National referendums are seldom used in Canada. The first two referendums in 1898 and 1942 saw a large number of voters in Quebec and in the remainder of Canada take dramatically-opposing stands, and the third in 1992 saw most of the voters take a stand opposed to that of the party in power.
Canada holds elections for legislatures or governments in several jurisdictions: for the federal (national) government, provincial and territorial governments, and municipal governments. Elections are also held for self-governing First Nations and for many other public and private organizations including corporations and trade unions. Municipal elections can also be held for both upper-tier and lower-tier governments.
The Citizens' Assembly on Electoral Reform was created by the government of British Columbia, Canada to investigate changes to the provincial electoral system. On October 25, 2004, the citizens' assembly proposed replacing the province's existing first past the post (FPTP) system with BC-STV, a single transferable vote (STV) system. This recommendation was put to the electorate in a referendum in 2005 held during that year's provincial election. The provincial government required the referendum to achieve a super-majority of 60 percent of voters and simple majorities in 60 percent of the 79 districts in order to pass. The second of these thresholds was easily met, with a majority supporting the reform in 77 out of 79 electoral districts, but the overall vote fell short of the 60 percent requirement, with 57.69 percent of the votes in favour. A second referendum in 2009 on adopting the STV system also failed to pass carrying 8 electoral districts and 39.09 percent of the overall vote.

The 2005 British Columbia general election was held on May 17, 2005, to elect members of the Legislative Assembly (MLAs) of the Province of British Columbia (BC), Canada. The British Columbia Liberal Party formed the government of the province prior to this general election under the leadership of Premier Gordon Campbell. The main opposition was the British Columbia New Democratic Party, whose electoral representation was reduced to two MLAs in the previous provincial election in 2001.

A referendum was held in the Canadian province of British Columbia on May 17, 2005, to determine whether or not to adopt the recommendation of the Citizens' Assembly on Electoral Reform to replace the existing first-past-the-post electoral system (FPTP) with a single transferable vote system (BC-STV). It was held in conjunction with the BC Legislative Assembly election of 2005. Voters were given two ballots at that time: a ballot to vote for a Member of the Legislative Assembly of British Columbia (MLA) in their constituency and a referendum ballot. The referendum received considerable support from the electorate but failed in meeting the 60-percent threshold that had been set. A second referendum was held in 2009.
The Citizens' Assembly on Electoral Reform was established by the government of the province of Ontario, Canada, in March 2006. Modelled on the British Columbia equivalent, it reviewed the first past the post electoral system currently in use to elect members of the Ontario Legislature, with the authority to recommend an alternative. In May 2007, the assembly recommended, in a decision of 94 to 8, that Ontario adopt a form of mixed member proportional representation (MMP).

A referendum was held on October 10, 2007, on the question of whether to establish a mixed member proportional representation (MMP) system for elections to the Legislative Assembly of Ontario. The vote was strongly in favour of the existing plurality voting or first-past-the-post (FPTP) system.

Elections BC is a non-partisan office of the British Columbia legislature responsible for conducting provincial and local elections, by-elections, petitions, referendums, plebiscites in the Canadian province of British Columbia. Its federal equivalent is Elections Canada.
BC-STV is the proposed voting system recommended by the Citizens' Assembly on Electoral Reform in October 2004 for use in British Columbia, and belongs to the single transferable vote family of voting systems. BC-STV was supported by a majority of the voters in a referendum held in 2005 but the government had legislated that it would not be bound by any vote lower than 60 percent in favour. Because of the strong majority support for BC-STV, the government elected to stage a second referendum in 2009, but with increased public funding for information campaigns to better inform the electorate about the differences between the existing and proposed systems. The leadership of both the "yes" side and the "no" side were assigned by the government. The proposal was rejected with 60.9 percent voting against, vs. 39.1 percent in favour, in the 2009 vote.
Historically, the single transferable vote (STV) electoral system has seen a series of relatively modest periods of usage and disusage throughout the world; however, today it is seeing increasing popularity and proposed implementation as a method of proportional representation and a goal of electoral reform. STV has been used in many different local, regional and national electoral systems, as well as in various other types of bodies, around the world.
Instant-runoff voting (IRV) is a ranked voting method used in single-winner elections. IRV is also known outside the US as the alternative vote (AV). Today it is in use at a national level to elect the Australian House of Representatives, the National Parliament of Papua New Guinea, the President of Ireland and President of India. In Australia it is also used for elections to the legislative assemblies of all states and territories except Tasmania and the Australian Capital Territory, and for the Tasmanian Legislative Council.
The Politics of British Columbia involve not only the governance of British Columbia, Canada, and the various political factions that have held or vied for legislative power, but also a number of experiments or attempts at political and electoral reform.

