
Argonne National Laboratory is a federally funded research and development center in Lemont, Illinois, United States. Founded in 1946, the laboratory is owned by the United States Department of Energy and administered by UChicago Argonne LLC of the University of Chicago. The facility is the largest national laboratory in the Midwest.

The IAS machine was the first electronic computer built at the Institute for Advanced Study (IAS) in Princeton, New Jersey. It is sometimes called the von Neumann machine, since the paper describing its design was edited by John von Neumann, a mathematics professor at both Princeton University and IAS. The computer was built under his direction, starting in 1946 and finished in 1951. The general organization is called von Neumann architecture, even though it was both conceived and implemented by others. The computer is in the collection of the Smithsonian National Museum of American History but is not currently on display.
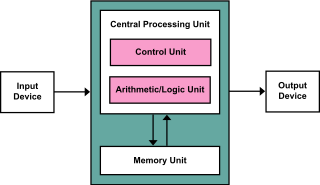
The von Neumann architecture—also known as the von Neumann model or Princeton architecture—is a computer architecture based on a 1945 description by John von Neumann, and by others, in the First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC. The document describes a design architecture for an electronic digital computer with these components:

The Advanced Photon Source (APS) at Argonne National Laboratory is a storage-ring-based high-energy X-ray light source facility. It is one of five X-ray light sources owned and funded by the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science. The APS began operation on March 26, 1995. It is operated as a user facility, meaning that it is open to the world’s scientific community, and more than 5,500 researchers make use of its resources each year.

The ORACLE or Oak Ridge Automatic Computer and Logical Engine, an early computer built by Oak Ridge National Laboratory, was based on the IAS architecture developed by John von Neumann.
GEORGE was an early computer built in 1957 by Argonne National Laboratory, was based on the IAS architecture developed by John von Neumann.. As with almost all computers of its era, it was a one of a kind machine that could not exchange programs with mother computers.

Elliott Brothers (London) Ltd was an early computer company of the 1950s and 1960s in the United Kingdom. It traced its descent from a firm of instrument makers founded by William Elliott in London around 1804. The research laboratories were originally set up in 1946 at Borehamwood and the first Elliott 152 computer appeared in 1950.
The ARRA was the first Dutch computer, and was built from relays for the Dutch Mathematical Centre, which later became the Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica (CWI).
The James H. Wilkinson Prize for Numerical Software is awarded every four years to honor outstanding contributions in the field of numerical software. The award is named to commemorate the outstanding contributions of James H. Wilkinson in the same field.
Michael Makepeace Thackeray is a South African chemist and battery materials researcher. He is mainly known for his work on electrochemically active cathode materials. In the mid-1980s he co-discovered the manganese oxide spinel family of cathodes for lithium ion batteries while working in the lab of John Goodenough at the University of Oxford. In 1998, while at Argonne National Laboratory, he led a team that first reported the NMC cathode technology. Patent protection around the concept and materials were first issued in 2005 to Argonne National Laboratory to a team with Thackeray, Khalil Amine, Jaekook Kim, and Christopher Johnson. The reported invention is now widely used in consumer electronics and electric vehicles.

The Model V was among the early electromechanical general purpose computers, designed by George Stibitz and built by Bell Telephone Laboratories, operational in 1946.

Convergent Science is an engineering software company which has its headquarters in Madison, Wisconsin. The company develops and supports CONVERGE CFD software, a general purpose computational fluid dynamics (CFD) solver.
Kawtar Hafidi is a Moroccan-American experimental nuclear physicist and the Associate Laboratory Director for Physical Sciences and Engineering at Argonne National Laboratory. She researches nucleon and nuclear structure using major accelerator facilities, e.g., Jefferson Lab, DESY, and Fermilab. She is also an advocate for diversity and almost became a professional soccer player when she was 16.
Jeffrey Elam is a Distinguished Fellow, Senior Chemist and Group Leader in the Applied Materials Division at the U.S. Department of Energy's Argonne National Laboratory. He leads Argonne's atomic layer deposition (ALD) research program, where he directs research and development and commercialization of thin film coating technologies for energy applications.
Khalil Amine is a materials scientist at Argonne National Laboratory, an Argonne distinguished fellow, and group leader of the Battery Technology group. His research team is focused on the development of advanced battery systems for transportation applications. In addition to his Argonne appointment, he is an adjunct professor at Stanford University, Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal University, Hong Kong University of Science & Technology, King Abdulaziz University, Hanyang University, and Peking University.
Katarzyna Keahey is a Senior Computer Scientist at Argonne National Laboratory and the Consortium for Advanced Science and Engineering (CASE) of the University of Chicago. She is a Principal Investigator (PI) of the Chameleon project, which provides an innovative experimentation platform for computer science systems experiments. She created Nimbus, one of the first open source implementations of infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), and co-founded the SoftwareX journal, publishing software as a scientific instrument.

Seth B. Darling is the Chief Science & Technology Officer of the Advanced Energy Technologies Directorate at Argonne National Laboratory. He previously served as director of the Center for Molecular Engineering, a research and development organization partnered with the University of Chicago focusing on advanced materials for cleaning water, quantum information science, and polymer science. Darling is also a senior scientist at both the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory and the University of Chicago’s Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering. He also directs the Advanced Materials for Energy-Water Systems (AMEWS) Center, a DOE Energy Frontier Research Center formed in 2018.
Valerii Vinokur is a condensed matter physicist who works on superconductivity, the physics of vortices, disordered media and glasses, nonequilibrium physics of dissipative systems, quantum phase transitions, quantum thermodynamics, and topological quantum matter. He is a senior scientist and Argonne Distinguished Fellow at Argonne National Laboratory and a senior scientist at the Consortium for Advanced Science and Engineering, Office of Research and National Laboratories, The University of Chicago. He is a Foreign Member of the National Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters and a Fellow of the American Physical Society.
Argonne Fast Source Reactor (AFSR) was a research reactor which was located at the Argonne National Laboratory, a United States Department of Energy national laboratory, facility located in the high desert of southeastern Idaho between Idaho Falls, Idaho and Arco, Idaho.










