
A sphere is a geometrical object that is a three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. Formally, a sphere is the set of points that are all at the same distance r from a given point in three-dimensional space. That given point is the center of the sphere, and r is the sphere's radius. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the ancient Greek mathematicians.

In mathematics, a spherical coordinate system is a coordinate system for three-dimensional space where the position of a given point in space is specified by three numbers, : the radial distance of the radial liner connecting the point to the fixed point of origin ; the polar angle θ of the radial line r; and the azimuthal angle φ of the radial line r.
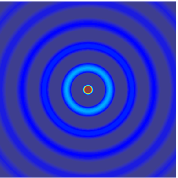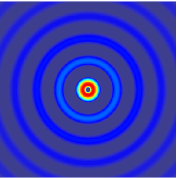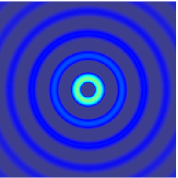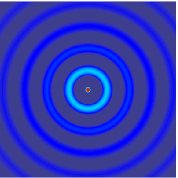
The wave equation is a second-order linear partial differential equation for the description of waves or standing wave fields such as mechanical waves or electromagnetic waves. It arises in fields like acoustics, electromagnetism, and fluid dynamics.

In mathematics and physics, Laplace's equation is a second-order partial differential equation named after Pierre-Simon Laplace, who first studied its properties. This is often written as

In mathematics, an n-sphere or hypersphere is an n-dimensional generalization of the 1-dimensional circle and 2-dimensional sphere to any non-negative integer n. The n-sphere is the setting for n-dimensional spherical geometry.

The Navier–Stokes equations are partial differential equations which describe the motion of viscous fluid substances. They were named after French engineer and physicist Claude-Louis Navier and the Irish physicist and mathematician George Gabriel Stokes. They were developed over several decades of progressively building the theories, from 1822 (Navier) to 1842–1850 (Stokes).
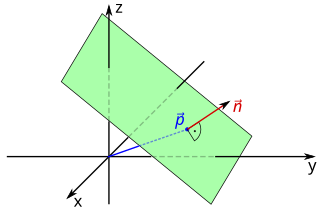
In Euclidean geometry, a plane is a flat two-dimensional surface that extends indefinitely. Euclidean planes often arise as subspaces of three-dimensional space . A prototypical example is one of a room's walls, infinitely extended and assumed infinitesimal thin. While a pair of real numbers suffices to describe points on a plane, the relationship with out-of-plane points requires special consideration for their embedding in the ambient space .
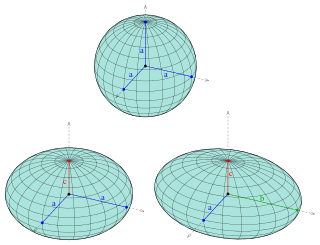
An ellipsoid is a surface that can be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation.
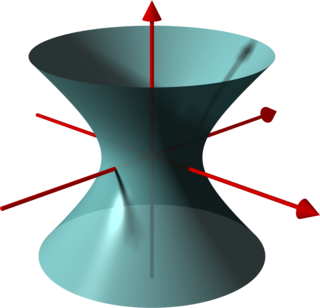
In geometry, a hyperboloid of revolution, sometimes called a circular hyperboloid, is the surface generated by rotating a hyperbola around one of its principal axes. A hyperboloid is the surface obtained from a hyperboloid of revolution by deforming it by means of directional scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation.
In mathematics, the Laplace operator or Laplacian is a differential operator given by the divergence of the gradient of a scalar function on Euclidean space. It is usually denoted by the symbols , (where is the nabla operator), or . In a Cartesian coordinate system, the Laplacian is given by the sum of second partial derivatives of the function with respect to each independent variable. In other coordinate systems, such as cylindrical and spherical coordinates, the Laplacian also has a useful form. Informally, the Laplacian Δf (p) of a function f at a point p measures by how much the average value of f over small spheres or balls centered at p deviates from f (p).
The primitive equations are a set of nonlinear partial differential equations that are used to approximate global atmospheric flow and are used in most atmospheric models. They consist of three main sets of balance equations:
- A continuity equation: Representing the conservation of mass.
- Conservation of momentum: Consisting of a form of the Navier–Stokes equations that describe hydrodynamical flow on the surface of a sphere under the assumption that vertical motion is much smaller than horizontal motion (hydrostasis) and that the fluid layer depth is small compared to the radius of the sphere
- A thermal energy equation: Relating the overall temperature of the system to heat sources and sinks

In quantum mechanics, a spherically symmetric potential is a system of which the potential only depends on the radial distance from the spherical center and a location in space. A particle in a spherically symmetric potential will behave accordingly to said potential and can therefore be used as an approximation, for example, of the electron in a hydrogen atom or of the formation of chemical bonds.
In analytical mechanics, generalized coordinates are a set of parameters used to represent the state of a system in a configuration space. These parameters must uniquely define the configuration of the system relative to a reference state. The generalized velocities are the time derivatives of the generalized coordinates of the system. The adjective "generalized" distinguishes these parameters from the traditional use of the term "coordinate" to refer to Cartesian coordinates.

