Related Research Articles

A bulletin board system (BBS), also called a computer bulletin board service (CBBS), was a computer server running software that allowed users to connect to the system using a terminal program. Once logged in, the user could perform functions such as uploading and downloading software and data, reading news and bulletins, and exchanging messages with other users through public message boards and sometimes via direct chatting. In the early 1980s, message networks such as FidoNet were developed to provide services such as NetMail, which is similar to internet-based email.

Digital Research, Inc. was a privately held American software company created by Gary Kildall to market and develop his CP/M operating system and related 8-bit, 16-bit and 32-bit systems like MP/M, Concurrent DOS, FlexOS, Multiuser DOS, DOS Plus, DR DOS and GEM. It was the first large software company in the microcomputer world. Digital Research was originally based in Pacific Grove, California, later in Monterey, California.
NAPLPS is a graphics language for use originally with videotex and teletext services. NAPLPS was developed from the Telidon system developed in Canada, with a small number of additions from AT&T Corporation. The basics of NAPLPS were later used as the basis for several other microcomputer-based graphics systems.

Telidon was a videotex/teletext service developed by the Canadian Communications Research Centre (CRC) during the late 1970s and supported by commercial enterprises led by Infomart in the early 1980s. Most work on the system ended after 1985, having failed to build critical mass.

Videotex was one of the earliest implementations of an end-user information system. From the late 1970s to early 2010s, it was used to deliver information to a user in computer-like format, typically to be displayed on a television or a dumb terminal.

The Osborne 1 is the first commercially successful portable computer, released on April 3, 1981 by Osborne Computer Corporation. It weighs 24.5 lb (11.1 kg), cost US$1,795, and runs the CP/M 2.2 operating system. It is powered from a wall socket, as it has no on-board battery, but it is still classed as a portable device since it can be hand-carried when the keyboard is closed.

The Minitel, officially known as TELETEL, was an interactive videotex online service accessible through telephone lines. It was the world's first and most successful mass-market online service prior to the World Wide Web. It was developed in Cesson-Sévigné, Brittany by government-owned France Télécom.
An online service provider (OSP) can, for example, be an Internet service provider, an email provider, a news provider (press), an entertainment provider, a search engine, an e-commerce site, an online banking site, a health site, an official government site, social media, a wiki, or a Usenet newsgroup.

Prestel, the brand name for the UK Post Office Telecommunications's Viewdata technology, was an interactive videotex system developed during the late 1970s and commercially launched in 1979. It achieved a maximum of 90,000 subscribers in the UK and was eventually sold by BT in 1994.

MicroBee was a series of networkable home computers by Applied Technology, which became publicly listed company MicroBee Systems Limited soon after its release. The original Microbee computer was designed in Australia by a team including Owen Hill and Matthew Starr.

Alex was an interactive videotex information service offered by Bell Canada in market research from 1988 to 1990 and thence to the general public until 1994.
The Acorn Communicator is a discontinued business computer developed by Acorn Computers. Mentioned in the computing press in late 1984 as the C30, previewed in early 1985 with estimated pricing between £500 and £800, in late 1985 with a built-in LCD display, and subsequently unveiled in a slightly different form, the system sold in very low numbers to companies requiring a computer with a built-in modem.

Teletext, or broadcast teletext, is a standard for displaying text and rudimentary graphics on suitably equipped television sets. Teletext sends data in the broadcast signal, hidden in the invisible vertical blanking interval area at the top and bottom of the screen. The teletext decoder in the television buffers this information as a series of "pages", each given a number. The user can display chosen pages using their remote control. In broad terms, it can be considered as Videotex, a system for the delivery of information to a user in a computer-like format, typically displayed on a television or a dumb terminal, but that designation is usually reserved for systems that provide bi-directional communication, such as Prestel or Minitel.

The 3M computer industrial goal was first proposed in the early 1980s by Raj Reddy and his colleagues at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) as a minimum specification for academic and technical workstations. It requires at least one megabyte of memory, a one megapixel display with 1024×1024 1-bit pixels, and one million instructions per second (MIPS) of processing power. It was also often said that it should cost no more than one "megapenny" or $10,000.

A BBC Micro expansion unit, for the BBC Micro is one of a number of peripherals in a box with the same profile and styling as the main computer.
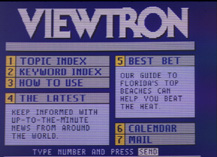
Viewtron was an online service offered by Knight-Ridder and AT&T from 1983 to 1986. Patterned after the British Post Office's Prestel system, it started as a videotex service requiring users to have a special terminal, the AT&T Sceptre. As home computers became important in the marketplace, the development focus shifted to IBM, Apple, Commodore and other personal computers.

The BBC Microcomputer System, or BBC Micro, is a series of microcomputers designed and built by Acorn Computers Limited in the 1980s for the Computer Literacy Project of the BBC. The machine was the focus of a number of educational BBC TV programmes on computer literacy, starting with The Computer Programme in 1982, followed by Making the Most of the Micro, Computers in Control in 1983, and finally Micro Live in 1985.

Home computers were a class of microcomputers that entered the market in 1977 and became common during the 1980s. They were marketed to consumers as affordable and accessible computers that, for the first time, were intended for the use of a single, non-technical user. These computers were a distinct market segment that typically cost much less than business, scientific, or engineering-oriented computers of the time, such as those running CP/M or the IBM PC, and were generally less powerful in terms of memory and expandability. However, a home computer often had better graphics and sound than contemporary business computers. Their most common uses were word processing, playing video games, and programming.
Started in 1983, Boston CitiNet was a local online service developed by Applied Videotex Systems, Inc. of Belmont, Massachusetts. The service allowed modem-equipped personal computer users to dial-in and access a range of information and messaging services including chat, forums, email and a variety of content. There were several other companies offering paid/subscription services as the time like The Source, CompuServe and Boston-based Delphi. Boston Citinet was unique since it was free to access and was supported by advertising. Messaging services such as email and chat required registration and a monthly fee of $9.95 - an early example of the now popular freemium business model.

The Dimension 68000 is a microcomputer introduced by the Micro Craft Corporation in 1983 that sought to emulate the Apple II, the IBM PC, and various CP/M-centric computers through a family of coprocessor expansion cards and emulation software. The Dimension 68000 can also run as a standalone computer based on the Motorola 68000 from which it gets its namesake. The computer is mostly the brainchild of Mike Carpenter, a former executive of a scientific instrument manufacturer who incorporated Micro Craft in Dallas, Texas, to develop the Dimension 68000. It had a market lifespan of three years and received mixed, mostly positive, reception from the technology press. Criticism was leveled at the $6,250 price tag for the computer with the full deck of coprocessor cards, as well as the extent of the emulation power of those cards.
References
- 1 2 David Needle, Bell announces videotex terminal, InfoWorld , 18 July 1983, pp.1 and 4–5
- ↑ David Carlson, Viewtron, University of Florida Interactive Media Center
- ↑ Howard I. Finberg, Before the web, there was Viewtron Archived 2010-09-04 at the Wayback Machine , Poynter Institute
- ↑ Sharman Stein, Videotex market slow to develop, Orlando Sentinel , May 13, 1985
- ↑ Bob Wallace, Viewtron cashiered; cost: $50M, Network World , March 24, 1986
- ↑ Keyfax television commercial, 6 November 1984, via YouTube
- ↑ M. Edwards, Brighter picture is emerging for business videotex, Communications News , August 1985
- ↑ Jim Bartimo, Micros get videotex support, InfoWorld , 14 May 1984, p. 11
