Fentanyl is a highly potent synthetic piperidine opioid primarily used as an analgesic. It is 30 to 50 times more potent than heroin and 100 times more potent than morphine; its primary clinical utility is in pain management for cancer patients and those recovering from painful surgeries. Fentanyl is also used as a sedative. Depending on the method of delivery, fentanyl can be very fast acting and ingesting a relatively small quantity can cause overdose. Fentanyl works by activating μ-opioid receptors. Fentanyl is sold under the brand names Actiq, Duragesic, and Sublimaze, among others.

Lysergic acid, also known as D-lysergic acid and (+)-lysergic acid, is a precursor for a wide range of ergoline alkaloids that are produced by the ergot fungus and found in the seeds of Turbina corymbosa (ololiuhqui), Argyreia nervosa, and Ipomoea tricolor.

Alfentanil (R-39209), sold under the brand name Alfenta among others, is a potent but short-acting synthetic opioid analgesic drug used for anesthesia in surgery. It is an analogue of fentanyl with around one-fourth to one-tenth the potency, one-third the duration of action, and an onset of action four times faster than that of fentanyl. Alfentanil has a pKa of approximately 6.5, which leads to a very high proportion of the drug being uncharged at physiologic pH, a characteristic responsible for its rapid-onset. It is an agonist of the μ-opioid receptor.

Piperonal, also known as heliotropin, is an organic compound which is commonly found in fragrances and flavors. The molecule is structurally related to other aromatic aldehydes such as benzaldehyde and vanillin.

Dipipanone, sold under the brand names of Pipadone and Diconal is a strong opioid analgesic drug, used for acute pain by mouth (PO) for adults. It is often used in instances where morphine is indicated but cannot be used due to the patient being allergic to morphine. In analgesic potency 25 mg dipipanone is approximately equivalent to 10 mg morphine.

Dextromoramide is a powerful opioid analgesic approximately three times more potent than morphine but shorter acting. It is subject to drug prohibition regimes, both internationally through UN treaties and by the criminal law of individual nations, and is usually prescribed only in the Netherlands.

Aminorex is a weight loss (anorectic) stimulant drug. It was withdrawn from the market after it was found to cause pulmonary hypertension. In the U.S., it is an illegal Schedule I drug, meaning it has high abuse potential, no accepted medical use, and a poor safety profile.

Etonitazene, also known as EA-4941 or CS-4640, is a benzimidazole opioid, first reported in 1957, that has been shown to have approximately 1,000 to 1,500 times the potency of morphine in animals.

Phenoperidine, is an opioid analgesic which is structurally related to pethidine and is used clinically as a general anesthetic.

Piritramide(R-3365, trade names Dipidolor, Piridolan, Pirium and others) is a synthetic opioid analgesic that is marketed in certain European countries including: Austria, Belgium, Czech Republic, Slovenia, Germany and the Netherlands. It comes in free form, is about 0.75x times as potent as morphine and is given parenterally for the treatment of severe pain. Nausea, vomiting, respiratory depression and constipation are believed to be less frequent with piritramide than with morphine, and it produces more rapid-onset analgesia when compared to morphine and pethidine. After intravenous administration the onset of analgesia is as little as 1–2 minutes, which may be related to its great lipophilicity. The analgesic and sedative effects of piritramide are believed to be potentiated with phenothiazines and its emetic (nausea/vomiting-inducing) effects are suppressed. The volume of distribution is 0.7-1 L/kg after a single dose, 4.7-6 L/kg after steady-state concentrations are achieved and up to 11.1 L/kg after prolonged dosing.

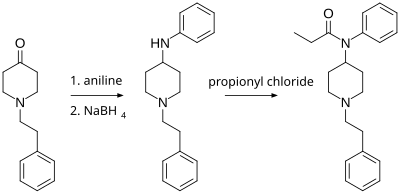
N-Phenethyl-4-piperidinone (NPP) is a derivative of 4-piperidinone with the molecular formula C13H17NO. It is used as an intermediate in the manufacture of chemicals and pharmaceutical drugs such as fentanyl.