In mathematics, a Dupin cyclide or cyclide of Dupin is any geometric inversion of a standard torus, cylinder or double cone. In particular, these latter are themselves examples of Dupin cyclides. They were discovered c. 1802 by Charles Dupin, while he was still a student at the École polytechnique following Gaspard Monge's lectures. The key property of a Dupin cyclide is that it is a channel surface in two different ways. This property means that Dupin cyclides are natural objects in Lie sphere geometry.
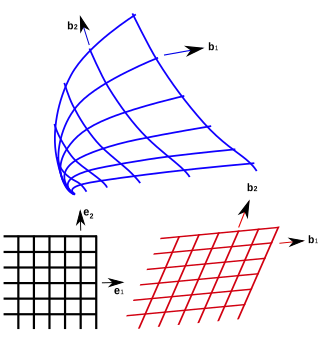
In geometry, curvilinear coordinates are a coordinate system for Euclidean space in which the coordinate lines may be curved. These coordinates may be derived from a set of Cartesian coordinates by using a transformation that is locally invertible at each point. This means that one can convert a point given in a Cartesian coordinate system to its curvilinear coordinates and back. The name curvilinear coordinates, coined by the French mathematician Lamé, derives from the fact that the coordinate surfaces of the curvilinear systems are curved.

In geometry, a three-dimensional space is a mathematical space in which three values (coordinates) are required to determine the position of a point. Most commonly, it is the three-dimensional Euclidean space, that is, the Euclidean space of dimension three, which models physical space. More general three-dimensional spaces are called 3-manifolds. The term may also refer colloquially to a subset of space, a three-dimensional region, a solid figure.
In mathematics, orthogonal coordinates are defined as a set of d coordinates in which the coordinate hypersurfaces all meet at right angles (note that superscripts are indices, not exponents). A coordinate surface for a particular coordinate qk is the curve, surface, or hypersurface on which qk is a constant. For example, the three-dimensional Cartesian coordinates (x, y, z) is an orthogonal coordinate system, since its coordinate surfaces x = constant, y = constant, and z = constant are planes that meet at right angles to one another, i.e., are perpendicular. Orthogonal coordinates are a special but extremely common case of curvilinear coordinates.
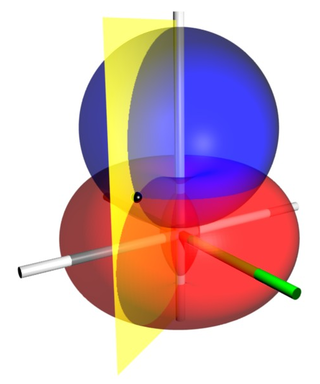
Bispherical coordinates are a three-dimensional orthogonal coordinate system that results from rotating the two-dimensional bipolar coordinate system about the axis that connects the two foci. Thus, the two foci and in bipolar coordinates remain points in the bispherical coordinate system.
In mathematics, the slow manifold of an equilibrium point of a dynamical system occurs as the most common example of a center manifold. One of the main methods of simplifying dynamical systems, is to reduce the dimension of the system to that of the slow manifold—center manifold theory rigorously justifies the modelling. For example, some global and regional models of the atmosphere or oceans resolve the so-called quasi-geostrophic flow dynamics on the slow manifold of the atmosphere/oceanic dynamics, and is thus crucial to forecasting with a climate model.
Spherical wave transformations leave the form of spherical waves as well as the laws of optics and electrodynamics invariant in all inertial frames. They were defined between 1908 and 1909 by Harry Bateman and Ebenezer Cunningham, with Bateman giving the transformation its name. They correspond to the conformal group of "transformations by reciprocal radii" in relation to the framework of Lie sphere geometry, which were already known in the 19th century. Time is used as fourth dimension as in Minkowski space, so spherical wave transformations are connected to the Lorentz transformation of special relativity, and it turns out that the conformal group of spacetime includes the Lorentz group and the Poincaré group as subgroups. However, only the Lorentz/Poincaré groups represent symmetries of all laws of nature including mechanics, whereas the conformal group is related to certain areas such as electrodynamics. In addition, it can be shown that the conformal group of the plane is isomorphic to the Lorentz group.

















