
Terpenes are a class of natural products consisting of compounds with the formula (C5H8)n for n ≥ 2. Terpenes are major biosynthetic building blocks. Comprising more than 30,000 compounds, these unsaturated hydrocarbons are produced predominantly by plants, particularly conifers. In plants, terpenes and terpenoids are important mediators of ecological interactions, while some insects use some terpenes as a form of defense. Other functions of terpenoids include cell growth modulation and plant elongation, light harvesting and photoprotection, and membrane permeability and fluidity control.
Nepetalactone is a name for multiple iridoid analog stereoisomers. Nepetalactones are produced by Nepeta cataria (catnip) and many other plants belonging to the genus Nepeta, in which they protect these plants from herbivorous insects by functioning as insect repellents. They are also produced by many aphids, in which they are sex pheromones. Nepetalactones are cat attractants, and cause the behavioral effects that catnip induces in domestic cats. However, they affect visibly only about two thirds of adult cats. They produce similar behavioral effects in many other felids, especially in lions and jaguars. In 1941, the research group of Samuel M. McElvain was the first to determine the structures of nepetalactones and several related compounds.

A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical synthesis and have played a central role in the development of the field of organic chemistry by providing challenging synthetic targets. The term natural product has also been extended for commercial purposes to refer to cosmetics, dietary supplements, and foods produced from natural sources without added artificial ingredients.

Geraniol is a monoterpenoid and an alcohol. It is the primary component of citronella oil and is a primary component of rose oil and palmarosa oil. It is a colorless oil, although commercial samples can appear yellow. It has low solubility in water, but it is soluble in common organic solvents. The functional group derived from geraniol is called geranyl.

Linalool refers to two enantiomers of a naturally occurring terpene alcohol found in many flowers and spice plants. Together with geraniol, nerol, citronellol, linalool is one of the rose alcohols. Linalool has multiple commercial applications, the majority of which are based on its pleasant scent.
Spermine is a polyamine involved in cellular metabolism that is found in all eukaryotic cells. The precursor for synthesis of spermine is the amino acid ornithine. It is an essential growth factor in some bacteria as well. It is found as a polycation at physiological pH. Spermine is associated with nucleic acids and is thought to stabilize helical structure, particularly in viruses. It functions as an intracellular free radical scavenger to protect DNA from free radical attack. Spermine is the chemical primarily responsible for the characteristic odor of semen.

Geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP), also known as geranyl diphosphate (GDP), is the pyrophosphate ester of the terpenoid geraniol. Its salts are colorless. It is a precursor to many thousands of natural products.

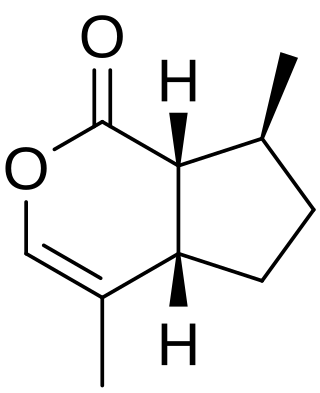
Grandisol is a natural organic compound with the molecular formula C10H18O. It is a monoterpene containing a cyclobutane ring, an alcohol group, an alkene group and two chiral centers (one of which is quaternary).
Monoterpenes are a class of terpenes that consist of two isoprene units and have the molecular formula C10H16. Monoterpenes may be linear (acyclic) or contain rings (monocyclic and bicyclic). Modified terpenes, such as those containing oxygen functionality or missing a methyl group, are called monoterpenoids. Monoterpenes and monoterpenoids are diverse. They have relevance to the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, agricultural, and food industries.

In molecular biology, this protein domain belongs to the terpene synthase family (TPS). Its role is to synthesize terpenes, which are part of primary metabolism, such as sterols and carotene, and also part of the secondary metabolism. This entry will focus on the N terminal domain of the TPS protein.
8-hydroxygeraniol dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.324, 8-hydroxygeraniol oxidoreductase, CYP76B10, G10H, CrG10H, SmG10H, acyclic monoterpene primary alcohol:NADP+ oxidoreductase) is an enzyme with systematic name (6E)-8-hydroxygeraniol:NADP+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Geranial dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.86, GaDH, geoB (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name geranial:NAD+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) synthase is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing the formation of THCA from cannabigerolic acid (CBGA). THCA is the direct precursor of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the principal psychoactive component of cannabis, which is produced from various strains of Cannabis sativa. Therefore, THCA synthase is considered to be a key enzyme controlling cannabis psychoactivity. Polymorphisms of THCA synthase result in varying levels of THC in Cannabis plants, resulting in "drug-type" and "fiber-type" C. sativa varieties.
Linalool dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.127, linalool hydro-lyase (myrcene-forming)) is an enzyme with systematic name (3S)-linalool hydro-lyase (myrcene-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
(−)-α-Pinene synthase is an enzyme with systematic name geranyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase [cyclizing, (−)-α-pinene-forming]. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Geraniol isomerase is an enzyme with systematic name geraniol hydroxymutase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Akuammicine is a monoterpene indole alkaloid of the Vinca sub-group. It is found in the Apocynaceae family of plants including Picralima nitida, Vinca minor and the Aspidosperma.

8-Oxogeranial is a chemical substance, that is a monoterpene. The terpenoid is produced by 8-hydroxygeraniol dehydrogenase which uses 8-hydroxygeraniol as its substrate. 8-Oxogeranial is itself a substrate for iridoid synthase which synthesizes cis–trans-iridodial and cis–trans-nepetalactol.

Harpagoside is a natural product found in the plant Harpagophytum procumbens, also known as devil's claw. It is the active chemical constituent responsible for the medicinal properties of the plant, which have been used for centuries by the Khoisan people of southern Africa to treat diverse health disorders, including fever, diabetes, hypertension, and various blood related diseases.
Cytochrome P450, family 76, also known as CYP76, is a cytochrome P450 family in land plants, related to the biosynthesis of many plant monoterpenes and diterpenes such as 8-hydroxygeraniol, tanshinone and alkannin. The first gene identified in this family is the CYP76A1 and CYP76A2 from the eggplant.












