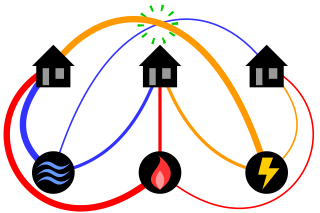
The classical mathematical puzzle known as the three utilities problem or sometimes water, gas and electricity asks for non-crossing connections to be drawn between three houses and three utility companies in the plane. When posing it in the early 20th century, Henry Dudeney wrote that it was already an old problem. It is an impossible puzzle: it is not possible to connect all nine lines without crossing. Versions of the problem on nonplanar surfaces such as a torus or Möbius strip, or that allow connections to pass through other houses or utilities, can be solved.
A sigmatropic reaction in organic chemistry is a pericyclic reaction wherein the net result is one σ-bond is changed to another σ-bond in an uncatalyzed intramolecular reaction. The name sigmatropic is the result of a compounding of the long-established sigma designation from single carbon–carbon bonds and the Greek word tropos, meaning turn. In this type of rearrangement reaction, a substituent moves from one part of a π-bonded system to another part in an intramolecular reaction with simultaneous rearrangement of the π system. True sigmatropic reactions are usually uncatalyzed, although Lewis acid catalysis is possible. Sigmatropic reactions often have transition-metal catalysts that form intermediates in analogous reactions. The most well-known of the sigmatropic rearrangements are the [3,3] Cope rearrangement, Claisen rearrangement, Carroll rearrangement, and the Fischer indole synthesis.
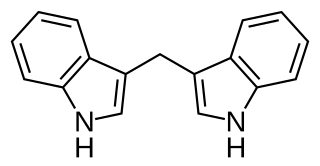
3,3′-Diindolylmethane (DIM) is a compound derived from the digestion of indole-3-carbinol, found in cruciferous vegetables, such as broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cabbage and kale. It and its parent compound – indole-3-carbinol – are under laboratory research to determine their possible biological properties, particularly in anti-cancer mechanisms. DIM is sold as a dietary supplement.

Benzidine (trivial name), also called 1,1'-biphenyl-4,4'-diamine (systematic name), is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4NH2)2. It is an aromatic amine. It is a component of a test for cyanide. Related derivatives are used in the production of dyes. Benzidine has been linked to bladder and pancreatic cancer.

Thyroxine 5-deiodinase also known as type III iodothyronine deiodinase (EC number 1.21.99.3) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DIO3 gene. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Reverse triiodothyronine (3,3′,5′-triiodothyronine, reverse T3, or rT3) is an isomer of triiodothyronine (3,5,3′ triiodothyronine, T3).
Diiodothyronine may refer to:
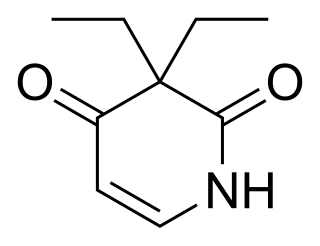
Pyrithyldione is a psychoactive drug invented in 1949. An improved method of manufacture was patented by Roche in 1959. It was used as a hypnotic or sedative and presumed to be less toxic than barbiturates. Today, this substance is no longer used. Agranulocytosis was sometimes reported as adverse effect. Pyrithyldione is also a CYP2D6 inducer but is not as potent as glutethimide. In studies, it increased the O-demethylation of codeine by 20%.

2-MDP (U-23807A) is a dissociative anaesthetic drug which has been found to be an NMDA antagonist and produces similar effects to PCP in animals. The levo or (−)-isomer is the active form of the drug. It also has stimulant effects, having only around one third the potency of amphetamine by weight, but with a long duration of action, lasting more than 24 hours from a single oral dose.

3,3'-Dichlorobenzidine is an organic compound with the formula (C6H3Cl(NH2))2. The pure compound is pale yellow, but commercial samples are often colored. It is barely soluble in water and is often supplied as a wet paste. It is widely used in the production of diarylide yellow pigments used in the production of printing inks. Its use in the production of dyes has been largely discontinued because of concerns about carcinogenicity.

3-Iodotyrosine is an intermediate in the synthesis of thyroid hormones which is derived from iodination of tyrosine at the meta-position of the benzene ring. One unit can combine with diiodotyrosine to form triiodothyronine, as occurs in the colloid of the thyroid follicle. Two units can combine to form 3,3'-diiodothyronine.

3,3,-Diphenylcyclobutanamine is a psychostimulant drug which was originally prepared as an antidepressant in the late 1970s. It appears to inhibit the reuptake of serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, and may also induce their release as well. The N-methyl and N,N-dimethyl analogues of the compound are also known and are more potent. All three agents produce locomotor stimulation in animal studies, with the tertiary amine being the strongest.

3-Benzhydrylmorpholine is a drug that was developed by American Home Products in the 1950s. It has stimulant and anorectic effects and is related to both pipradrol and phenmetrazine.

In geometry, Coxeter notation is a system of classifying symmetry groups, describing the angles between fundamental reflections of a Coxeter group in a bracketed notation expressing the structure of a Coxeter-Dynkin diagram, with modifiers to indicate certain subgroups. The notation is named after H. S. M. Coxeter, and has been more comprehensively defined by Norman Johnson.

Hexapradol (INN) is a psychostimulant drug which was never marketed.
Diarylide pigments are organic compounds that are used as pigments in inks and related materials. They often are yellow or yellow-green. To some extent, these organic compounds have displaced cadmium sulfide from the market. They exist as yellow powders of low solubility in water.

3,5-Diiodothyronine (3,5-T2) is an active thyroid hormone within the class of iodothyronines. It has two iodine atoms at positions 3 and 5 of its inner ring.
The molecular formula C15H13I2NO4 (molar mass: 525.08 g/mol) may refer to:
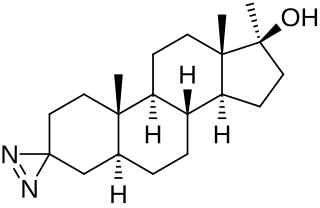
Methyldiazinol is a synthetic and orally active androgen/anabolic steroid (AAS) which was never marketed. It is a 17α-methylated derivative of dihydrotestosterone (DHT); specifically, it is the C3 azi analogue of mestanolone (17α-methyl-DHT). The drug has been found to possess a high ratio and dissociation of myotrophic to androgenic activity; relative to methyltestosterone, its ratio was 15 (3:0.2), among the highest observed.
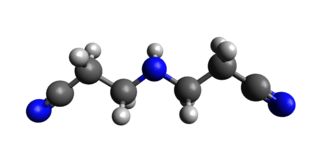
IDPN (3,3'-iminodipropanenitrile) is a neurotoxin with ototoxic and hepatotoxic effects. It causes irreversible movement disorder.


















