
Narcissus is a genus of predominantly spring flowering perennial plants of the amaryllis family, Amaryllidaceae. Various common names including daffodil, narcissus and jonquil, are used to describe all or some members of the genus. Narcissus has conspicuous flowers with six petal-like tepals surmounted by a cup- or trumpet-shaped corona. The flowers are generally white and yellow, with either uniform or contrasting coloured tepals and corona.
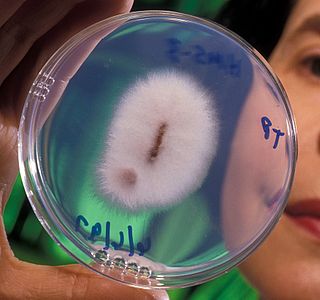
Fusarium oxysporum, an ascomycete fungus, comprises all the species, varieties and forms recognized by Wollenweber and Reinking within an infrageneric grouping called section Elegans. It is part of the family Nectriaceae.

Fusarium is a large genus of filamentous fungi, part of a group often referred to as hyphomycetes, widely distributed in soil and associated with plants. Most species are harmless saprobes, and are relatively abundant members of the soil microbial community. Some species produce mycotoxins in cereal crops that can affect human and animal health if they enter the food chain. The main toxins produced by these Fusarium species are fumonisins and trichothecenes. Despite most species apparently being harmless, some Fusarium species and subspecific groups are among the most important fungal pathogens of plants and animals.

Gymnoconia nitens is a species of rust fungus in the Phragmidiaceae family. It is a plant pathogen, and causes orange rust on various berries. The species was originally described in 1822 by mycologist Lewis David de Schweinitz as Aecidium luminatum.
Aecidium campanulastri is a species of fungus in the Pucciniales order. A plant pathogen, it was described as new to science in 1910.
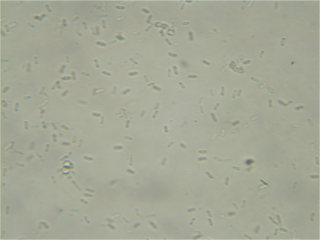
Phoma is a genus of common coelomycetous soil fungi. It contains many plant pathogenic species.

Aecidium magellanicum, commonly known as the calafate rust, is a species of rust fungi. This fungus can cause a growth defect known as a witches broom, an excessive growth of stems from a single point on a branch. The species is known to infect the evergreen shrub Berberis buxifolia in Argentina and Chile.
Peter Nielsen was a Danish botanist and plant pathologist.
Hans Sydow was a German mycologist and the son of mycologist and lichenologist, Paul Sydow (1851–1925).

An aecium is a specialised reproductive structure found in some plant pathogenic rust fungi that produce aeciospores. Aecia may also be referred to as "cluster cups". The term aecidium is used interchangeably but is not preferred.

Puccinia sessilis is a fungal species and plant pathogen, which is also known as arum rust or ramsons rust. It commonly infects Arum maculatum and Allium ursinum causing yellow to orange circular patches on leaves. On the underside of the leaves, it produces raised orange aecia commonly covered in spores. It is common in Eurasia in the spring.

Aecidium is a genus of rust fungi in the order Pucciniales.

Ceratocystis is a genus of fungi in the family Ceratocystidaceae. Several species are important plant pathogens, causing diseases such as oak wilt and pineapple black rot.
Aecidium mori is a species of fungus in the order Pucciniales. It can only be found on flowering plants of the species Morus, the mulberries. It is found in Asia.
The Adanson system, published by French botanist Michel Adanson as the Familles des plantes in two volumes in 1763, was an important step in botanical nomenclature by establishing the ordering of genera into families.
Phoma narcissi is a fungal plant pathogen of Narcissus, Hippeastrum and other Amaryllidaceae, where it causes a leaf scorch, neck rot and red leaf spot disease
Uromyces elegans is a species of rust fungi in the family Pucciniaceae.

The Valley of Narcissi is a nature reserve in Kireshi, Zakarpattia Oblast, Ukraine. Part of the Carpathian Biosphere Reserve, it has an area of 256 ha.









