Related Research Articles
The enzyme cystathionine γ-lyase (EC 4.4.1.1, CTH or CSE; also cystathionase; systematic name L-cystathionine cysteine-lyase (deaminating; 2-oxobutanoate-forming)) breaks down cystathionine into cysteine, 2-oxobutanoate (α-ketobutyrate), and ammonia:

The transsulfuration pathway is a metabolic pathway involving the interconversion of cysteine and homocysteine through the intermediate cystathionine. Two transsulfurylation pathways are known: the forward and the reverse.
Alanine dehydrogenase (EC 1.4.1.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme carbamoyl-serine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.13) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme cysteine-S-conjugate β-lyase (EC 4.4.1.13) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme D-cysteine desulfhydrase (EC 4.4.1.15) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme diaminopropionate ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.15) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme D-serine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.18), with systematic name D-serine ammonia-lyase (pyruvate-forming), catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme Glucosaminate ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.9) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme homocysteine desulfhydrase (EC 4.4.1.2) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme L-2-amino-4-chloropent-4-enoate dehydrochlorinase (EC 4.5.1.4) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme L-cysteate sulfo-lyase (EC 4.4.1.25) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme L-serine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.17) catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme methionine γ-lyase (EC 4.4.1.11, MGL) is in the γ-family of PLP-dependent enzymes. It degrades sulfur-containing amino acids to α-keto acids, ammonia, and thiols:
The enzyme S-carboxymethylcysteine synthase catalyzes the reaction

Threonine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.19, systematic name L-threonine ammonia-lyase (2-oxobutanoate-forming), also commonly referred to as threonine deaminase or threonine dehydratase, is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing the conversion of L-threonine into α-ketobutyrate and ammonia:
The enzyme 4-(2-carboxyphenyl)-2-oxobut-3-enoate aldolase (EC 4.1.2.34) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme tryptophanase (EC 4.1.99.1) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme tyrosine phenol-lyase (EC 4.1.99.2) catalyzes the chemical reaction
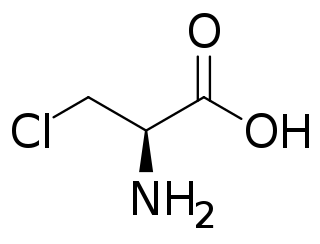
Chloroalanine (3-chloroalanine) is an unnatural amino acid with the formula ClCH2CH(NH2)CO2H. It is a white, water-soluble solid. The compound is usually derived from chlorination of serine. The compound is used in the synthesis of other amino acids by replacement of the chloride. Protected forms of the related iodoalanine are also known.
References
- Nagasawa T, Ishii T, Yamada H (1988). "Physiological comparison of D-cysteine desulfhydrase of Escherichia coli with 3-chloro-D-alanine dehydrochlorinase of Pseudomonas putida CR 1-1". Archives of Microbiology. 149 (5): 413–6. doi:10.1007/BF00425580. PMID 3132906.
- Yamada H, Nagasawa T, Ohkishi H, Kawakami B, Tani Y (June 1981). "Synthesis of D-cysteine from 3-chloro-D-alanine and hydrogen sulfide by 3-chloro-D-alanine hydrogen chloride-lyase (deaminating) of Pseudomonas putida". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 100 (3): 1104–10. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(81)91937-9. PMID 6791643.