino acids for peptide synthesis and as a reagent in organic synthesis.

In stereochemistry, a chiral auxiliary is a stereogenic group or unit that is temporarily incorporated into an organic compound in order to control the stereochemical outcome of the synthesis. The chirality present in the auxiliary can bias the stereoselectivity of one or more subsequent reactions. The auxiliary can then be typically recovered for future use.
In organic chemistry, the Arndt–Eistert reaction is the conversion of a carboxylic acid to its homologue. It is named for the German chemists Fritz Arndt (1885–1969) and Bernd Eistert (1902–1978). The method entails treating an acid chlorides with diazomethane. It is a popular method of producing β-amino acids from α-amino acids.

Trimethylsilyldiazomethane is the organosilicon compound with the formula (CH3)3SiCHN2. It is classified as a diazo compound. Trimethylsilyldiazomethane, which is a commercially available, reagent used in organic chemistry as a methylating agent of carboxylic acids. Its behavior is akin to the reagent diazomethane, but the trimethylsilyl (TMS) analog is nonexplosive.
Oseltamivir total synthesis concerns the total synthesis of the antiinfluenza drug oseltamivir marketed by Hoffmann-La Roche under the trade name Tamiflu. Its commercial production starts from the biomolecule shikimic acid harvested from Chinese star anise and from recombinant E. coli. Control of stereochemistry is important: the molecule has three stereocenters and the sought-after isomer is only 1 of 8 stereoisomers.
The total synthesis of quinine, a naturally-occurring antimalarial drug, was developed over a 150-year period. The development of synthetic quinine is considered a milestone in organic chemistry although it has never been produced industrially as a substitute for natural occurring quinine. The subject has also been attended with some controversy: Gilbert Stork published the first stereoselective total synthesis of quinine in 2001, meanwhile shedding doubt on the earlier claim by Robert Burns Woodward and William Doering in 1944, claiming that the final steps required to convert their last synthetic intermediate, quinotoxine, into quinine would not have worked had Woodward and Doering attempted to perform the experiment. A 2001 editorial published in Chemical & Engineering News sided with Stork, but the controversy was eventually laid to rest once and for all when Williams and coworkers successfully repeated Woodward's proposed conversion of quinotoxine to quinine in 2007.
The Kulinkovich reaction describes the organic synthesis of substituted cyclopropanols through reaction of esters with dialkyldialkoxytitanium reagents, which are generated in situ from Grignard reagents containing a hydrogen in beta-position and titanium(IV) alkoxides such as titanium isopropoxide. This reaction was first reported by Oleg Kulinkovich and coworkers in 1989.
The Yamaguchi esterification is the chemical reaction of an aliphatic carboxylic acid and 2,4,6-trichlorobenzoyl chloride to form a mixed anhydride which, upon reaction with an alcohol in the presence of stoichiometric amount of DMAP, produces the desired ester. It was first reported by Masaru Yamaguchi et al. in 1979.
Isamu Shiina is professor of chemistry at Tokyo University of Science (TUS), Japan. He completed his BSc and MSc at TUS, and he joined the group of Prof. Teruaki Mukaiyama at TUS as an assistant professor in 1992. After receiving his PhD from the University of Tokyo (UT) in 1997, he was promoted to lecturer at the TUS, and then appointed to an associate professor (2003) and a full professor (2008). He has received the Chemical Society of Japan (CSJ) Award for Young Chemists (1997), the CSJ Award for Creative Work (2013), and the Commendation for Science and Technology Prizes by the Ministries of Japan (2015). His research interests include the development of useful synthetic methods and the total synthesis of natural products. In particular, the dehydration condensation reaction using MNBA is suitable for synthesis of unstable molecules and is now being widely used around the world in fields such as pharmaceutical production.
Shiina macrolactonization is an organic chemical reaction that synthesizes cyclic compounds by using aromatic carboxylic acid anhydrides as dehydration condensation agents. In 1994, Prof. Isamu Shiina reported an acidic cyclization method using Lewis acid catalyst, and, in 2002, a basic cyclization using nucleophilic catalyst.
Shiina esterification is an organic chemical reaction that synthesizes carboxylic esters from nearly equal amounts of carboxylic acids and alcohols by using aromatic carboxylic acid anhydrides as dehydration condensation agents. In 1994, Prof. Isamu Shiina reported an acidic coupling method using Lewis acid, and, in 2002, a basic esterification using nucleophilic catalyst.

Tris(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl) borate, also commonly referred to as the Sheppard amidation reagent, is a chemical compound with the formula B(OCH2CF3)3. This borate ester reagent is used in organic synthesis.

Corey–Nicolaou macrolactonization is a named reaction of organic chemistry, for the synthesis of lactones from hydroxy acids, found in 1974. The reaction uses 2,2'-dipyridyldisulfide and triphenylphosphine as reagents and runs in polar aprotic solvent under mild conditions.

Teruaki Mukaiyama was a Japanese organic chemist. One of the most prolific chemists of the 20th century in the field of organic synthesis, Mukaiyama helped establish the field of organic chemistry in Japan after World War II.











