
QuarkXPress is desktop publishing software for creating and editing complex page layouts in a WYSIWYG environment. It runs on macOS and Windows. It was first released by Quark, Inc. in 1987 and is still owned and published by them.

Microsoft PowerPoint is a presentation program, created by Robert Gaskins, Tom Rudkin, and Dennis Austin at a software company named Forethought, Inc. It was released on April 20, 1987, initially for Macintosh computers only. Microsoft acquired PowerPoint for about $14 million three months after it appeared. This was Microsoft's first significant acquisition, and Microsoft set up a new business unit for PowerPoint in Silicon Valley where Forethought had been located.

Ventura Publisher was the first popular desktop publishing package for IBM PC compatible computers running the GEM extension to the DOS operating system. The software was originally developed by Ventura Software, a small software company founded by John Meyer, Don Heiskell, and Lee Jay Lorenzen, all of whom met while working at Digital Research. It ran under an included run-time copy of Digital Research's GEM.

Aldus Corporation was an American software company best known for its pioneering desktop publishing software. PageMaker, the company's most well-known product, ushered in the modern era of desktop computers such as the Macintosh seeing widespread use in the publishing industry. Paul Brainerd, the company's co-founder, coined the term desktop publishing to describe this paradigm. The company also originated the Tag Image File Format (TIFF) file format, widely used in the digital graphics profession.

Adobe Illustrator is a vector graphics editor and design software developed and marketed by Adobe. Originally designed for the Apple Macintosh, development of Adobe Illustrator began in 1985. Along with Creative Cloud, Illustrator CC was released. The latest version, Illustrator 2025, was released on October 14, 2024, and is the 29th generation in the product line. Adobe Illustrator was reviewed as the best vector graphics editing program in 2021 by hpMagazine.

Adobe InDesign is a desktop publishing and page layout designing software application produced by Adobe and first released in 1999. It can be used to create works such as posters, flyers, brochures, magazines, newspapers, presentations, books and ebooks. InDesign can also publish content suitable for tablet devices in conjunction with Adobe Digital Publishing Suite. Graphic designers and production artists are the principal users.

Quark Software Inc. is a privately owned software company which specializes in enterprise publishing software for automating the production of customer communications. The company's original goal was to "create software that would be the platform for publishing", just as quarks are the basis for all matter.
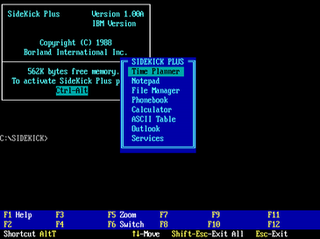
Borland Sidekick was a personal information manager (PIM) launched by American software company Borland in 1984 under Philippe Kahn's leadership. It was an early and popular terminate-and-stay-resident program (TSR) for MS-DOS which enabled computer users to activate the program using a hot key combination while working in other programs. Although a text-mode program, Sidekick's window-based interface echoed that of the Apple Macintosh and anticipated the eventual look of Microsoft Windows 2.0. It included a personal calendar, text editor, calculator, ASCII chart, address book, and phone dialer. According to the prospectus for Borland's initial public offering of stock to the public, Sidekick sold more than 1 million copies in its first three years.

Adobe Persuasion is a discontinued presentation program developed for the Macintosh platform by Aldus Corporation. After it was acquired by Adobe Systems in 1994, when the two companies merged, a Microsoft Windows version was released. Adobe discontinued production from September 1997.
Canvas X is a drawing, imaging, and publishing computer program from Canvas GFX for personal computers.
PageMill is a WYSIWYG HTML editor developed by Adobe Systems in 1994. After PageMill 3.0, it was discontinued in favor of GoLive.

Freeway is a WYSIWYG web design application for Mac OS X developed by the British company Softpress Systems.

SuperPaint is a graphics program capable of both bitmap painting and vector drawing. SuperPaint was one of the first programs of its kind, combining the features of MacPaint and MacDraw while adding many new features of its own.
Mosaic was a Macintosh scorewriter application for producing music notation, developed by Mark of the Unicorn.
Meeting Maker is a cross-platform personal calendar and group scheduling software application from PeopleCube. First released in 1991 for Macintosh by ON Technology, support for other platforms followed in 1993 with Meeting Maker XP. Alongside Windows and Mac, native clients were released for OS/2 and Solaris, and later also for other platforms. Some support was also introduced for mobile platforms like Apple Newton, PalmPilot and Windows CE. Although powerful, its user interface - aiming at uniformity across multiple platforms — was criticized as weak and not supporting all features of target platforms.
Aldus PhotoStyler was a graphics software program developed by the Taiwanese company Ulead. Released in June 1991 as the first 24 bit image editor for Windows, it was bought the same year by the Aldus Prepress group. Its main competition was Adobe Photoshop. Version 2.0 introduced a new user interface and improved color calibration. PhotoStyler SE - lacking some features of the version 2.0 - was bundled with scanners like HP ScanJet. The product disappeared from the Adobe product line after Adobe acquired Aldus in 1994.
Windows 2.0 is a major release of Microsoft Windows, a family of graphical operating systems for personal computers developed by Microsoft. It was released to manufacturing on December 9, 1987, as a successor to Windows 1.0.

Adobe FreeHand is a discontinued computer application for creating two-dimensional vector graphics oriented primarily to professional illustration, desktop publishing and content creation for the Web. FreeHand was similar in scope, intended market, and functionality to Adobe Illustrator, CorelDRAW and Xara Designer Pro. Because of FreeHand's dedicated page layout and text control features, it also compares to Adobe InDesign and QuarkXPress. Professions using FreeHand include graphic design, illustration, cartography, fashion and textile design, product design, architects, scientific research, and multimedia production.
Boeing Calc was a spreadsheet package written by Boeing Computer Services, an independent subsidiary of aviation manufacturer Boeing. It had originally been developed as an in-house accounting tool, but was launched as a commercial product in April 1985 for IBM 4300 mainframes running IBM MVS and IBM PC microcomputers running DOS. The original launch price was $399 per copy for the PC version and $8,899 for a combined PC/mainframe bundle.

Dr. Halo is a raster graphics editor developed by Media Cybernetics and released for computers running MS-DOS. It was among the first graphics editors available for MS-DOS with its initial release in 1984. Media Cybernetics boasted about three million users of Dr. Halo between 1984 and 1993.













