
The Chlorophyceae are one of the classes of green algae, distinguished mainly on the basis of ultrastructural morphology. They are usually green due to the dominance of pigments chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. The chloroplast may be discoid, plate-like, reticulate, cup-shaped, spiral- or ribbon-shaped in different species. Most of the members have one or more storage bodies called pyrenoids located in the chloroplast. Pyrenoids contain protein besides starch. Some green algae may store food in the form of oil droplets. They usually have a cell wall made up of an inner layer of cellulose and outer layer of pectose.

Chlamydomonas is a genus of green algae consisting of about 150 species of unicellular flagellates, found in stagnant water and on damp soil, in freshwater, seawater, and even in snow as "snow algae". Chlamydomonas is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics. One of the many striking features of Chlamydomonas is that it contains ion channels (channelrhodopsins) that are directly activated by light. Some regulatory systems of Chlamydomonas are more complex than their homologs in Gymnosperms, with evolutionarily related regulatory proteins being larger and containing additional domains.

The glaucophytes, also known as glaucocystophytes or glaucocystids, are a small group of unicellular algae found in freshwater and moist terrestrial environments, less common today than they were during the Proterozoic. The stated number of species in the group varies from about 14 to 26. Together with the red algae (Rhodophyta) and the green algae plus land plants, they form the Archaeplastida.

The Zygnemataceae are a family of filamentous or unicellular, uniseriate (unbranched) green algae. The filaments are septated and reproduction is by conjugation; Spirogyra is commonly used in schools to demonstrate this kind of reproduction. The family is notable for its diversely shaped chloroplasts, such as stellate in Zygnema, helical in Spirogyra, and flat in Mougeotia. The Zygnemataceae are cosmopolitan, but though all generally occur in the same types of habitats, Mougeotia, Spirogyra, and Zygnema are by far the most common; in one study across North America, 95% of the Zygnemataceae collected were in these three genera. Classification and identification is primarily by the morphology of the conjugation, which is somewhat rare to find in natural populations of permanent water bodies; when in the vegetative state, the rarer genera resemble the three most common, and are often mistaken for them and catalogued as such. Conjugation can be induced in low-nitrogen culture. While they occupy many habitats, in North America all are found solely in freshwater or subaerial habitats. Species typically exist as floating mats in stagnant water in ditches and ponds, but some also grow in moving water, attaching themselves to a substrate by rhizoid-like projections of the basal cells of the filament. The mat species rise to the surface in early spring, grow rapidly through the summer, disappearing by late summer. Members of the Zygnemataceae, such as Spirogyra, fall prey to parasites, especially chytrids. Most genera previously assigned to Mesotaeniaceae as well as the Desmidiales actually emerged in the Zygnematacae.

Eustigmatophytes are a small group of eukaryotic forms of algae that includes marine, freshwater and soil-living species.

Chlamydomonadaceae is a family of algae within the order Chlamydomonadales. Traditionally, it has been defined as containing single-celled flagellates with a cell wall.
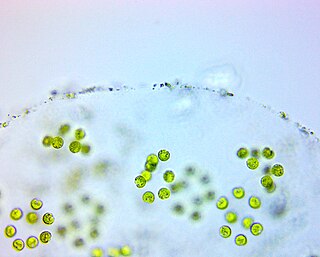
The Tetrasporaceae are a family of green algae, specifically of the Chlamydomonadales. They are found in freshwater habitats.
Actinochloris is a genus of green algae, in the family Actinochloridaceae, with a single species Actinochloris sphaerica. It is a subaerial to terrestrial alga.

Ankistrodesmus is a genus of green algae in the family Selenastraceae. It is one of the most common types of phytoplankton in freshwater habitats around the world.

Asterococcus is a genus of green algae in the order Chlamydomonadales. It is planktonic in freshwater ponds and lakes, or benthic within mires and swamps. It is a common and widespread genus, but is rarely abundant.
Asteromonas is a genus of green algae in the family Asteromonadaceae. It has been described from saline, marine, and brackish environments. It is closely related to the genus Dunaliella, another genus common in saline waters.

Brachiomonas is a genus of thalloid biflagellate green algae. These algae generally are found in marine or brackish waters, but can tolerate wide range of salinities. They may occur in freshwater pools near the sea and, occasionally, in polluted inland freshwater habitats.
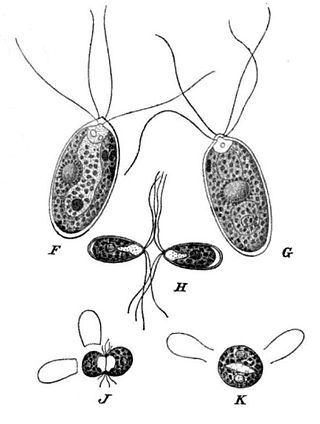
Carteria is a genus of green algae in the family Chlamydomonadaceae. Carteria are similar in morphology to the common genus Chlamydomonas and differ by having four, rather than two, flagella at the vegetative stage.
Characiochloris is a genus of green algae in the family Characiochloridaceae. Characiochloris is epiphytic on freshwater algae, or found in soil.
Characiopodium is a genus of green algae in the family Sphaeropleaceae. It occurs in soils.

Characium is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae. It is very commonly found in freshwater habitats, where it is attached to phytoplankton or zooplankton.
Chlorococcum is a genus of green algae, in the family Chlorococcaceae. The alga may be useful in the flocculation of lipids from wastewater. It can be found in fresh water, but is more commonly found in soil or subaerial habitats.
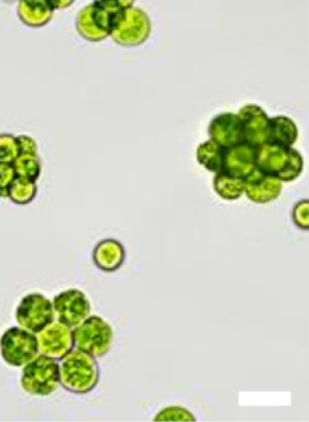
Deasonia is a genus of green algae, in the family Actinochloridaceae. It is found in soils.
Follicularia is a genus of green algae, in the family Schizochlamydaceae. It is found in terrestrial habitats, mainly soil.
Pseudodictyochloris is a genus of green algae, in the family Actinochloridaceae. It is found in soils.













