
The first fully democratic Presidential election since 1960 occurred on 11 March 2007. The election was the final transfer from military to civilian rule following the military coup in 2005. This was the first time the president was selected by ballot in the country's history. The election was won by Sidi Ould Cheikh Abdallahi, who was ousted by a military coup in 2008 and replaced by general Mohamed Ould Abdel Aziz.
Switzerland elects on national level a collective head of state, the Federal Council, and a legislature, the Federal Assembly.
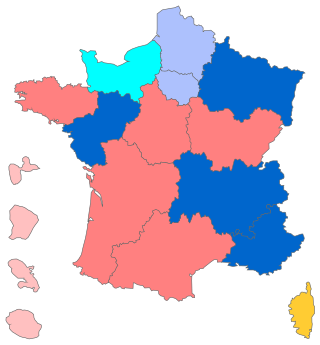
A regional council is the elected assembly of a region of France.

The National Assembly is the unicameral legislative house of the Parliament of Mauritania. The legislature currently has 157 members, elected for five-year terms in electoral districts or nationwide proportional lists.

Sidi Mohamed Ould Cheikh Abdallahi was a Mauritanian politician who was President of Mauritania from 2007 to 2008. He served in the government during the 1970s, and after a long period of absence from politics he won the March 2007 presidential election, taking office on 19 April 2007. He was deposed in a military coup d'état on 6 August 2008.

The Council of Paris is the deliberative body responsible for governing Paris, the capital of France. It possesses both the powers of a municipal council and those of a departmental council for the département de Paris, as defined by the so-called PLM Law of 1982 that redefined the governance of Paris, Lyon and Marseille. Paris is the only territorial collectivity in France to be both a commune and a département.

The 2008 Mauritanian coup d'état was a military coup that took place in Mauritania on August 6, 2008, when President Sidi Ould Cheikh Abdallahi was ousted from power by the Armed Forces of Mauritania, led by a group of high-ranking generals he had dismissed from office earlier that day.

Mohamed Ould Abdel Aziz is a former Mauritanian politician who was the 8th President of Mauritania, in office from 2009 to 2019. A career soldier and high-ranking officer, he was a leading figure in the August 2005 coup that deposed President Maaouya Ould Sid'Ahmed Taya, and in August 2008 he led another coup, which toppled President Sidi Ould Cheikh Abdallahi. Following the 2008 coup, Abdel Aziz became President of the High Council of State as part of what was described as a political transition leading to a new election. He resigned from that post in April 2009 in order to stand as a candidate in the July 2009 presidential election, which he won. He was sworn in on 5 August 2009. He was subsequently re-elected in 2014, then did not seek re-election in 2019. He was succeeded by Mohamed Ould Ghazouani, who assumed office on 1 August 2019.

Presidential elections were held in Mauritania on 18 July 2009. Mohamed Ould Abdel Aziz, who led the 2008 coup d'état, won a narrow first-round majority in the election, according to official results. A second round, if necessary, would have been held on 1 August 2009.

Parliamentary elections were held in Mauritania on 23 November. The opposition has vowed to boycott the election unless the president steps down beforehand. A total of 1,096 candidates have registered to compete for the leadership of 218 local councils across Mauritania, whilst 438 candidates are contesting for the 146 parliamentary seats. Some 1.2 million Mauritanians were eligible to vote in the election. The first round results yielded a landslide victory for the ruling UPR winning 56 seats and their 14 coalition partners winning 34 seats. The Islamist Tewassoul party won 12 seats. The remaining seats were contested in a runoff on 21 December 2013. The UPR won the majority with 75 seats in the Assembly.

Presidential elections were held in Mauritania on 21 June 2014, with a second round planned for 5 July if no candidate received more than 50% of the vote. The result was a first round victory for incumbent President Mohamed Ould Abdel Aziz of the Union for the Republic, who received 82% of the vote. Most of the opposition parties boycotted the election.

Fatimatou Mint Abdel Malick is a Mauritanian politician who has served as mayor of Tevragh-Zeina since 2001. She was the first woman in her country to hold the position of mayor. From 2012 to 2015 she served as president of The Network for Locally Elected Women of Africa (REFELA).
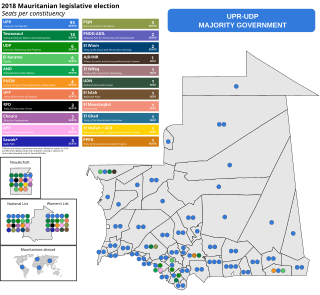
Parliamentary elections was held in Mauritania in September 2018; the first round took place on 1 September, with a second round held on 15 September. At the national level, elections were held in 157 constituencies, each electing one member to the National Assembly. Elections were also held in 13 regional councils and 219 municipalities.

Presidential elections were held in Mauritania on 22 June 2019, with a second round planned for 6 July if no candidate had received more than 50% of the vote. The result was a first round victory for Mohamed Ould Ghazouani who won with 52 percent of the vote. However, opposition rejected the results, calling it "another army coup." On 1 July 2019, Mauritania's constitutional council confirmed Ghazouani as president and rejected a challenge by opposition.

Parliamentary elections will be held in Mauritania on 13 and 27 May 2023, alongside regional and local elections.

Mauritania is divided into several electoral districts for the election of deputies to the National Assembly, based on the departments of the country. The city of Nouakchott is treated as a single department for election purposes.

Hope Mauritania is a coalition of several political movements in Mauritania with the intention of running in the upcoming 2023 parliamentary, regional and local elections.

Regional elections will be held in Mauritania on 13 May 2023, alongside parliamentary and local elections.

Regional elections were held in Mauritania on 1 and 15 September 2023, alongside parliamentary and local elections. They were the first elections to the newly created regional councils.
Regional elections will be held on 13 May 2023 to elect the 37 members of the Regional Council of Nouakchott, as part of the 2023 Mauritanian regional elections.


















