Intense Tropical Cyclone Leon–Eline was the second longest-lived cyclone in the Indian Ocean, behind Cyclone Freddy, traveling over 11,000 km (6,800 mi) during its 29-day track through the Indian Ocean, throughout the month of February. The cyclone formed on 1 February 2000, in the Australian basin as Tropical Cyclone Leon, and was renamed Eline after crossing 90° E into the South-West Indian Ocean; there, the Météo-France office in Réunion (MFR) tracked the storm's movement and intensity. Late on 17 February, Eline made landfall near Mahanoro, Madagascar, with 10‑minute winds of 165 km/h (103 mph). The storm rapidly weakened over land, but restrengthened in the Mozambique Channel to reach peak 10‑minute winds of 185 km/h (115 mph), making it an intense tropical cyclone. On 22 February, Eline made landfall about 80 km (50 mi) south of Beira, Mozambique, near peak intensity. Eline quickly weakened over land as it moved across Southern Africa, finally dissipating over eastern Namibia on 29 February.

The 1999–2000 South-West Indian Ocean tropical cyclone season was the first on record in which two storms – Leon–Eline and Hudah – struck Mozambique at tropical cyclone intensity, or with maximum sustained winds of at least 120 km/h (75 mph). The most notable storm of the season was Eline, which was the third longest-lasting storm on record in the basin. It lasted for 29 days while traversing the southern Indian Ocean, making the strongest landfall in decades along eastern Madagascar in late February. The storm was the first in a series of three storms that struck the country in early 2000, along with Gloria in March and Hudah in April. Collectively, the three storms killed at least 316 people. The season started on November 1, 1999, and ended for most of the basin on April 30, 2000; for Mauritius and the Seychelles, the season continued until May 15. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the basin.

The 2011–12 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season was a slightly above average event in tropical cyclone formation. It began on November 15, 2011, and ended on April 30, 2012, with the exception for Mauritius and the Seychelles, for which it ended on May 15, 2012. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the region; however, Severe Tropical Storm Kuena developed in early June, after the season had officially ended. The basin is defined as the area west of 90°E and south of the Equator in the Indian Ocean, which includes the waters around Madagascar westward to the east coast of Africa. Tropical cyclones in this basin are monitored by the Regional Specialised Meteorological Centre in Réunion.

Severe Tropical Storm Domoina in 1984 caused 100-year floods in South Africa and record rainfall in Swaziland. The fourth named storm of the season, Domoina developed on January 16 off the northeast coast of Madagascar. With a ridge to the north, the storm tracked generally westward and later southwestward. On January 21, Domoina struck eastern Madagascar, the third storm in six weeks to affect the nation; collectively, the storms caused 242 deaths and $25 million in damage (1984 USD). After crossing the country, Domoina strengthened in the Mozambique Channel to peak 10-minute sustained winds of 95 km/h (60 mph). On January 28, the storm made landfall in southern Mozambique, and slowly weakened over land. Domoina crossed into Swaziland and later eastern South Africa before dissipating on February 2.
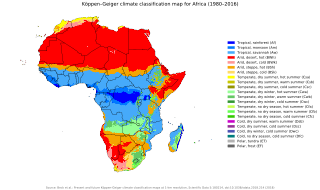
The climate of Africa is a range of climates such as the equatorial climate, the tropical wet and dry climate, the tropical monsoon climate, the semi-arid climate, the desert climate, the humid subtropical climate, and the subtropical highland climate. Temperate climates are rare across the continent except at very high elevations and along the fringes. In fact, the climate of Africa is more variable by rainfall amount than by temperatures, which are consistently high. African deserts are the sunniest and the driest parts of the continent, owing to the prevailing presence of the subtropical ridge with subsiding, hot, dry air masses. Africa holds many heat-related records: the continent has the hottest extended region year-round, the areas with the hottest summer climate, the highest sunshine duration, and more.

Intense Tropical Cyclone Funso was a powerful tropical cyclone which produced flooding in Mozambique and Malawi in January 2012. It was the eighth tropical cyclone, the sixth named storm and the second tropical cyclone to form during the 2011–12 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season. Funso was also the first intense tropical cyclone since Gelane in 2010 and the first storm to affect Mozambique since Jokwe in 2008.
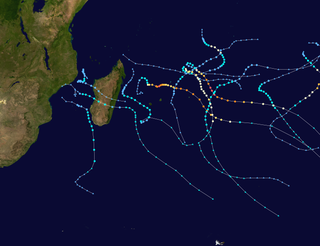
The 2014–15 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season was an above average event in tropical cyclone formation. It began on November 15, 2014, and ended on April 30, 2015, with the exception for Mauritius and the Seychelles, for which it ended on May 15, 2015. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical and subtropical cyclones form in the basin, which is west of 90°E and south of the Equator. Tropical and subtropical cyclones in this basin are monitored by the Regional Specialised Meteorological Centre in Réunion.

Severe Tropical Storm Delfina was a damaging tropical cyclone that affected southeastern Africa in January 2003. The fourth named storm of the 2002–03 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season, Delfina formed off the northwest coast of Madagascar on December 30, 2002. It quickly intensified while moving westward, becoming a strong tropical storm before hitting northeastern Mozambique on December 31. Delfina weakened while moving inland, and it was no longer classifiable as a tropical cyclone by January 1, 2003. However, its remnants moved across the country and into Malawi, later looping around and crossing back over Mozambique; the remnants of Delfina were last observed on January 9.

