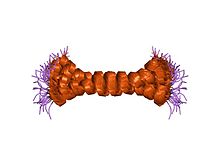
ATP synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) using adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi). ATP synthase is a molecular machine. The overall reaction catalyzed by ATP synthase is:

MT-ATP8 is a mitochondrial gene with the full name 'mitochondrially encoded ATP synthase membrane subunit 8' that encodes a subunit of mitochondrial ATP synthase, ATP synthase Fo subunit 8. This subunit belongs to the Fo complex of the large, transmembrane F-type ATP synthase. This enzyme, which is also known as complex V, is responsible for the final step of oxidative phosphorylation in the electron transport chain. Specifically, one segment of ATP synthase allows positively charged ions, called protons, to flow across a specialized membrane inside mitochondria. Another segment of the enzyme uses the energy created by this proton flow to convert a molecule called adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to ATP. Subunit 8 differs in sequence between Metazoa, plants and Fungi.
MT-ATP6 is a mitochondrial gene with the full name 'mitochondrially encoded ATP synthase membrane subunit 6' that encodes the ATP synthase Fo subunit 6. This subunit belongs to the Fo complex of the large, transmembrane F-type ATP synthase. This enzyme, which is also known as complex V, is responsible for the final step of oxidative phosphorylation in the electron transport chain. Specifically, one segment of ATP synthase allows positively charged ions, called protons, to flow across a specialized membrane inside mitochondria. Another segment of the enzyme uses the energy created by this proton flow to convert a molecule called adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to ATP. Mutations in the MT-ATP6 gene have been found in approximately 10 to 20 percent of people with Leigh syndrome.

ATP synthase F1 subunit beta, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ATP5F1B gene.

ATP synthase F1 subunit alpha, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ATP5F1A gene.

ATP synthase-coupling factor 6, mitochondrial is an enzyme subunit that in humans is encoded by the ATP5PF gene.

The ATP5MF gene encodes the ATP synthase subunit f, mitochondrial enzyme in humans.

ATP synthase subunit g, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ATP5MG gene.

The human ATP5F1C gene encodes the gamma subunit of an enzyme called mitochondrial ATP synthase.

ATP synthase subunit b, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ATP5PB gene.

ATP synthase subunit s, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ATP5S gene.

The ATP5MC2 gene is one of three human paralogs that encode membrane subunit c of the mitochondrial ATP synthase.

ATP synthase subunit e, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ATP5ME gene.

The human gene ATP5PD encodes subunit d of the peripheral stalk part of the enzyme mitochondrial ATP synthase.

ATP synthase subunit delta, mitochondrial, also known as ATP synthase F1 subunit delta or F-ATPase delta subunit is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ATP5F1D gene. This gene encodes a subunit of mitochondrial ATP synthase. Mitochondrial ATP synthase catalyzes ATP synthesis, utilizing an electrochemical gradient of protons across the inner membrane during oxidative phosphorylation.

ATP synthase F1 subunit epsilon, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ATP5F1E gene. The protein encoded by ATP5F1E is a subunit of ATP synthase, also known as Complex V. Variations of this gene have been associated with mitochondrial complex V deficiency, nuclear 3 (MC5DN3) and Papillary Thyroid Cancer.

The ATP5MC3 gene is one of three human paralogs that encode membrane subunit c of the mitochondrial ATP synthase.

ATP synthase subunit O, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ATP5PO gene.

DnaJ homolog subfamily C member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNAJC1 gene.

ATP synthase mitochondrial F1 complex assembly factor 1, also known as ATP11 homolog, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ATPAF1 gene.