The 2009 British Columbia general election was held on May 12, 2009, to elect members of the Legislative Assembly in the Canadian province of British Columbia. The British Columbia Liberal Party formed the government of the province prior to this general election under the leadership of Premier Gordon Campbell. The British Columbia New Democratic Party under the leadership of Carole James was the Official Opposition.
Geoff Plant, is a Canadian lawyer and retired politician known for his interest in citizen's legal and electoral rights and aboriginal rights. He was a member of the Legislative Assembly (MLA) of British Columbia, representing Richmond-Steveston from 1996 to 2005. A caucus member of the British Columbia Liberal Party, he served in the cabinet of Premier Gordon Campbell as Attorney General and Minister Responsible for Treaty Negotiations from 2001 to 2005.

Anita Mae Joan Hagen was a Canadian politician who represented the riding of New Westminster in the Legislative Assembly of British Columbia from 1986 to 1996. As part of the British Columbia New Democratic Party caucus, she served as the province's Deputy Premier, Minister of Education, and Minister Responsible for Multiculturalism and Human Rights from 1991 to 1993.
Electoral reform is a change in electoral systems which alters how public desires are expressed in election results.
Bill Tieleman is a lobbyist and former NDP political strategist in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. He is known for opposing the 2009 referendum on electoral reform, and the 2018 referendum on whether to hold a second vote to choose a proportional voting system. Tieleman is also known for strongly advocating hydraulic fracturing to extract methane for export from British Columbia, and for denying the role of global warming in forest fires. Tieleman supported the Site C dam and opposed the 2017 confidence and supply agreement between the BC Green caucus and BC NDP caucus under leader John Horgan, which gave Horgan a legislative majority to become premier.

A referendum on electoral reform took place by mail-in ballot between October 22 and December 7, 2018, in the Canadian province of British Columbia. 61.3 percent of voters supported maintaining the first-past-the-post voting system rather than switching to a proportional representation voting system, which was supported by 38.7 percent of voters. This was British Columbia's third referendum on electoral reform, following ones in 2005 and 2009.
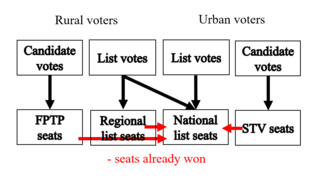
Rural–urban proportional representation (RUP), also called flexible district PR, is a supermixed electoral system which combines the use of single- and multi-member constituencies in a lower tier and top-up seats in an upper tier to meet the different needs of both rural and urban areas, while protecting the objective of proportionality. The term was coined by Fair Vote Canada, which devised a rural–urban system with the intention of meeting the special challenges of Canada's geography, which includes wide-flung, sparsely populated areas.
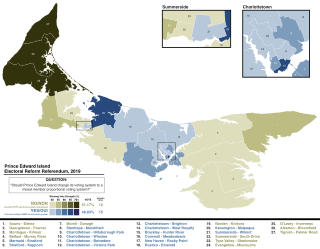
A referendum on electoral reform was held on April 23, 2019, in the Canadian province of Prince Edward Island – simultaneously with the 2019 provincial election – to determine if the province should adopt a mixed-member proportional representation voting system (MMP). A narrow majority voted to keep the existing first-past-the-post system. However, the referendum was not binding, as neither the yes or no side received majority support in 60% or more of the province's 27 electoral districts.