Severe Tropical Storm Chedza was a deadly tropical cyclone that struck Madagascar in January 2015. It formed from the Intertropical Convergence Zone and moved over Mozambique, After moving open waters, the system began organizing on January 14, becoming Tropical Storm Chedza two days later. It quickly intensified over the Mozambique Channel due to warm waters and favorable conditions, and the storm attained peak 10 minute sustained winds of 100 km/h (60 mph) on January 16. That day, Chedza moved ashore western Madagascar between Belo sur Mer and Morondava, and it quickly crossed the island while weakening. The storm briefly re-intensified, passing southwest of Réunion before turning to the southeast. Chedza became extratropical on January 19, and was last noted two days later.

During 2015, tropical cyclones formed in seven major bodies of water, commonly known as tropical cyclone basins. Tropical cyclones will be assigned names by various weather agencies if they attain maximum sustained winds of 35 knots. During the year, one hundred thirty-four systems have formed and ninety-two were named. The most intense storm of the year was Hurricane Patricia, with maximum 1-minute sustained wind speeds of 345 km/h (215 mph) and a minimum pressure of 872 hPa (25.75 inHg). The deadliest tropical cyclone was Cyclone Komen, which caused 280 fatalities in Southeast India and Bangladesh, while the costliest was Typhoon Mujigae, which caused an estimated $4.25 billion USD in damage after striking China. Forty Category 3 tropical cyclones formed, including nine Category 5 tropical cyclones in the year. The accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) index for the 2015, as calculated by Colorado State University (CSU) was 1047 units.
The 2018–2021 Southern Africa drought was a period of drought that took place in Southern Africa. The drought began in late October 2018, and negatively affected food security in the region. In mid-August 2019, the drought was classified as a level 2 Red-Class event by the Global Disaster Alert and Coordination System. The alert level was reduced to the Orange-1.7 by 12 December 2019, as the new wet season had started. In September 2020, the drought was classified as a level 2 Red-Class event. The drought continued into early 2021. Beginning in October 2021, South Africa experienced above average rainfall and reservoirs refilled by early 2022.

Intense Tropical Cyclone Idai was one of the worst tropical cyclones on record to affect Africa and the Southern Hemisphere. The long-lived storm caused catastrophic damage, and a humanitarian crisis in Mozambique, Zimbabwe, and Malawi, leaving more than 1,500 people dead and many more missing. Idai is the deadliest tropical cyclone recorded in the South-West Indian Ocean basin. In the Southern Hemisphere, which includes the Australian, South Pacific, and South Atlantic basins, Idai ranks as the second-deadliest tropical cyclone on record. The only system with a higher death toll is the 1973 Flores cyclone that killed 1,650 off the coast of Indonesia.

At least 30 tropical cyclones have affected the Southern African mainland. Three southeastern African countries border the Indian Ocean – Tanzania, Mozambique, and South Africa. Other inland countries also experience the effects of tropical cyclones, including Botswana, Eswatini, Lesotho, Malawi, Namibia, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.

Tropical Cyclone Eloise was the strongest tropical cyclone to impact the country of Mozambique since Cyclone Kenneth in 2019 and the second of three consecutive tropical cyclones to impact Mozambique in the 2020–21 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season. The seventh tropical depression, fifth named storm and the second tropical cyclone of the season, Eloise's origins can be traced to a disturbance over the central portion of the South-West Indian Ocean basin which developed into a tropical depression on 16 January, and strengthened into a tropical storm on 17 January, though the storm had limited strength and organization. On the next day, the storm entered a more favorable environment, and it soon intensified to a severe tropical storm on 18 January. Late on 19 January, Eloise made landfall in northern Madagascar as a moderate tropical storm, bringing with it heavy rainfall and flooding. The storm traversed Madagascar and entered the Mozambique Channel in the early hours of 21 January. After moving southwestward across the Mozambique Channel for an additional 2 days, Eloise strengthened into a Category 1-equivalent cyclone, due to low wind shear and high sea surface temperatures. Early on 23 January, Eloise peaked as a Category 2-equivalent tropical cyclone on the Saffir–Simpson scale as the center of the storm began to move ashore in Mozambique. Shortly afterward, Eloise made landfall just north of Beira, Mozambique, before rapidly weakening. Subsequently, Eloise weakened into a remnant low over land on 25 January, dissipating soon afterward.

Severe Tropical Storm Ana was a deadly tropical cyclone that affected the African nations of Madagascar, Malawi and Mozambique and was the third-deadliest tropical cyclone in 2022, after the Western Pacific Tropical Storm Megi and Atlantic Hurricane Ian. The first named storm of the 2021–22 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season, Ana developed from an area of convection that was designated as Invest 93S northeast of Madagascar.

The following is a list of weather events that occurred on Earth in 2015. There were several natural disasters around the world from various types of weather, including blizzards, cold waves, droughts, heat waves, tornadoes, and tropical cyclones.

Throughout 2022, floods affected most of Africa, killing over 2,100 people. The worst affected country was Nigeria, with over 610 deaths.

The following is a list of weather events that occurred on Earth in the year 2023. The year saw a transition from La Niña to El Niño, with record high global average surface temperatures. The several weather events which had a significant impact were blizzards, cold waves, droughts, heat waves, wildfires, floods, tornadoes, and tropical cyclones.
From February to late-December 2023, floods killed over 2,600 people in 15 countries across Africa.