Mechanical properties
| Head marking | Grade, material & condition | Nominal thread diameter size range [mm] | Proof strength [MPa] | Yield strength (min) [MPa] | Tensile strength (min) [MPa] | Core hardness [Rockwell] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Class 4.6 Low or medium carbon steel | 5–100 | 225 | 240 | 400 | B67–95 |
 | Class 4.8 Low or medium carbon steel; fully or partially annealed | 1.6–16 | 310 | 340 | 420 | B71–95 |
 | Class 5.8 Low or medium carbon steel; cold worked | 5–24 | 380 | 420 | 520 | B82–95 |
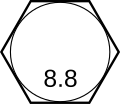 | Class 8.8 [6] Medium carbon steel; quench and tempered | Under 16 (inc.) | 580 | 640 | 800 | C18-31 |
| 17–72 | 600 | 660 | 830 | C23–34 | ||
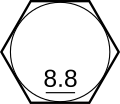 | Class 8.8 low carbon Low carbon boron steel; quench and tempered | |||||
 | Class 8.8.3 [1] Atmospheric corrosion resistant steel; quench and tempered | |||||
 | Class 9.8 Medium carbon steel; quench and tempered | 1.6–16 | 650 | 720 | 900 | C28–37 |
 | Class 9.8 low carbon Low carbon boron steel; quench and tempered | |||||
 | Class 10.9 Alloy steel; quench and tempered | 5–100 | 830 | 940 | 1040 | C32–39 |
 | Class 10.9 low carbon Low carbon boron steel; quench and tempered | |||||
 | Class 10.9.3 [1] Atmospheric corrosion resistant steel; quench and tempered | |||||
 | Class 12.9 Alloy steel; quench and tempered | 1.6–100 | 970 | 1100 | 1220 | C39–44 |