
In computer architecture, a bus is a communication system that transfers data between components inside a computer, or between computers. This expression covers all related hardware components and software, including communication protocols.

Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) is the 16-bit internal bus of IBM PC/AT and similar computers based on the Intel 80286 and its immediate successors during the 1980s. The bus was (largely) backward compatible with the 8-bit bus of the 8088-based IBM PC, including the IBM PC/XT as well as IBM PC compatibles.

A motherboard is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expandable systems. It holds and allows communication between many of the crucial electronic components of a system, such as the central processing unit (CPU) and memory, and provides connectors for other peripherals. Unlike a backplane, a motherboard usually contains significant sub-systems, such as the central processor, the chipset's input/output and memory controllers, interface connectors, and other components integrated for general use.

A sound card is an internal expansion card that provides input and output of audio signals to and from a computer under the control of computer programs. The term sound card is also applied to external audio interfaces used for professional audio applications.

PC Card is a parallel peripheral interface for laptop computers and PDAs. The PCMCIA originally introduced the 16-bit ISA-based PCMCIA Card in 1990, but renamed it to PC Card in March 1995 to avoid confusion with the name of the organization. The CardBus PC Card was introduced as a 32-bit version of the original PC Card, based on the PCI specification. The card slots are backward compatible for the original 16-bit card, older slots are not forward compatible with newer cards.

In computing, an expansion card is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an electrical connector, or expansion slot on a computer's motherboard to add functionality to a computer system. Sometimes the design of the computer's case and motherboard involves placing most of these slots onto a separate, removable card. Typically such cards are referred to as a riser card in part because they project upward from the board and allow expansion cards to be placed above and parallel to the motherboard.

A graphics card is a computer expansion card that generates a feed of graphics output to a display device such as a monitor. Graphics cards are sometimes called discrete or dedicated graphics cards to emphasize their distinction to an integrated graphics processor on the motherboard or the central processing unit (CPU). A graphics processing unit (GPU) that performs the necessary computations is the main component in a graphics card, but the acronym "GPU" is sometimes also used to erroneously refer to the graphics card as a whole.

PCI Express, officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common motherboard interface for personal computers' graphics cards, capture cards, sound cards, hard disk drive host adapters, SSDs, Wi-Fi, and Ethernet hardware connections. PCIe has numerous improvements over the older standards, including higher maximum system bus throughput, lower I/O pin count and smaller physical footprint, better performance scaling for bus devices, a more detailed error detection and reporting mechanism, and native hot-swap functionality. More recent revisions of the PCIe standard provide hardware support for I/O virtualization.

Data acquisition is the process of sampling signals that measure real-world physical conditions and converting the resulting samples into digital numeric values that can be manipulated by a computer. Data acquisition systems, abbreviated by the acronyms DAS,DAQ, or DAU, typically convert analog waveforms into digital values for processing. The components of data acquisition systems include:
GeoPort is a serial data system used on some models of the Apple Macintosh that could be externally clocked to run at a 2 megabit per second data rate. GeoPort slightly modified the existing Mac serial port pins to allow the computer's internal DSP hardware or software to send data that, when passed to a digital-to-analog converter, emulated various devices such as modems and fax machines. GeoPort could be found on late-model 68K-based machines as well as many pre-USB Power Macintosh models and PiPPiN. Some later Macintosh models also included an internal GeoPort via an internal connector on the Communications Slot. Apple GeoPort technology is now obsolete, and modem support is typically offered through USB.

A network interface controller is a computer hardware component that connects a computer to a computer network.

The game port is a device port that was found on IBM PC compatible and other computer systems throughout the 1980s and 1990s. It was the traditional connector for joystick input, and occasionally MIDI devices, until made obsolete by USB in the late 1990s.

In computer hardware a host controller, host adapter or host bus adapter (HBA) connects a computer system bus which acts as the host system to other network and storage devices. The terms are primarily used to refer to devices for connecting SCSI, SAS, NVMe, Fibre Channel and SATA devices. Devices for connecting to FireWire, USB and other devices may also be called host controllers or host adapters.
A USB and Firewire Host Controller Interface (UFHC) is a register-level interface that enables a host controller for USB or IEEE 1394 hardware to communicate with a host controller driver in software. The driver software is typically provided with an operating system of a personal computer, but may also be implemented by application-specific devices such as a microcontroller.
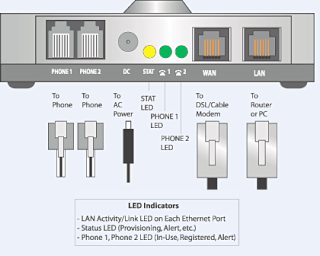
An analog telephone adapter (ATA) or FXS gateway is a device for connecting traditional analog telephones, fax machines, and similar customer-premises devices to a digital telephone system or a voice over IP telephone network.
An output device is any piece of computer hardware that converts information or data into a human-perceptible form or, historically, into a physical machine-readable form for use with other non-computerized equipment. It can be text, graphics, tactile, audio, or video. Examples include monitors, printers, speakers, headphones, projectors, GPS devices, optical mark readers, and braille readers.

A wireless network interface controller (WNIC) is a network interface controller which connects to a wireless network, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or LTE (4G) or 5G rather than a wired network, such as an Ethernet network. A WNIC, just like other NICs, works on the layers 1 and 2 of the OSI model and uses an antenna to communicate via radio waves.

A VoIP phone or IP phone uses voice over IP technologies for placing and transmitting telephone calls over an IP network, such as the Internet. This is in contrast to a standard phone which uses the traditional public switched telephone network (PSTN).
This glossary of computer hardware terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts related to computer hardware, i.e. the physical and structural components of computers, architectural issues, and peripheral devices.

A dongle is a small piece of computer hardware that connects to a port on another device to provide it with additional functionality, or enable a pass-through to such a device that adds functionality.

















