
A nebula is a distinct luminescent part of interstellar medium, which can consist of ionized, neutral, or molecular hydrogen and also cosmic dust. Nebulae are often star-forming regions, such as in the Pillars of Creation in the Eagle Nebula. In these regions, the formations of gas, dust, and other materials "clump" together to form denser regions, which attract further matter and eventually become dense enough to form stars. The remaining material is then thought to form planets and other planetary system objects.
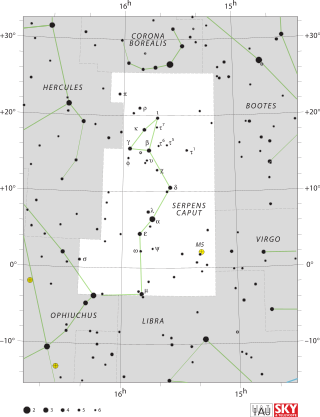
Serpens is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations designated by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput to the west and Serpens Cauda to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the "Serpent-Bearer". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.

A planetary nebula is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives.

The Cat's Eye Nebula is a planetary nebula in the northern constellation of Draco, discovered by William Herschel on February 15, 1786. It was the first planetary nebula whose spectrum was investigated by the English amateur astronomer William Huggins, demonstrating that planetary nebulae were gaseous and not stellar in nature. Structurally, the object has had high-resolution images by the Hubble Space Telescope revealing knots, jets, bubbles and complex arcs, being illuminated by the central hot planetary nebula nucleus (PNN). It is a well-studied object that has been observed from radio to X-ray wavelengths. At the centre of the Cat's Eye Nebula is a dying Wolf Rayet star, the sort of which can be seen in the Webb Telescope's image of WR 124. The Cat's Eye Nebula's central star shines at magnitude +11.4. Hubble Space Telescope images show a sort of dart board pattern of concentric rings emanating outwards from the centre.

NGC 2346 is a planetary nebula near the celestial equator in the constellation of Monoceros, less than a degree to the ESE of Delta Monocerotis. It is informally known as the Butterfly Nebula. The nebula is bright and conspicuous with a visual magnitude of 9.6, and has been extensively studied. Among its most remarkable characteristics is its unusually cool central star, which is a spectroscopic binary, and its unusual shape.

Draco is a constellation in the far northern sky. Its name is Latin for dragon. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. The north pole of the ecliptic is in Draco. Draco is circumpolar from northern latitudes, meaning that it never sets and can be seen at any time of year.

The Little Dumbbell Nebula, also known as Messier 76, NGC 650/651, the Barbell Nebula, or the Cork Nebula, is a planetary nebula in the northern constellation of Perseus. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1780 and included in Charles Messier's catalog of comet-like objects as number 76. It was first classified as a planetary nebula in 1918 by the astronomer Heber Doust Curtis. However, others might have previously recognized it as a planetary nebula; for example, William Huggins found its spectrum indicated it was a nebula ; and Isaac Roberts in 1891 suggested that M76 might be similar to the Ring Nebula (M57), as seen instead from the side view.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to astronomy:

Abell 39 is a low surface brightness planetary nebula in the constellation of Hercules. It is the 39th entry in George Abell's 1966 Abell Catalog of Planetary Nebulae of 86 old planetary nebulae which either Abell or Albert George Wilson discovered before August 1955 as part of the National Geographic Society - Palomar Observatory Sky Survey. It is estimated to be about 3,800 light-years from earth and thus 2,600 light-years above the Galactic plane. It is almost perfectly spherical and also one of the largest known spheres with a radius of about 1.4 light-years.

Abell 33 is a faint spherical planetary nebula located 2700 light years away in the constellation of Hydra. It lies just behind the star HD 83535 which has no relation to the nebula. The star HD 83535 is also responsible for the "diamond ring" effect seen in the photograph.

Abell 31 is an ancient planetary nebula in the constellation of Cancer. It is estimated to be about 2,000 light years away. Although it is one of the largest planetary nebulae in the sky, it is not very bright. The central star of the planetary nebula is a white dwarf with a spectral type of DAO. The white dwarf is the dead remains of a star that existed but had died leaving behind Abell 31 and the white dwarf.

Abell 78 is a planetary nebula located in the constellation of Cygnus at a distance of about 5,000 light years. It has a fainter halo consisting mostly hydrogen, an inner elliptical ring that is mostly made of helium and some inner knots that surround the central star and are extremely depleted in hydrogen. These inner knots were created by a very late thermal pulse, a re-ignition of thermonuclear activity in the helium shell of the star observed after the star left the asymptotic giant branch and is accompanied by strong stellar winds.

Abell 7 is a faint planetary nebula located 1800 light-years away in the constellation of Lepus. It has a generally spherical shape about 8 light-years in diameter. Within the sphere are complex details that are brought out by narrowband filters. Abell 7 is estimated to be only 20,000 years old, but the central star, a fading white dwarf, is estimated to be some 10 billion years old.

Abell 36 is a faint barrel shaped planetary nebula located 780 light years from Earth in the constellation of Virgo. It was discovered by the American astronomer George Ogden Abell in 1955.
LoTr 5 is a large, faint planetary nebula in the constellation of Coma Berenices. In 2018, its parallax was measured by Gaia, giving a distance of about 1,650 light-years.

Abell 63 is a planetary nebula with an eclipsing binary central star system in the northern constellation of Sagitta. Based on parallax measurements of the central star, it is located at a distance of approximately 8,810 light years from the Sun. The systemic radial velocity of the nebula is +41±2 km/s. The nuclear star system is the progenitor of the nebula and it has a combined apparent visual magnitude of 14.67. During mid eclipse the magnitude drops to 19.24.

Abell 48 is a planetary nebula likely located around 14,000 light years away in the constellation of Aquila. It is noteworthy among planetary nebulae for hosting a rare WN-type Wolf-Rayet-type central star, a [WN4]-type star, which was once thought to be a bona-fide Wolf-Rayet star, and received the name WR 120–6. The nebula is made up of two rings surrounding the central star, and is heavily reddened, with an E(B-V) value of 2.14 and a visual extinction of 6.634 magnitudes, which is why it appears so dim.

Abell 35, also known as Sh 2-313, is a nebula located in the constellation of Hydra, at a distance of 400 light years. The nebula is characterised by its unusual appearance, which features a central bow shock surrounded by symmetric emission. In the centre of the nebula lies a binary star, composed of a G-type star and a white dwarf. Although it is commonly referred to as a planetary nebula, it has been suggested that the nebula wasn't created by a post-AGB star shedding its outer shells but it is interstellar medium photoionised by the passing binary system, leading also to the creation of the bow shock.

















