
Shareaza is a peer-to-peer file sharing client running under Microsoft Windows which supports the gnutella, Gnutella2 (G2), eDonkey, BitTorrent, FTP, HTTP and HTTPS network protocols and handles magnet links, ed2k links, and the now deprecated gnutella and Piolet links. It is available in 30 languages.
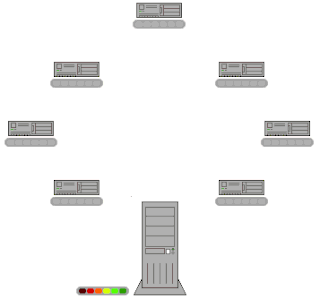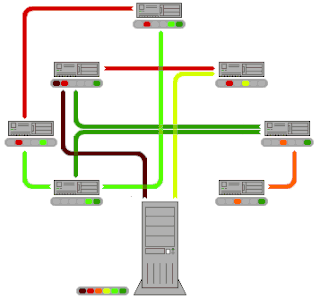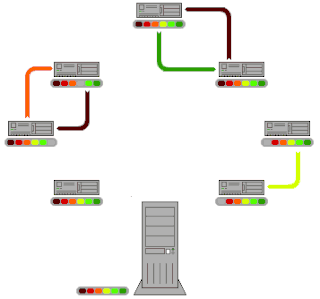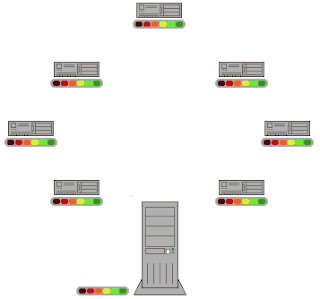
BitTorrent is a communication protocol for peer-to-peer file sharing (P2P) which is used to distribute data and electronic files over the Internet in a decentralized manner.

BitTornado is a free BitTorrent client for transfer of computer files over networks, including the Internet. It is developed by John Hoffman, who also created its predecessor, Shad0w's Experimental Client. Based on the original BitTorrent client, the interface is largely the same, with added features such as:
In file sharing, super-seeding is an algorithm developed by John Hoffman for the BitTorrent communications protocol that helps downloaders become uploaders more quickly, but it introduces the danger of total seeding failure if there is only one downloader.
BitTorrent is an ad-supported BitTorrent client developed by Bram Cohen and BitTorrent, Inc. used for uploading and downloading files via the BitTorrent protocol. BitTorrent was the first client written for the protocol. It is often nicknamed Mainline by developers denoting its official origins. Since version 6.0 the BitTorrent client has been a rebranded version of μTorrent. As a result, it is no longer open source. It is currently available for Microsoft Windows, Mac, Linux, iOS and Android.

KTorrent is a BitTorrent client that is part of the KDE Software Compilation.
TorrentFlux is a free and open source multi-user GUI for BitTornado. Unlike most BitTorrent clients, its main user interface is a web interface. It is scripted in PHP, with a MySQL database and runs on a web server.
File sharing is a method of distributing electronically stored information such as computer programs and digital media. Below is a list of file sharing applications, most of them make use of peer-to-peer file sharing technologies.

Transmission is a BitTorrent client which features a variety of user interfaces on top of a cross-platform back-end. Transmission is free software licensed under the terms of the GNU General Public License, with parts under the MIT License.

Metalink is an extensible metadata file format that describes one or more computer files available for download. It specifies files appropriate for the user's language and operating system; facilitates file verification and recovery from data corruption; and lists alternate download sources.

eMule is a free peer-to-peer file sharing application for Microsoft Windows. Started in May 2002 as an alternative to eDonkey2000, eMule now connects to both the eDonkey network and the Kad network. Often used by clients looking for extremely rare content, the distinguishing features of eMule are the direct exchange of sources between client nodes, fast recovery of corrupted downloads, and the use of a credit system to reward frequent uploaders. Furthermore, eMule transmits data in zlib-compressed form to save bandwidth.
qBittorrent is a cross-platform free and open-source BitTorrent client.
Rainberry, Inc., formerly known as BitTorrent, Inc., is an American company that is responsible for the ongoing development of the BitTorrent peer-to-peer protocol, as well as the ongoing development of μTorrent and BitTorrent Mainline, two clients for that protocol. Files transferred using the BitTorrent protocol constitute a significant slice of all Internet traffic. At its peak, 170 million people used the protocol every month, according to the company's website. The company was founded on September 22, 2004 by Bram Cohen and Ashwin Navin. In 2018, the company was acquired by cryptocurrency startup TRON, and Bram Cohen left the company.

Tribler is an open source decentralized BitTorrent client which allows anonymous peer-to-peer by default. Tribler is based on the BitTorrent protocol and uses an overlay network for content searching. Due to this overlay network, Tribler does not require an external website or indexing service to discover content. The user interface of Tribler is very basic and focused on ease of use instead of diversity of features. Tribler is available for Linux, Windows, and OS X.
The following is a general comparison of BitTorrent clients, which are computer programs designed for peer-to-peer file sharing using the BitTorrent protocol.
This is a glossary of jargon related to peer-to-peer file sharing via the BitTorrent protocol.
BitLet, abbreviation for BitTorrent Applet, was a BitTorrent program that enabled the use of this file sharing protocol inside any Java-enabled web browser, without the need of an external dedicated client program. It is open-source software under the Apache License (ASL) 2.0. Prior to December 28, 2013, it was released under the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) 2.1.
libtorrent is an open-source implementation of the BitTorrent protocol. It is written in and has its main library interface in C++. Its most notable features are support for Mainline DHT, IPv6, HTTP seeds and μTorrent's peer exchange. libtorrent uses Boost, specifically Boost.Asio to gain its platform independence. It is known to build on Windows and most Unix-like operating systems.
The usage share of BitTorrent clients is the percentage of users that use a particular BitTorrent client, regardless of version.
In the BitTorrent file distribution system, a torrent file or meta-info file is a computer file that contains metadata about files and folders to be distributed, and usually also a list of the network locations of trackers, which are computers that help participants in the system find each other and form efficient distribution groups called swarms. A torrent file does not contain the content to be distributed; it only contains information about those files, such as their names, folder structure, and sizes obtained via cryptographic hash values for verifying file integrity. The term torrent may refer either to the metadata file or to the files downloaded, depending on the context.