Diampromide is an opioid analgesic from the ampromide family of drugs, related to other drugs such as propiram and phenampromide. It was invented in the 1960s by American Cyanamid, and can be described as a ring-opened analogue of fentanyl.
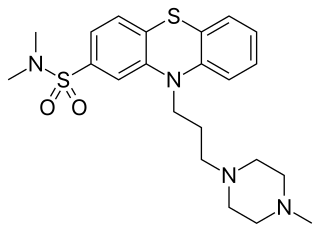
Thioproperazine, sold under the brand name Majeptil, is a typical antipsychotic of the phenothiazine group which is used as a tranquilizer, antiemetic, sedative, and in the treatment of schizophrenia and manic phase of bipolar disorder. Majeptil is available in 10 mg tablets.
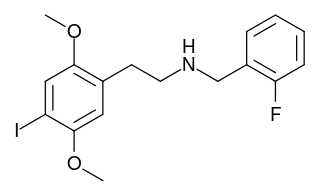
25I-NBF is a derivative of the phenethylamine hallucinogen 2C-I, which acts as a highly potent partial agonist for the human 5-HT2A receptor, with bias towards the β-arrestin 2 coupled signalling pathway. It has been studied in its 11C radiolabelled form as a potential ligand for mapping the distribution of 5-HT2A receptors in the brain, using positron emission tomography (PET).
Drug precursors, also referred to as precursor chemicals or simply precursors, are substances used to manufacture illicit drugs. Most precursors also have legitimate commercial uses and are legally used in a wide variety of industrial processes and consumer products, such as medicines, flavourings, and fragrances.

Acetylfentanyl is an opioid analgesic drug that is an analog of fentanyl. Studies have estimated acetylfentanyl to be 15 times more potent than morphine, which would mean that despite being somewhat weaker than fentanyl, it is nevertheless still several times stronger than pure heroin. It has never been licensed for medical use and instead has only been sold on the illicit drug market. Acetylfentanyl was discovered at the same time as fentanyl itself and had only rarely been encountered on the illicit market in the late 1980s. However, in 2013, Canadian police seized 3 kilograms of acetylfentanyl. As a μ-opioid receptor agonist, acetylfentanyl may serve as a direct substitute for oxycodone, heroin or other opioids. Common side effects of fentanyl analogs are similar to those of fentanyl itself, which include itching, nausea, and potentially fatal respiratory depression. Fentanyl analogs have killed hundreds of people throughout Europe and the former Soviet republics since the most recent resurgence in use began in Estonia in the early 2000s, and novel derivatives continue to appear.
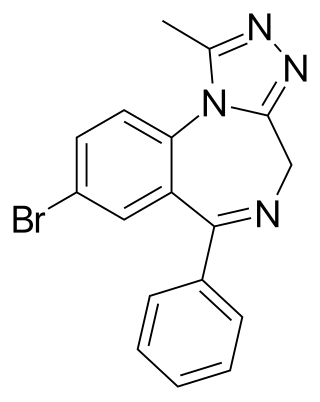
Bromazolam (XLI-268) is a triazolobenzodiazepine (TBZD) which was first synthesised in 1976, but was never marketed. It has subsequently been sold as a designer drug, first being definitively identified by the EMCDDA in Sweden in 2016. It is the bromo instead of chloro analogue of alprazolam and has similar sedative and anxiolytic effects to it and other benzodiazepines. Bromazolam is a non subtype selective agonist at the benzodiazepine site of GABAA receptors, with a binding affinity of 2.81 nM at the α1 subtype, 0.69 nM at α2 and 0.62 nM at α5. The "common" dosage range for users of bromazolam was reported to be 1–2 mg, suggesting its potency is similar to alprazolam.

Hydroxyphenamate or oxyfenamate is a sedative and anxiolytic drug of the carbamate class which is no longer marketed in the US. Like other carbamate sedatives, it is chemically related to meprobamate (Miltown). It was introduced to the US market in 1961. The dosage for adults is 200 mg 3 to 4 times daily.

Norfentanyl is an inactive synthetic opioid analgesic drug precursor. It is an analog and metabolite of fentanyl with the removal of the phenethyl moiety from fentanyl chemical structure.