
Dicentra, known as bleeding-hearts, is a genus of eight species of herbaceous plants with oddly shaped flowers and finely divided leaves, native to eastern Asia and North America.

The Australian hornet, actually a type of potter wasp or "mason wasp", is a vespid native to the Australian states and territories of the Australian Capital Territory, New South Wales, Northern Territory, Victoria, Queensland and Western Australia.

Dicentra formosa is a flowering plant with fern-like leaves and an inflorescence of drooping pink, purple, yellow or cream flowers native to the Pacific Coast of North America.
This is an article on the grading that is used in Finland. Several systems are in use in different educational institutions in Finland.

Protea eximia, the broad-leaved sugarbush, is a shrub from South Africa that may become a small tree. It occurs in mountain fynbos on mainly acidic sandy soils; the species was very well known under its old name of Protea latifolia. The flowers have awns that are covered in purple-black velvety hairs, and are contained within a series of rings of involucral bracts that have the appearance of petals. The fruit is a densely hairy nut, many of which are inserted on a woody base. The flowers are borne terminally on long shoots, and have a tendency to become very untidy as they age.

The white-flanked sunbird is a species of bird in the family Nectariniidae. It is endemic to Indonesia.

Abispa is a genus of large Australasian potter wasps belonging to the subfamily Eumeninae.

Dicentra eximia is a flowering plant with fernlike leaves and oddly shaped flowers native to the Appalachian Mountains. It is similar to the Pacific bleeding-heart, which grows on the Pacific Coast. Dicentra eximia is a perennial herb in the Papaveraceae family.

Enypniastes is a genus of deep-sea sea cucumber. It is monotypic, being represented by the single species Enypniastes eximia. Due to its unique appearance, the species has been dubbed the headless chicken fish, headless chicken monster, and the Spanish dancer. It is also known as the swimming sea cucumber, and some are called the pink see-through fantasia.

Corymbia eximia, commonly known as yellow bloodwood, is a bloodwood native to New South Wales. It occurs around the Sydney Basin often in high rainfall areas on shallow sandstone soils on plateaux or escarpments, in fire prone areas. Growing as a gnarled tree to 20 m (66 ft), it is recognisable by its distinctive yellow-brown tessellated bark. The greyish green leaves are thick and veiny, and lanceolate spear- or sickle-shaped. The cream flowerheads grow in panicles in groups of seven and appear in spring. Known for many years as Eucalyptus eximia, the yellow bloodwood was transferred into the new genus Corymbia in 1995 when it was erected by Ken Hill and Lawrie Johnson. It is still seen under the earlier name in some works.
Melaleuca eximia is a plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is endemic to the south of Western Australia. It is distinguished by its leaf arrangement, its large, showy red inflorescences and the large, furry bracts under the flowers.

Dicentra peregrina is a herbaceous perennial growing from a rhizome, native to mountains in Japan and nearby areas of East Asia.

Nyceryx eximia is a moth of the family Sphingidae. It is known from Panama, Costa Rica, Guatemala and Mexico, as well as Ecuador.
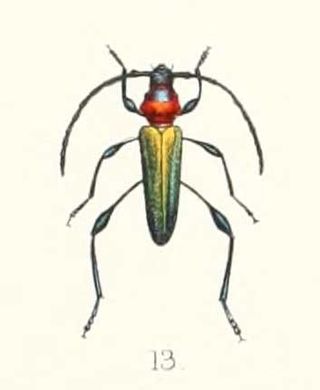
Eximia is a genus of round-necked longhorn beetles of the subfamily Cerambycinae.

Abispa splendida is a species of wasp in the Vespidae family.
Abispa ruficornis is a species of wasp in the Vespidae family.
Abispa laticincta is a species of wasp in the Vespidae family.
Mylothris eximia is a butterfly in the family Pieridae. It is found in Nigeria.

Morchella eximia is a globally-occurring fungus in the family Morchellaceae (Ascomycota), first described by Émile Boudier in 1910. In an elaborate phylogenetic and nomenclatural revision of the genus in 2014, Richard and colleagues showed that the taxa Morchella anthracophila, Morchella carbonaria, and Morchella septimelata, proposed in 2012 by Clowez and Kuo et al. respectively, are all later synonyms of this old taxon.

Myosotis eximia is a species of flowering plant in the family Boraginaceae endemic to the North Island of New Zealand. The species was described by Donald Petrie. Plants of this species of forget-me-not are perennial and erect, and have ebracteate inflorescences with white corollas.















